The eminent Spanish painter Francisco Goya is acclaimed for his artistic masterpieces and the profound events that molded his life and craft.
One such defining moment took place in 1792 when Goya, at 46, encountered a debilitating illness. This event, which led to his deafness, profoundly influenced his subsequent art, manifesting in changes to his style and subjects. Read on as we explore more about this illness and his art.
Table of Contents
- Francisco Goya’s Silence: The Artistic Transformation After Deafness
- The Evolution Of His Art Post Illness
- The Legacy Of The Silent Artist
- What Is A Cerebral Stroke, And How Could It Have Affected Francisco Goya?
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Related Questions
Francisco Goya’s Silence: The Artistic Transformation After Deafness
Francisco Goya, a renowned Spanish artist, is as much celebrated for his masterpieces as he is known for the significant events that shaped his life and work. One of the most pivotal events occurred in 1792 when, at age 46, Goya faced a life-altering illness. While Goya’s contributions to the art world were already remarkable by this age, the subsequent changes in his style and subjects are profoundly tied to this personal crisis.

Francisco Goya And His Illness
In 1792, at age 46, Goya endured a severe health scare accompanied by various symptoms: loss of vision and hearing, tinnitus, dizziness, paralysis affecting his right side, fatigue, and an overall sense of malaise.
A cerebral stroke was diagnosed, and although Goya gradually regained many of his faculties, the deafness persisted, turning his world into a silence that lastest forever.
Francisco Goya The Person And His Deafness
The onset of deafness in a world filled with sound can be an incredibly isolating experience. This sudden barrier must have been harrowing for Goya, who was accustomed to engaging with his environment and patrons vocally.
He no longer could participate in spoken conversations, overhear murmurs of the court, or listen to the ambient sounds of life that often inform an artist’s perception.
Yet, amidst this silence, Goya developed an intensified introspection. His ‘self-portraits’ post the illness exhibit a profound depth. In them, we see not just an artist, but a man grappling with his newfound condition, evoking a sense of vulnerability and contemplation.
The Evolution Of His Art Post Illness
Goya’s artistry underwent a significant transformation post his illness. The jovial tapestry cartoons and light-hearted Rococo influences of his early work gave way to a more profound, contemplative, and at times, disturbing palette.
Darkness And Depth
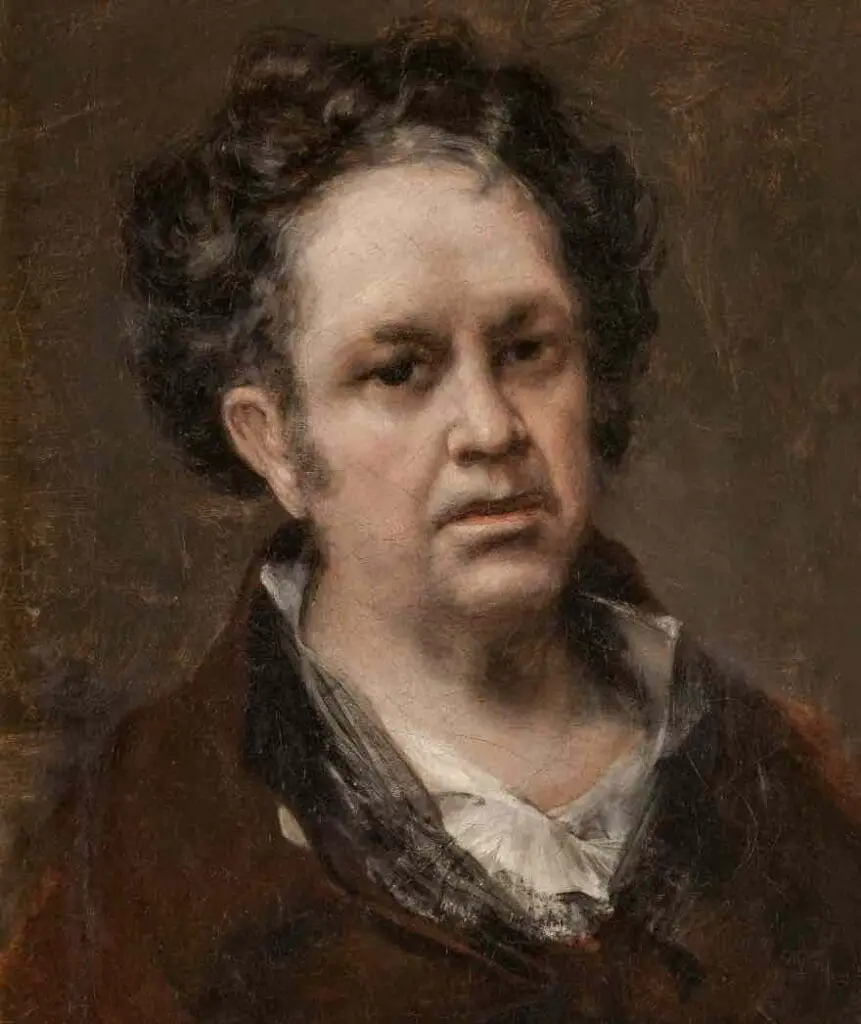
One can argue that the absence of sound in Goya’s life made his visual narratives more potent.
