Leonardo da Vinci, a polymath of the Italian Renaissance, stands among art history’s most celebrated and scrutinized figures. His oeuvre captivates not merely because of its aesthetic beauty but also because of the intricate techniques and profound ideas woven into each canvas and sketch.
The layers of meaning, from the deft application of light and shadow to the subtle gradations of tone creating ethereal forms, exemplify a timeless dance between art and science. As we embark on this exploratory journey into da Vinci’s world, we will unfold the tapestry of skills and symbolism that have cemented Leonardo’s position as an unparalleled maestro whose works continue to resonate with audiences centuries after their creation.
Table of Contents
- The Mastery of Technique
- Symbolism and Hidden Messages
- The Fusion of Art and Science
- Leonardo’s Artistic Legacy
- Conservation and Restoration Challenges
- The Enigma of Lost and Attributed Works
- Related Questions
The Mastery of Technique
Decoding the Genius: Exploring Leonardo da Vinci’s Artistic Techniques

The oeuvre of Leonardo da Vinci, a luminary of the Renaissance period, continues to captivate scholars and enthusiasts alike. His emblematic techniques transcend aesthetics, manifesting a confluence of art and scientific inquiry. A rigorous analysis of his methods reveals secrets that not only illuminate his creative process but also provide a window into the mind of a genius.
Chiaroscuro, a technique mastered by da Vinci, entails the strategic use of light and shadow to endow paintings with a three-dimensional quality. By moderating the contrast and transitions between the two, Leonardo could mimic the subtlety of human contours, giving life to the figures on canvas. ‘The Virgin of the Rocks’ exemplifies this application, where light seemingly radiates from the subjects, engendering an ethereal atmosphere.

Beyond chiaroscuro, Leonardo’s finesse in sfumato—the delicate blending of colors without discernible transitions—further enhanced the realism of his characters. This technique created soft gradients rather than harsh lines, as seen in the iconic ‘Mona Lisa.’ The subject’s enigmatic expression owes its realism to this deft handling of tone and contour.
Further scrutiny of Leonardo’s works reveals his preference for anatomical accuracy. His meticulous study of the human body, supported by dissections, enabled him to portray the human form with unprecedented precision. His sketches exhibit a deep understanding of musculature and articulation, which he adeptly transferred to his paintings, enhancing their authenticity.
Leonardo’s obsession with detail did not end in the human form. He extended this meticulousness to depicting nature, where each element held symbolic significance. His observations of plant life, water, and rock formations were not merely decorative but were composed to evoke a harmonious natural world. The background of ‘The Annunciation’ is a testament to this, wherein every botanical element is rendered with scientific exactitude.
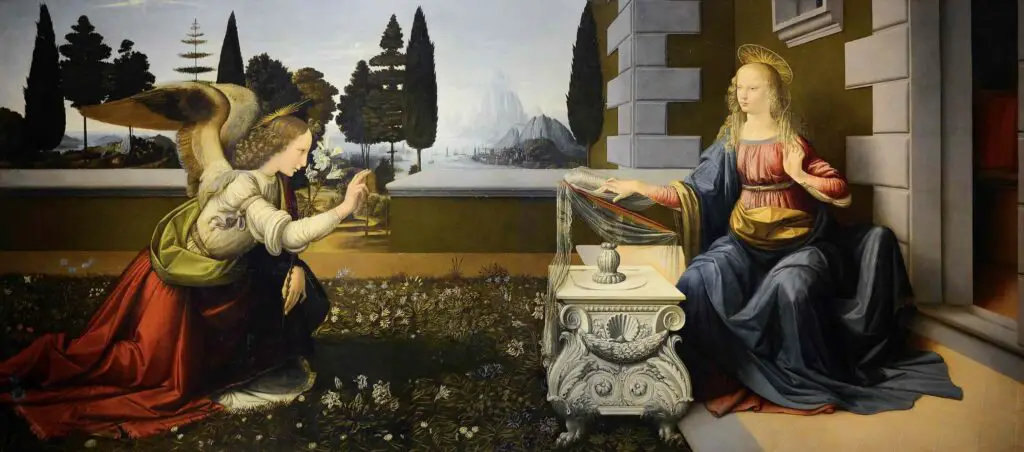

Lastly, it is imperative to acknowledge Leonardo’s prodigious use of perspective. He developed techniques that gave depth to flat surfaces, transforming two-dimensional spaces into windows of a palpable world.
