In the hushed halls of the world’s most prestigious art museums, the works of the great masters—Rembrandt, Vermeer, Michelangelo—stand as timeless testaments to human creativity, emotion, and genius. These masterpieces, with their intricate brushstrokes and profound emotional resonance, are more than just paintings; they are windows into the soul of their creators and the eras they inhabited. But as we march deeper into the digital age, a provocative question looms large: Can artificial intelligence (AI) replicate the nuanced brushstrokes, emotional depth, and intangible “soul” of a master artist?
The answer is far from simple. While AI has made staggering leaps in its ability to mimic human creativity, true replication of a master’s touch remains elusive. Read on as we delves into the burgeoning world of digital forgery, exploring how AI attempts to capture the inimitable spirit of legendary artists and what this means for our understanding of authenticity and artistic genius.
Table of Contents
- The Master’s Touch: A Human Imprint
- The Rise of the Algorithmic Artisan
- Simulating Genius: AI’s Forgery Toolkit
- The Authenticity Conundrum: A Digital Dilemma
- Beyond Replication: The Future of Art and AI
- The Enduring Human Spirit
- Deep Dive Podcast
- Related Questions
The Master’s Touch: A Human Imprint
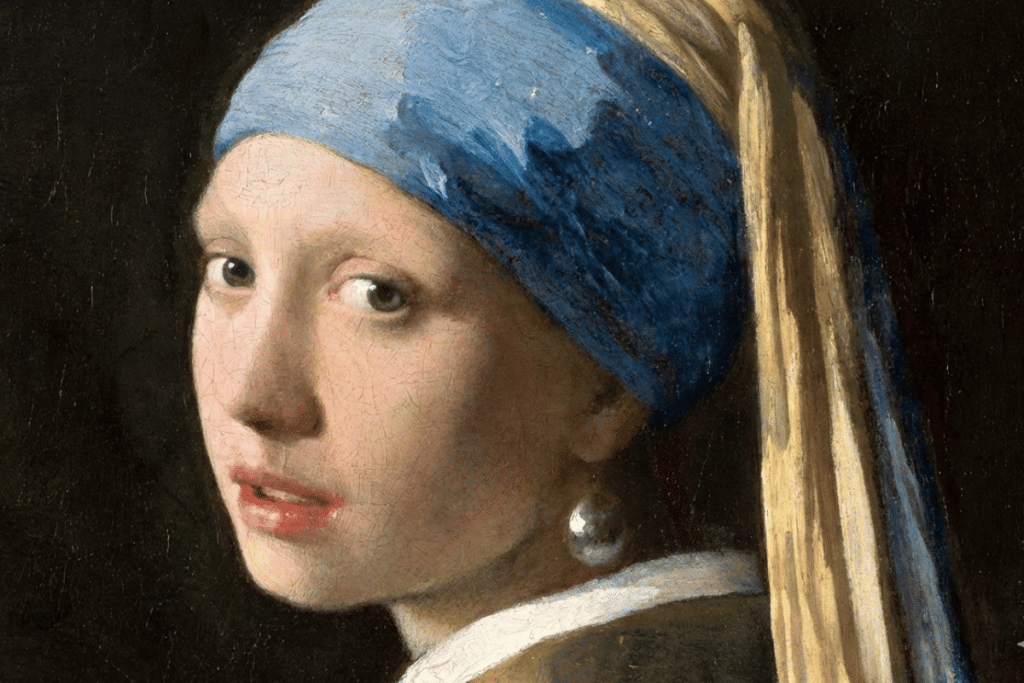
Imagine standing before Vermeer’s Girl with a Pearl Earring. The soft glow of light on her skin, the glint of her earring, and the enigmatic expression that seems to hold a thousand stories—these elements create an emotional resonance that transcends time.
The same can be said for the dramatic interplay of light and shadow in Rembrandt’s self-portraits or the intricate details of Michelangelo’s Sistine Chapel ceiling. These works are not just visually stunning; they are imbued with the unique personalities, cultural contexts, and emotional depths of their creators.
What makes a master’s work irreplaceable is not just their technical skill, but their ability to capture the intangible. The human experience—its joys, sorrows, and complexities—finds expression in every brushstroke.
It’s this “soul” that seems impossible to encode into an algorithm. And yet, as AI continues to evolve, it’s worth asking: Can machines ever truly grasp and replicate these profound qualities? Or will they always fall short, creating mere facsimiles devoid of the human touch?