His famous “Black Paintings” series, including the haunting “Saturn Devouring His Son,” showcases a profoundly reflective artist, perhaps channeling his turmoil and the silence around him into raw, emotional artwork.
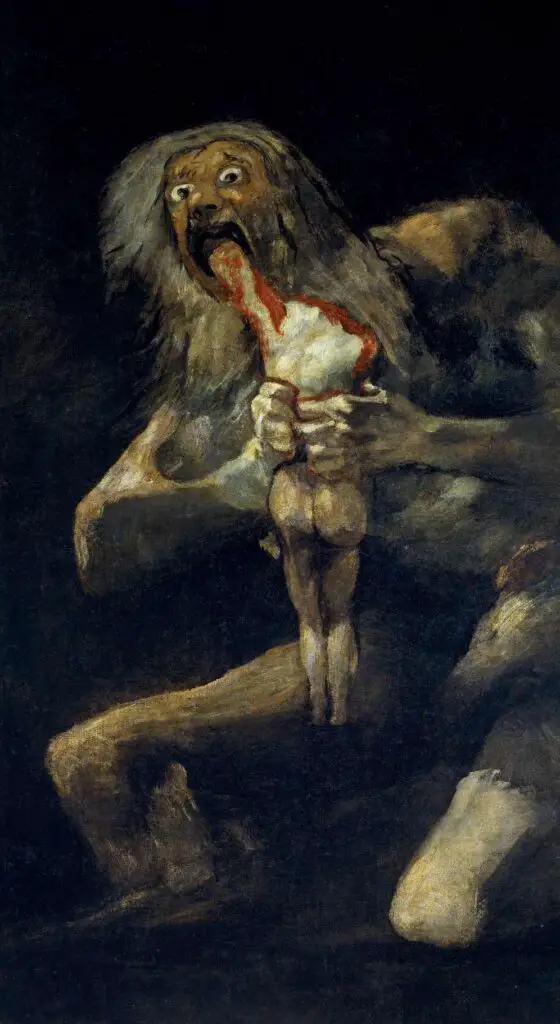

Political And Social Critique
Goya’s deafness and political upheavals in Spain also honed his focus on the world’s darker aspects. Works like “The Third of May 1808” are not just masterpieces of art but also influential commentaries on societal tumult, war atrocities, and human suffering.
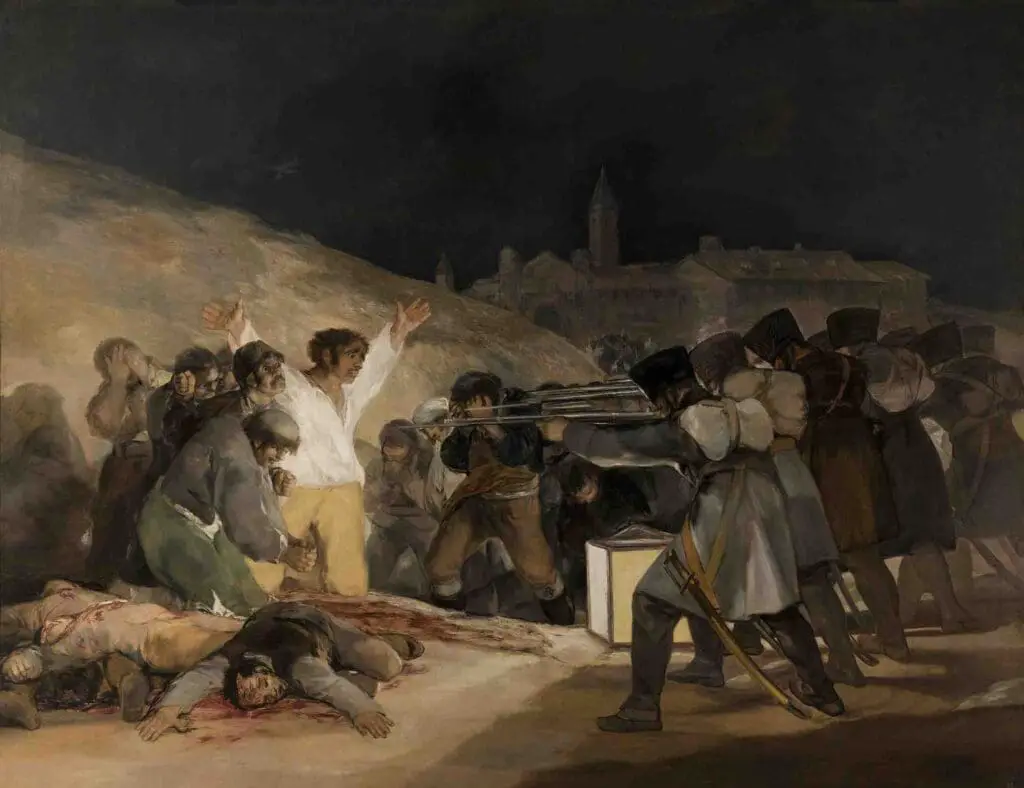

Personal Symbolism
His later works became rich with symbolism. “The Sleep of Reason Produces Monsters,” a part of his ‘Los Caprichos’ series, might be seen as an introspection into his mental state during his illness and the fears that consumed him.

The Legacy Of The Silent Artist
Deafness undeniably, added layers of complexity to Goya’s personality and art. However, rather than diminishing his prowess, this adversity amplified his creativity. It pushed him to venture deeper into the realms of the human psyche, emotion, and the society around him.
His ability to adapt, evolve, and continue producing groundbreaking work despite personal challenges makes Goya a brilliant artist and an emblem of resilience and innovation.
Francisco Goya’s journey from sound to silence isn’t just a tale of personal tragedy but a testament to the indomitable human spirit. His art, post the onset of deafness, serves as a beacon for all – proving that even in profound silence, a creative voice can resonate louder than ever.
What Is A Cerebral Stroke, And How Could It Have Affected Francisco Goya?
Most historians concur that Francisco Goya likely suffered from what we now recognize as a cerebral stroke. While it’s evident that this stroke resulted in his deafness, he recovered from several aspects of its aftermath.
Nonetheless, the stroke might have impacted him in various other capacities.
What Is A Cerebral Stroke?