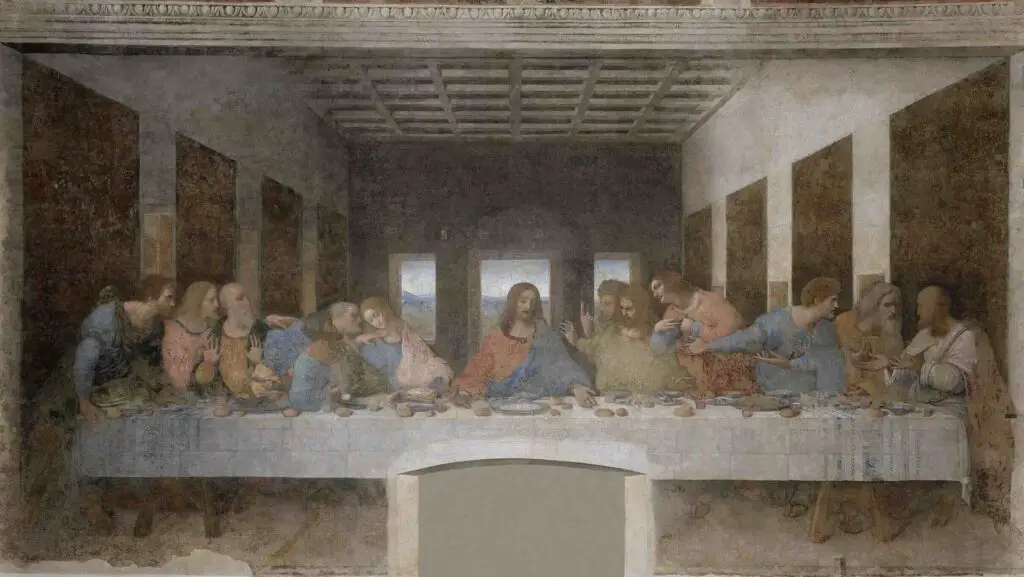
His understanding of linear perspective and vanishing points allowed him to create scenes where the observer could be immersed. ‘The Last Supper’ remains a sterling illustration of this skill, where the perspectival lines converge at the figure of Christ, establishing him as the focal point.

These covert expedients employed by Leonardo da Vinci are not merely artistic choices but are symbolic of a mind that perceived art as an embodiment of nature and knowledge.
His art is a palimpsest that invites us to delve beyond the surface and engage with the profound intellectual currents that underpin his creative legacy. In the pursuit of uncovering the secrets of Leonardo’s techniques, one encounters the foundations of his art and the unparalleled curiosity and intellect that redefined the boundaries of human expression.
Symbolism and Hidden Messages
Leonardo da Vinci’s art is an everlasting source of intrigue and mystery, captivating scholars and laypersons alike. Embedded within the intricate layers of his paintings are symbols and secrets that transcend mere artistic achievement, speaking to a blend of science, philosophy, and spirituality.
One of the hallmarks of Leonardo’s masterpieces is his utilization of emblematic content that communicates and conceals ideas. He often infused his subject matter with symbolic references, tailoring his imagery to resonate with a select audience with specialized knowledge.

For instance, in “The Last Supper,” each apostle is portrayed with a distinct emotional response, and their gestures and placement within the scene are rich with symbolic intent and biblical allusions.