The Rise of the Algorithmic Artisan
To understand AI’s role in the art world, it’s important to first explore the technologies that power it. At the heart of many AI-generated artworks are tools like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), deep learning algorithms, and style transfer techniques. These systems analyze vast datasets of images, learning patterns, textures, and styles to create new works that mimic existing ones.
For instance, GANs operate through a process of creative competition. Two neural networks, the generator and the discriminator, are pitted against each other.
The generator creates images, while the discriminator evaluates them, determining whether they are real or fake. Over time, this iterative process allows the generator to produce increasingly convincing images that resemble the style of a particular artist.
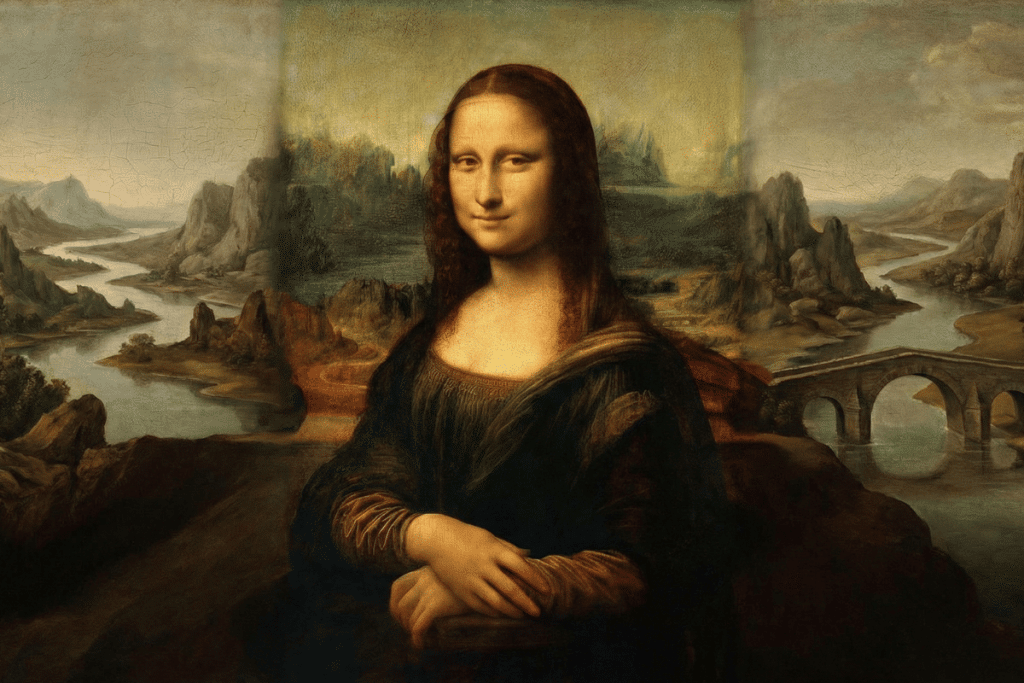
One of the most famous examples of AI art is The Next Rembrandt project, where an AI was trained on thousands of Rembrandt’s works to produce a new painting in his style.
The result? A stunningly accurate piece that, at first glance, could easily be mistaken for an original. However, despite its technical brilliance, the AI-generated painting lacked the emotional depth and historical context that define Rembrandt’s genius.
This highlights a key limitation of AI: while it can mimic the surface-level aesthetics of a master’s work, it struggles to replicate the deeper, intangible qualities that make art truly meaningful.

Simulating Genius: AI’s Forgery Toolkit
How exactly does AI attempt to replicate a master’s hand? The process involves several sophisticated techniques, each designed to analyze and mimic specific aspects of an artist’s style:
- Brushstroke Pattern Recognition: AI can analyze the unique brushstroke patterns of a painter, identifying recurring motifs, textures, and techniques. For example, Van Gogh’s swirling, dynamic strokes or Vermeer’s delicate layering are studied in microscopic detail.
- Color Palette Analysis: AI algorithms can dissect an artist’s use of color, learning to replicate their signature palettes and tonal variations.
- Composition and Layout: By examining the spatial arrangement of elements in a painting, AI can recreate compositions that mimic the balance and harmony of a master’s work.
Despite these advancements, there are still notable shortcomings. From my own experience working with AI, I’ve found that it often struggles with consistency.
You can give an AI the same prompt twice and receive two entirely different results. This inconsistency can be both a strength and a limitation, depending on the context.
Additionally, AI sometimes falters when given too much information, requiring a step-by-step approach to achieve the desired outcome. This reinforces the idea that AI, at least for now, still needs human guidance and input to be truly effective.