A cerebral stroke, commonly called a “stroke,” is a medical condition where the blood supply is interrupted to a part of the brain. This can lead to brain tissue damage because brain cells begin to die when they are deprived of oxygen and nutrients.
What Are The Effects Of A Cerebral Stroke?
A cerebral stroke can have a wide range of effects, depending on the brain region affected, the damage’s extent, and how quickly medical treatment is received. The consequences of a stroke can be temporary or permanent, mild or severe.
Here are some potential effects of a stroke:
1. Physical Effects:
- Motor Skills: Weakness or paralysis on one side of the body (hemiparesis) or both sides (paraplegia). This can affect the ability to walk, grasp objects, or perform other everyday activities.
- Coordination and Balance: Difficulty with movement coordination might lead to falls.
- Facial drooping: One side of the face might droop or become numb.
- Swallowing Difficulties (dysphagia): This can increase the risk of choking or aspirating food into the lungs.
- Vision Problems: Blurred vision, double vision, or even blindness in one eye or part of the visual field.
- Speech and Language Difficulties (aphasia): Problems understanding speech (receptive aphasia) or expressing thoughts (expressive aphasia).
2. Cognitive Effects:
- Memory Loss: Especially with strokes that affect the temporal lobes or hippocampus.
- Impaired Judgment and Problem-Solving: Difficulties in making decisions, reasoning, or recognizing problems.
- Decreased Attention and Concentration: Difficulty focusing on tasks or being easily distracted.
- Spatial Awareness Issues: Difficulty understanding spatial relationships, which might lead to issues with mobility or recognizing familiar places.
- Perceptual Changes: Problems interpreting sensations or difficulty recognizing objects by touch.
3. Emotional And Psychological Effects:
- Depression: Many stroke survivors experience sadness, frustration, or helplessness.
- Anxiety: Concerns about future strokes or the challenges of coping with disabilities.
- Emotional Lability: Rapid and often exaggerated changes in mood, such as sudden bouts of crying or laughing.