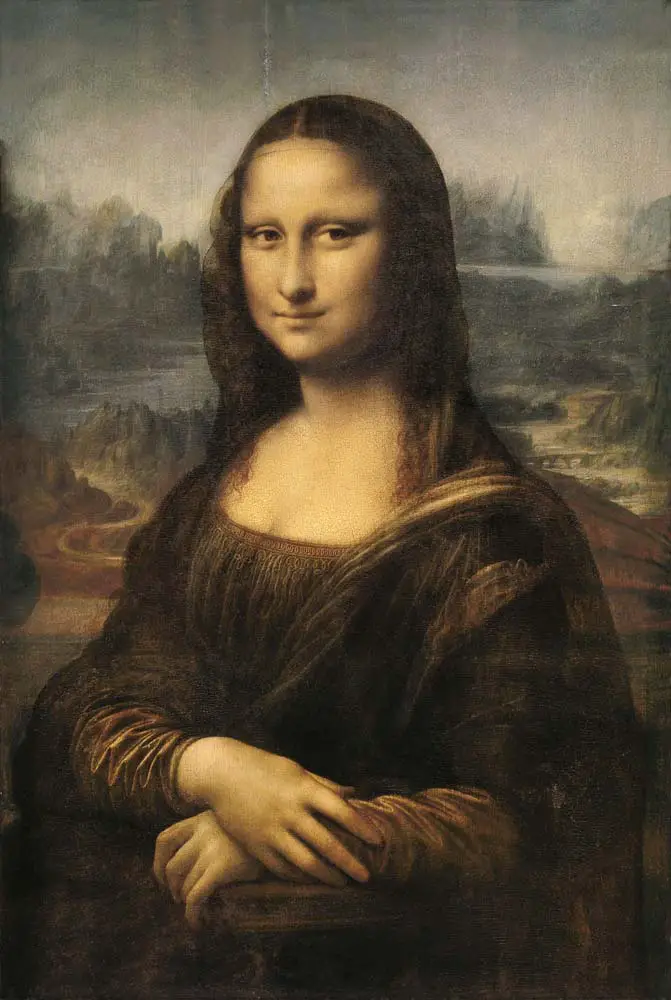

In addition to religious iconography, Leonardo’s paintings are replete with subtle nods to his fascinations, particularly in his secular works. The “Mona Lisa,” perhaps his most renowned work, is a compendium of veiled symbolism. The subject’s enigmatic smile has led to myriad interpretations—some see an underlying representation of a motherly figure, while others speculate about hidden identities or psychological states.

Moreover, Leonardo’s interest in the natural world often materialized through botanical symbolism. He meticulously painted various plants in “Madonna of the Rocks,” each chosen for its symbolic associations. This careful selection of flora demonstrated his deep understanding of botany and imbued the painting with layers of symbolic meaning regarding purity, the divine, and the cycle of life.
Another noteworthy aspect is Leonardo’s incorporation of codes and puzzles within his art. The seemingly random arrangement of letters and numbers within his works has been the subject of intense analysis. In “The Last Supper,” conjectures about musical notations hidden within the bread rolls and hands of the apostles have been posited, hypothesizing that Leonardo left behind a celestial hymn.
Furthermore, Leonardo’s close association with secretive societies, like the Sforza court and possibly even the fabled Priory of Sion, has fuelled speculation that his art contained coded messages intended for a select few. However, many of these theories lack robust scholarly backing and veer into the domain of speculative fiction rather than objective analysis.
In conclusion, Leonardo da Vinci’s artistry is a confluence of observable representation and enigmatic depth. His employment of symbolism and mysteries within his works is a testament to his attempt to harmonize his intellectual pursuits with his artistic ventures.
The layers of meaning that permeate his art reflect a mind that was ceaselessly searching for a greater comprehension of the interconnectedness of all things. The quest to fully decipher Leonardo’s visual codes may remain beyond reach, ensuring his art’s eternal relevance and fascination.
