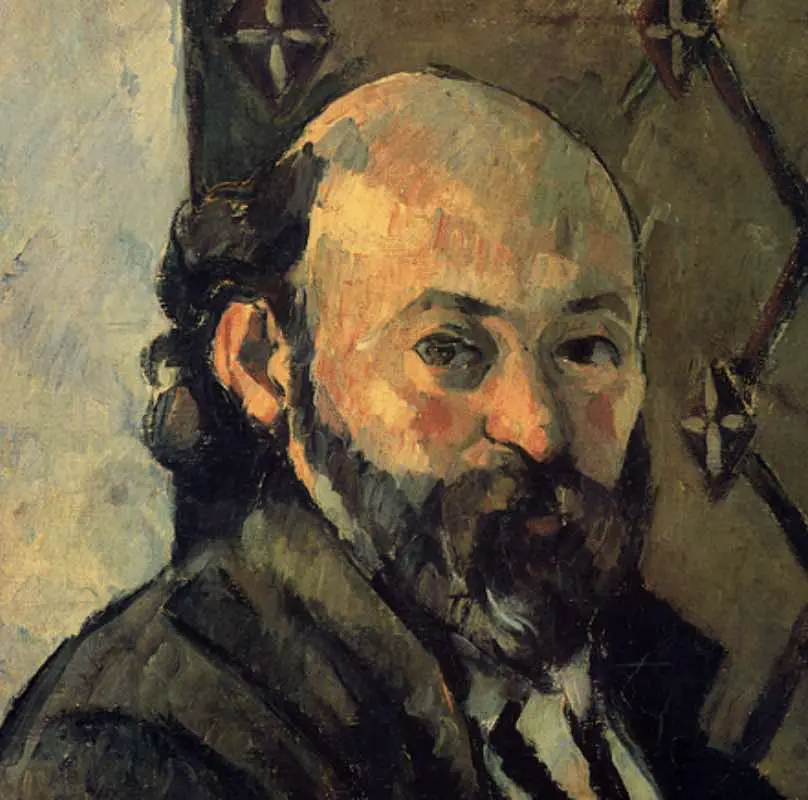
Paul Cézanne is regarded as one of the greatest artists in history and is often dubbed the “father of modern art.” As a French artist, his profound influence has guided numerous other artists as a pivotal bridge to modern art.
Paul Cézanne’s life and work cement his legacy as one of the most eminent artists in history. Explore Cézanne’s journey and discover answers to the 50 most frequently asked questions about him.
Table of Contents
- About The French Artist Paul Cezanne
- 50 Frequently Asked Questions About The French Artist Paul Cezanne
- Related Questions
About The French Artist Paul Cezanne
Paul Cézanne, born on January 19, 1839, in Aix-en-Provence and passing away in the same town on October 22, 1906, was one of the most innovative and influential artists in the annals of Western art.

His work laid the foundations for the transition from the 19th-century conception of artistic endeavor to a new, drastically different world of art in the 20th century. Today, he’s frequently hailed as the bridge between Impressionism and Cubism.
From the outset of his artistic career, Cézanne was fascinated with color, light, and form. While his early works took on a darker, more impressionistic tone, they gradually evolved, revealing his unique ability to capture the essence of his subjects.

He once said, “I want to make of Impressionism something solid and lasting, like the art in the museums.” And, in a way, he did just that. Instead of the fleeting moments captured by the Impressionists, Cézanne sought a deeper, more structural understanding of the world around him.
One of the most significant aspects of Cézanne’s art is his exploration of geometric simplification. He often described nature using primary forms like cylinders, spheres, and cones.
This analytical approach to painting was revolutionary at the time, and it paved the way for the geometric abstraction seen in Cubism, a movement led by artists like Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque. His iconic series of the “Mont Sainte-Victoire,” a mountain in southern France, is a perfect example of this, where the mountain and its surroundings are broken down into a series of colors and shapes.
Cézanne was also known for his still-life compositions. Through these works, he redefined this genre by granting equal weight to each object, whether a fruit, a vase, or a tablecloth, emphasizing the interplay of color and light. His still-life paintings are not merely passive observations; they pulse with life and tension, showcasing his profound understanding of spatial relationships and the very nature of visual perception.