For instance, when AI attempts to replicate the works of a grandmaster, it can produce something similar, but it will never be the same. The subtle nuances, the imperfections that give a painting its character, and the emotional intent behind each stroke—these are elements that AI cannot fully grasp or reproduce.

The Authenticity Conundrum: A Digital Dilemma
The rise of AI-generated art raises profound philosophical and ethical questions about authenticity and originality. If an AI can perfectly mimic a master’s style, does it devalue the original? Or does it force us to rethink our definitions of artistic authenticity?
In the art market, these questions have practical implications. How do we authenticate works in an age where AI forgeries are becoming increasingly convincing? Will future museums house AI-generated “originals,” or will we need new categories to distinguish between human-made and machine-made art?
Some argue that AI-generated art lacks the “aura” of authenticity that Walter Benjamin described in his seminal essay, The Work of Art in the Age of Mechanical Reproduction.
According to Benjamin, the value of a work of art lies not only in its aesthetic qualities but also in its unique history and context. An AI-generated painting, no matter how visually stunning, cannot possess this aura because it lacks a human creator with a personal story and vision.
On the other hand, some see AI as a democratizing force, breaking down traditional barriers to artistic creation and allowing anyone with access to technology to produce works of art. In this view, the value of art lies not in its origin but in its ability to evoke emotion and provoke thought.

Beyond Replication: The Future of Art and AI
While much of the discussion around AI and art has focused on replication and forgery, the true potential of AI lies in its ability to augment human creativity. Rather than replacing artists, AI can serve as a tool that expands their creative possibilities.
For example, AI can be used to generate ideas, explore new styles, or even create interactive artworks that respond to viewers in real-time. Some artists are already using AI to push the boundaries of what’s possible, creating works that blend human creativity with machine intelligence.
Looking to the future, we can envision a world where AI and human artists collaborate to create entirely new artistic movements. Imagine AI-curated exhibitions that adapt in real-time to the preferences of visitors, or interactive installations that evolve based on audience participation. These innovations could redefine what art is and what it can be.
However, it’s important to remember that AI is not a replacement for human creativity. As I’ve observed in my own experiences with AI, the technology still relies on human input and guidance to be effective.
Whether it’s breaking down a complex task into manageable steps or providing the emotional context that machines lack, the human touch remains essential.
The Enduring Human Spirit
As we navigate the intersection of art and technology, one thing becomes clear: the relationship between AI and art is not about replacement but augmentation. While AI has made remarkable strides in mimicking the styles of master artists, it cannot replicate the emotional depth, historical context, or “soul” that make their works timeless.
Instead of fearing AI as a threat to artistic authenticity, we should embrace it as a tool that can enhance human creativity. By working together, humans and machines have the potential to create art that is not only visually stunning but also rich in meaning and emotion.
In the end, art is a deeply human endeavor. It is a reflection of our experiences, our emotions, and our unique perspectives on the world. No matter how advanced AI becomes, it will always lack the one thing that makes art truly special: the enduring human spirit. As we continue to explore the possibilities of AI in art, let us remember that the greatest masterpieces are not just products of skill, but of soul. And that, perhaps, is something no machine can ever truly replicate.
Deep Dive Podcast
Check out our Deep Dive Podcast.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you want to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you anytime. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend just 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Related Questions
Pulling Back the Curtain: Women Artists of the Baroque Era Who Shattered Conventions
The names Caravaggio, Bernini, and Rubens dominate the narrative, celebrated as the geniuses who defined one of art’s most theatrical and emotive periods. But what if that picture is incomplete? What if, hidden behind the shadows of these towering figures, there were women whose contributions were equally groundbreaking yet overlooked by history?
You can read Pulling Back the Curtain: Women Artists of the Baroque Era Who Shattered Conventions by clicking here.
Where Did The Renaissance Begin? Why It Was Essential
The Renaissance began in Florence, Italy in the 14th Century. Florence was essential for the Renaissance because of its location, wealth, and many other factors. As we explore the Renaissance and Florence, this vital movement started.
You can read more by reading our blog, Where Did The Renaissance Begin? Why It Was Essential by clicking here.
Italy – Renaissance Art Defined And Explored
Originating in Florence, Italy, the Italian Renaissance is pivotal in shaping this transformative era, laying the artistic foundations we continue to admire today. Celebrated for its revival of classical ideals and introduction of innovative artistic techniques, the period also stands as a staunch advocate of humanistic values. Join us as we delve deeper into this fascinating Italian Renaissance art history chapter.
By clicking here, you can discover more by reading Italy – Renaissance Art Defined And Explored.