The Fusion of Art and Science
Leonardo da Vinci’s scientific inquiries were not merely a sideline to his artistic endeavors; they were a critical component that elevated his work beyond that of his contemporaries. His inquisitive mind and rigorous approach to science and art resulted in an unparalleled fusion of the two fields, manifesting in every brushstroke and anatomical sketch.
One aspect of this fusion can be seen in Leonardo’s engagement with motion dynamics. His numerous drawings and notes on the movement of water, the flight of birds, and the mechanics of human movement informed his ability to depict motion in a way that was at once dynamic and accurate.
This understanding imbued his paintings with life. Each figure is composed within the canvas to reflect the natural grace and force of living beings in action. The cascading curls in “Leda and the Swan” betray a fascination with fluid dynamics that is as informed by observation as it is by imagination.
Leonardo’s engineering inquiries also resonated within his artistic production. His complex designs for machinery, studies of light, and explorations of architectural principles endowed his paintings with structural integrity and sophisticated play of light and shadow.

The architectural backgrounds in pieces like “The Annunciation” showcase a profound grasp of building design, geometric proportion, and the interplay between constructed environments and the natural world. These detailed representations of architecture and machinery are more than mere backdrops; they are integral elements that reflect Leonardo’s holistic view of the world as an interconnected system.
The light was a particular focus of Leonardo’s scientific exploration and pronounced impacted his artistic output. Intrigued by optics, he studied the nature of light and shadow and their effects on the human perception of three-dimensional space. This analysis of light contributed to a technique called “chiaroscuro” – previously mentioned but worth reiterating as a scientific influence – which creates a striking contrast between light and dark to give depth and volume to his subjects.
Furthermore, Leonardo’s botanical studies contributed to the authenticity of plant depictions in his artworks and their symbolic meaning. His meticulous observations of plant life led him to depict flora with unprecedented scientific accuracy, conferring a level of detail that can often go unnoticed at first glance. These plants, while capturing the beauty of nature, are often full of meaning, informing the narrative and mood of the piece in subtle but important ways.
In conclusion, Leonardo’s relentless pursuit of knowledge in his scientific inquiries was not tangential to his art but deeply ingrained in his creative process.
His paintings do not merely capture the surface appearance of subjects but reflect a profound understanding of the principles that govern light, motion, anatomy, and the natural world. Leonardo’s scientific brilliance enriches each of his artistic creations, making them masterpieces not only of aesthetic achievement but also of intellectual and empirical investigation.
This seamless integration of science and art cements Leonardo da Vinci’s place as a universal genius whose works continue to captivate and educate long past the Renaissance era in which he lived and worked.

Leonardo’s Artistic Legacy
The ramifications of Leonardo da Vinci’s artistic endeavors have reverberated through the annals of art history, profoundly influencing successive generations of artists and the trajectory of art itself. The multifaceted nature of Leonardo’s oeuvre meant that he did not merely leave behind a collection of artworks but rather a compendium of techniques, a philosophy of aesthetics that has cascaded through centuries.
One of the critical impacts of Leonardo’s art is the standards he set in painting. His meticulous attention to detail and his relentless pursuit of perfection inspired others to study their craft with a similar rigor.
His intricate dissections and how he translated this anatomical knowledge onto the canvas greatly expanded the scope of how the human form could be understood and depicted. These elements inspired artists to take a more scientific approach to art, incorporating diligent observation and experimentation.
Following Leonardo’s footsteps, artists began paying closer attention to the natural world around them. The pursuit of realistic landscapes, detailed botanical illustrations, and intricate depictions of various textures became more prominent. This attention to naturalism pushed art towards a more immersive experience, making viewers feel like they were part of the scene.
Moreover, Leonardo’s versatility and proficiency across multiple disciplines encouraged artists to explore beyond traditional boundaries. His belief that all areas of study were interconnected served as an encouragement to subsequent artists to cross-pollinate ideas from different fields into their artwork.
This sentiment laid the groundwork for the polymath artist archetype and helped herald the era of the “Renaissance man” who is often seen in creative circles as a figure striving for universal knowledge and application.