- Personality Changes: Differences in behavior, temperament, or emotional response.
4. Other Effects:
- Fatigue: Feeling tired or having decreased energy, not solely related to physical activity.
- Epileptic seizures: Some people might develop epilepsy after a stroke.
- Incontinence: Difficulty controlling the bladder and bowels.
- Changes in behavior and self-care ability: Leading to a potential need for long-term care or assistance with daily living activities.
A stroke can impact any part of the auditory pathway, potentially causing hearing reception or perception issues. Although sudden hearing loss following a stroke in the vertebrobasilar territory or lower brainstem is relatively uncommon, cortical or central deafness is even more infrequent.
It appears that Francisco Goya experienced a significant stroke that impacted his hearing and potentially other cognitive functions such as memory, thinking, and daily functioning. Recognizing this is crucial, as many theorize that the aftermath of his stroke influenced his visual perception and, subsequently, his artwork.
Despite facing health adversities, Francisco Goya continued to paint for many more years. Several of his creations from this period significantly influenced numerous artists and shaped the art world’s perceptions.
Due to these contributions, Goya holds a revered spot in history as one of the most exceptional artists ever.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you want to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you anytime. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.”Spend 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Frequently Asked Questions
When did Francisco Goya lose his hearing?
Francisco Goya began to experience a loss of hearing in 1792, at the age of 46. This marked a pivotal moment in his life and artistic career.
What was the cause of Goya’s deafness?
The exact cause of Goya’s deafness remains uncertain. Some theories suggest an illness, possibly lead poisoning, while others propose more complex factors such as syphilis or a viral infection.
How did Goya’s deafness impact his art?
Goya’s deafness significantly influenced his artistic style and subject matter. As he grappled with isolation, his works became more introspective and darker, reflecting the psychological toll of his condition.
Did Goya continue to paint after losing his hearing?
Despite his deafness, Goya continued to paint prolifically. In fact, some of his most renowned works, like the “Black Paintings,” were created during this period, showcasing his ability to channel personal struggles into powerful art.
How did Goya cope with his deafness?
Goya’s coping mechanisms for his deafness included using an ear trumpet and adapting his communication methods. His resilience is evident in his determination to persist as a prominent artist despite his physical challenges.
Were there any specific events or experiences that triggered Goya’s deafness?
The precise events leading to Goya’s deafness are unclear. Some accounts suggest a sudden illness, while others propose a gradual onset. Regardless, the impact on his life and art was profound.
Did Goya’s deafness affect his relationships with others?
Goya’s deafness strained his relationships, making communication difficult. However, it also allowed him to delve deeper into his inner world, fostering a unique perspective that found expression in his later works.
How did Goya’s style change after losing his hearing?
Post-deafness, Goya’s style became more intimate and intense. His brushwork became looser, and he delved into darker themes, reflecting a heightened emotional and psychological depth in his art.
Were there any famous paintings created during Goya’s deaf period?
Yes, some of Goya’s most famous works were created during his deaf period, including the “Saturn Devouring His Son” and the “Witches’ Sabbath.” These paintings are recognized for their emotional intensity and dark themes.
How long did Goya live with deafness, and when did he pass away?
Goya lived with deafness for the remainder of his life. He passed away on April 16, 1828, leaving behind a legacy of influential and groundbreaking art that continues to captivate audiences today.
Related Questions
How Did Mannerism Become An Offshoot Of The Works Of The Renaissance?
Mannerism is the art movement that emerged after the High Renaissance era. Mannerism art is an offshoot of the Renaissance; Renaissance artists such as Michelangelo and Raphael adopted mannerism techniques. Mannerism art exaggerated and distorted elements of Renaissance art while creating a sense of imbalance in their art.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading How Did Mannerism Become An Offshoot Of The Works Of The Renaissance?
What Did Leonardo da Vinci Contribute To The Renaissance?
Leonardo da Vinci made many contributions to the Renaissance in art, science, engineering, medicine, and architecture. He was a keen observer who wrote down much of what he discovered in his notebooks. His artistic techniques changed how artists painted and influenced many other Renaissance artists.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Did Leonardo da Vinci Contribute To The Renaissance?
Meaning Of “Art Speaks Where Words Are Unable To Explain”
“Art speaks where words are unable to explain” means that words, even though very powerful and pcannot alwayss able to convey the messagegetan convey. Words are powerfulimage or piece of art can be much more potent than the spoken or written word.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading the Meaning Of “Art Speaks Wher.Words .Are Unable To Explain”