Towards the end of his life, the artist’s style became even more abstract, hinting at the forthcoming changes in art. Despite facing criticism and misunderstanding from many of his contemporaries, Cézanne’s unwavering dedication to his vision changed the trajectory of modern art.
Today, he is celebrated not just as a master in his own right but as a trailblazer who illuminated new pathways for future generations of artists.
50 Frequently Asked Questions About The French Artist Paul Cezanne
1. Who is Paul Cézanne?
Paul Cézanne was a French artist often dubbed as the “father of modern art.” His work laid the foundations for the transition from the 19th-century artistic conceptions to the radical new world of art in the 20th century.
2. When was Cézanne born?
He was born on January 19, 1839.
3. Where was he born?
Cézanne was born in Aix-en-Provence, France.
4. How is Cézanne’s art characterized?
His art is characterized by its unique brushwork, color choices, and emphasis on geometric forms in nature.
5. What is Cézanne most known for?
He is best known for his series of still lifes, landscapes, and portraits.
6. Which art movement is he associated with?
He is associated with Post-Impressionism.
7. Did Cézanne have formal art education?
Yes, he studied at the École des Beaux-Arts in Aix.
8. What technique is Cézanne famous for?
Cézanne is known for his method of building up form with color and systematic brushstrokes.
9. Who were Cézanne’s contemporaries?
His contemporaries included Vincent van Gogh, Camille Pissarro, and Georges Seurat.
10. Was Cézanne’s work well-received during his lifetime?
His work was often criticized during his early career but gained acceptance and acclaim in his later years.
11. What’s his relationship with Impressionism?
Cézanne began his career with the Impressionists but later diverged in style and technique.
12. What are some of his most famous paintings?
“The Card Players,” “Mont Sainte-Victoire,” and “Still Life with Apples” are among his most celebrated works.
13. Did Cézanne influence other artists?
Yes, he greatly influenced Picasso, Matisse, and other 20th-century artists.
14. When did Cézanne die?
He died on October 22, 1906.
15. How did he die?
Cézanne died of pneumonia.
16. Is Cézanne considered a modernist?
Yes, he is often credited as a precursor to modern art.
17. How did Cézanne view nature?
He saw nature as composed of geometric forms and aimed to represent these in his paintings.
18. Did Cézanne paint en plein air (outdoors)?
Yes, like many Impressionists, Cézanne often painted outdoors.
19. Was Cézanne wealthy?
Though he struggled early on, he eventually achieved financial success through his art.
20. Did Cézanne get married?
Yes, he married Marie-Hortense Fiquet in 1886.
21. Did he have children?
Yes, he had a son named Paul.
22. Where can I see Cézanne’s paintings today?
His works are displayed in major museums worldwide, including the Louvre, the Metropolitan Museum of Art, and the Musée d’Orsay.
23. How many paintings did Cézanne create?
It’s estimated that he created over 900 oil paintings and 400 watercolors.
24. Was Cézanne ever involved in the Salon in Paris?
Yes, but his works were often rejected by the Salon’s conservative jury.
25. Why is Cézanne’s “The Bathers” significant?
The series showcased his innovative approach to form and composition, influencing future avant-garde artists.
26. How did Cézanne’s style change over time?
His early works were dark and moody, but they became increasingly abstract and bright in color over time.
27. What mediums did Cézanne use?
He primarily used oils but also created many watercolors.
28. Did Cézanne write about art?
While not prolifically, his letters often contained insights and thoughts on art.
29. Did Cézanne work with any other famous artists?
He was friends and sometimes collaborated with Camille Pissarro.
30. How has Cézanne influenced Cubism?
Cubists like Picasso and Braque drew inspiration from Cézanne’s approach to breaking down objects into geometric forms.
31. Why did Cézanne paint so many still lifes?
He was fascinated by the challenge of portraying three-dimensional objects on a two-dimensional plane.
32. Did Cézanne ever sculpt?
While primarily a painter, Cézanne did experiment with sculpture.
33. Why did Cézanne frequently paint Mont Sainte-Victoire?
The mountain was visible from his hometown and became a symbol of his emotional connection to the landscape.
34. What’s unique about Cézanne’s portraits?
His portraits are often noted for their psychological depth and unique sense of form.
35. How did Cézanne feel about Paris?
He had a love-hate relationship with the city, drawn to its art scene but often preferring the solitude of Aix.
36. How has Cézanne’s reputation evolved since his death?
While divisive during his life, Cézanne is now universally recognized as a foundational figure in modern art.
37. Did Cézanne paint self-portraits?
Yes, he painted several introspective self-portraits throughout his career.
38. How did Cézanne approach color?
He believed color was fundamental to capturing form and depth, often using it in bold and innovative ways.
39. Was Cézanne a recluse?
In his later years, he preferred solitude, but he wasn’t completely isolated.
40. How do art historians view Cézanne today?
He is celebrated as a pivotal figure who bridged 19th-century Impressionism and the birth of 20th-century modernism.
41. What were Cézanne’s personal challenges?
He grappled with self-doubt, depression, and criticism throughout his life.
42. Were any posthumous exhibitions of Cézanne’s work held?
Yes, several, most notably the 1907 retrospective at the Salon d’Automne in Paris.
43. What genres did Cézanne paint?
He painted landscapes, still lifes, portraits, and figure compositions.
44. How has Cézanne’s art influenced the Fauvists?
His bold use of color was a significant influence on Fauvist artists like Matisse.
45. Did Cézanne have a particular philosophy about art?
He believed in the importance of persistence, stating that “Art is a religion. Its aim is the elevation of the mind.”
46. Why did Cézanne often leave parts of his canvas unfinished?
He felt that some paintings reached a point where adding more would diminish their impact.
47. Did Cézanne influence Abstract Expressionism?
While not directly, his emphasis on the act of painting and form over representation paved the way for future movements like Abstract Expressionism.
48. How did Cézanne approach composition?
He often used diagonal lines and geometric forms to create a sense of depth and structure.
49. Was Cézanne a prolific letter writer?
Yes, many of his letters to friends and family have provided insights into his thoughts on art and life.
50. How does Cézanne’s legacy live on today?
Cézanne’s influence can be seen in countless art movements and artists who followed, making him a central figure in the narrative of art history.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you are interested to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel filled with great videos and information by clicking here.
Related Questions
Did Michelangelo And Leonardo Know Each Other?
Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci knew each other but were considered bitter rivals. Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo knew each other, but they did like each other. They were both asked to do a commission on the Council Hall of the Palazzo Vecchio and were supposed to work side-by-side; the project was never completed.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Did Michelangelo And Leonardo Know Each Other?.
What Was The Focus Of Renaissance Art?
The focus of Renaissance art was on the classics of Greek and Rome, humanist philosophy, and the study of the human figure. Realism was also an essential part of renaissance art. The great artists of the Renaissance also became great anatomists and studied human beings.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Was The Focus Of Renaissance Art?.
Michelangelo’s Sistine Chapel And His Payment
Michelangelo was paid 3200 gold ducats for his work on the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel, which would have been a very lucrative commission. We know that he stopped work on the ceiling for a while due to his not being paid by the Vatican. Michelangelo liked to give the impression that he was a very poor artist, but records have shown that he died an extremely wealthy man.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Michelangelo’s Sistine Chapel And His Payment.