The psychological depth that Leonardo afforded his subjects also left a significant imprint. Artists endeavored to imbue their portraits with a similar level of emotional complexity and humanism, striving to capture the spirit and inner life of the individual. This has had a lasting effect on portrait art, which still often seeks to express the intangible essence of the subject.
Lastly, Leonardo’s art was instrumental in questioning the artist’s societal role. By blending science and art, he established the artist as an intellectual, not just a craftsman. It led to the elevation of art as a noble pursuit capable of contributing to the broader dialogue of human knowledge and understanding.
Conservation and Restoration Challenges
Conservators tasked with preserving Leonardo da Vinci’s works face an array of formidable challenges, reflecting the artist’s intricate techniques and materials. A legacy of delicate preservation marks da Vinci’s oeuvre, yet as science has evolved, so too have the threats to his works’ longevity.
Environmental stability and control are at the forefront of conservation struggles. Da Vinci’s masterpieces require stringent regulation of temperature, humidity, and exposure to light. Deviations from optimal conditions can precipitate deterioration mechanisms such as fading, yellowing, or even the flaking of paint, which severely diminish the vivacity and definition integral to the artist’s vision.
Another salient challenge for conservators lies in the complexity of da Vinci’s media. His experimental approach often led to the mixing of diverse materials and techniques, presenting a unique preservation problem. Media such as oil and tempera, coupled with his application methods, have formed micro-fractures and paint instability over time. These necessitate therapeutic interventions sympathetic to the original work and aware of the chemical interactions that may further compromise the painting’s integrity.
The cleaning of da Vinci’s works is also a complex endeavor. It must address centuries of accreted grime and previous restoration attempts, which sometimes used materials that are now known to be detrimental to the longevity of the artwork. Modern conservators must carefully remove these layers without disturbing the vulnerable original surfaces beneath.
Conservators also grapple with the ethical dimensions of art restoration. There is a delicate balance in preserving the integrity of Leonardo’s original work while not imposing our contemporary or subjective interpretations upon it. The decision-making process involves understanding the artist’s intent and the historical significance of the artwork, leading to a conservation strategy that must be as meticulous and innovative as the pieces themselves.
Moreover, advancements in conservation technology have seen the development of imaging techniques such as X-radiography, infrared reflectography, and multispectral imaging, which allow for a deeper understanding of the underlying conditions and components of the artworks. However, these technologies do not alleviate preservation challenges but rather elucidate them further, often revealing unseen complications lurking below the surface.
As Leonardo’s art continues to withstand time, the conservation community remains vigilant and adaptive, evolving with new methodologies and practices to ensure these genius incarnations remain accessible to future generations.
In summary, the preservation of Leonardo’s artwork constitutes ongoing, rigorous work characterized by an ever-present need for research, specialized care, and a deep reverence for the cultural heritage vested within these Renaissance treasures. The commitment to their safekeeping is a testament to Leonardo’s ineffable legacy and the custodianship ethos at the core of art conservation.

The Enigma of Lost and Attributed Works
The Conundrum of Authentification: Deciphering the Provenance of Lost and Misattributed da Vinci Works
As the historical narrative of art unfolds, the quest to authenticate Leonardo da Vinci’s lost and misattributed works continues to captivate art historians. This reverence for authentication is due to the inherent value and significance of da Vinci’s oeuvre and the multi-layered complexities these artworks embody. Central to this endeavor is the rigorous examination of provenance—a comprehensive history of an artwork’s ownership.
Provenance research is a cornerstone in the identification and authentication process, serving as a historical lighthouse guiding scholars through murky waters of past ownership and dubious origin. This meticulous chronicle is often pieced together using archival records, sales receipts, gallery logs, images, historical documentation, and correspondences to establish a timeline that correlates an artwork’s existence with its purported creator.
In conjunction with provenance, stylistic analysis remains indispensable. Art historians engage in a comparative study of technique, form, composition, and material to establish a credible link with other authentic works of da Vinci.
This involves cross-referencing aspects undiscussed here, such as the peculiarities of brushwork, pigment preparation, and the subtleties of draughtsmanship. Quintessential to this analytical approach is the examination of underdrawings through infrared reflectography. This technological aid reveals hidden sketches beneath a painting’s surface, often providing insights into the work’s genesis.
Scientometric analysis, a scientific technique used to examine an artwork’s fingerprint, ‘ has become increasingly prominent. This method analyzes the elemental makeup of the pigments, supports, and binding agents employed, providing a tangible connection to the period and potentially to the artist himself. When coupled with pre-existing art historical knowledge, such scientific evidence can powerfully advocate for the authentication of previously lost or misattributed works.
Furthermore, there is the study of historical context. Remarkable talents like da Vinci did not create in a vacuum. Thus, understanding the social, political, and cultural milieu of the time can clarify the origins of an artwork. Scholars endeavor to align the thematic and iconographic content with the artist’s known interests and milieu, considering interactions with patrons and contemporary influences.
The pursuit of attribution also critically involves robust debate and scholarly discourse. Peer-reviewed publications, symposiums, and dynamic discussions form the crucible within which assertions of authenticity are forged or fractured. The intellectual rigor applied to such debates ensures that conclusions on attributions can be reached with confidence only through consensus and exhaustive deliberation.
Engagement with conservation and preservation issues underpins the understanding of da Vinci’s art. Art historians collaborate with conservators to ensure the artwork is examined and preserved with each intervention and understood in greater depth. These interdisciplinary efforts are vital in unraveling how a work may have been altered or conserved throughout history, potentially affecting its attribution.
Finally, art historians approach the enigma of da Vinci’s works with relentless determination and conscientious scholarship, acknowledging that with each inquiry and each discovery, the tapestry of Leonardo’s life and oeuvre becomes more complete. The endeavor to distill truth from obscurity respects the profound legacy of an artist who remains one of humanity’s greatest luminaries.
To grasp the full magnitude of Leonardo da Vinci’s legacy requires a venture beyond the mere surface of his canvases. It compels a deep dive into the very fabric of art history, unearthing the complexities of preservation and the intellectual vigor behind the attribution of his works.
Leonardo’s life and creations serve as cultural landmarks and enduring testimonies to the boundless potential of human curiosity and creativity. Exploring his mastery, analyzing his intent, and contemplating his scientific and artistic confluence extend an invitation to discover a mind that helped shape the Renaissance and, indeed, the modern perception of art and the natural world.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you are interested in seeing any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. I would be happy to talk to you if you have any questions. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend just 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Related Questions
Did They Use An Original Jackson Pollock Painting In Ex Machina Or A Replica?
They would have used a copy of painting No 5 (1948) as the painting was sold by David Geffen, a Hollywood producer and film studio executive, for over $140 million USD in 2006. Geffen would have sold the painting long before the movie was produced, and no respectable art collector would place such a valuable work of art on a film set or studio.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Did They Use An Original Jackson Pollock Painting In Ex Machina Or A Replica?.
What Makes Jackson Pollock’s Art So Valuable?
Jackson Pollock was a brilliant and creative artist who was not afraid to try new techniques with art. He is known for being a founder of Abstract Expressionism and the gestural technique, also known as action painting. He never saw much success in his lifetime, but today his paintings fetch millions of dollars and are considered extremely valuable.
By clicking here, you can discover more by reading What Makes Jackson Pollock’s Art So Valuable?.
Understanding Jackson Pollock’s Paintings And His Art
Understanding that Jackson Pollock has absolute honesty in his paintings, he shows us his great technique and ability to use paint in ways that have never been used before. His paintings are very dimensional, so when you look at them in one way but get up close, you may see another way. He’s not trying to fool us in any way but just saying here, view it as you want to see it.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Understanding Jackson Pollock’s Paintings And His Art.