Francisco Goya is one of the most pivotal figures in the annals of art history. Revered by countless artists, he has been a beacon of inspiration for generations.
Francisco Goya is recognized as a paramount Spanish artist from the late 18th to early 19th centuries; Goya intriguingly straddles two eras: he is celebrated as the finale of the Old Masters and the pioneer of modern artistry. Dive deeper as we delve into the world of Francisco Goya and tackle 50 of the most commonly posed questions about him.
Table of Contents
- Francisco Goya (1746-1828) – The Spanish Artist
- 50 Frequently Asked Questions About Francisco Goya
- Related Questions
Francisco Goya (1746-1828) – The Spanish Artist
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes, commonly known as Francisco Goya, was a Spanish Romantic painter and printmaker. He is considered one of the most important Spanish artists of the late 18th and early 19th centuries and is often referred to as both the last of the Old Masters and the first of the moderns.
Life And Work Of Francisco Goya
Born in Fuendetodos, Spain, in 1746, Goya began his art studies in Zaragoza before moving to Madrid. He was initially influenced by the Rococo style, which was popular in Europe then.
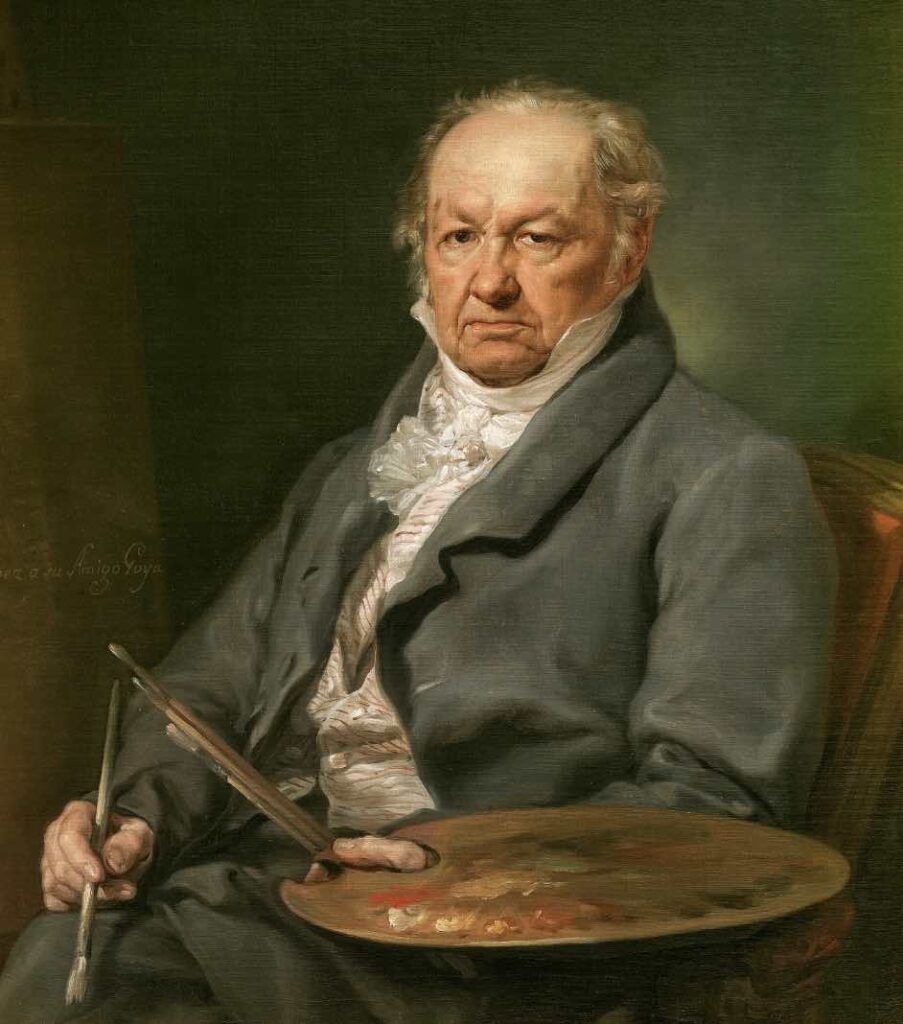
By the 1780s, Goya had become a prominent portrait painter to the Spanish aristocracy. He was appointed court painter to the Spanish Crown in 1786 and became the first Spanish artist to succeed at home and abroad.
Significance And Themes Of Francisco Goya’s Artwork
Goya’s creations carry profound themes that resonate deeply with art enthusiasts and scholars alike. Below, we’ve outlined these central motifs found within his masterpieces:
Mature Style:
Goya’s mature style is characterized by a shift from the light-hearted and playful Rococo works of his early years to darker, more introspective subjects. He began to depict the harsh realities of life, social injustices, and the human capacity for cruelty.
War And Critique of Society:
His series of 82 prints, “The Disasters of War” (1810-1820), depicts the Peninsular War’s atrocities and aftermath. This work and others offer a critical view of society, challenging traditional institutions like the church and the monarchy.
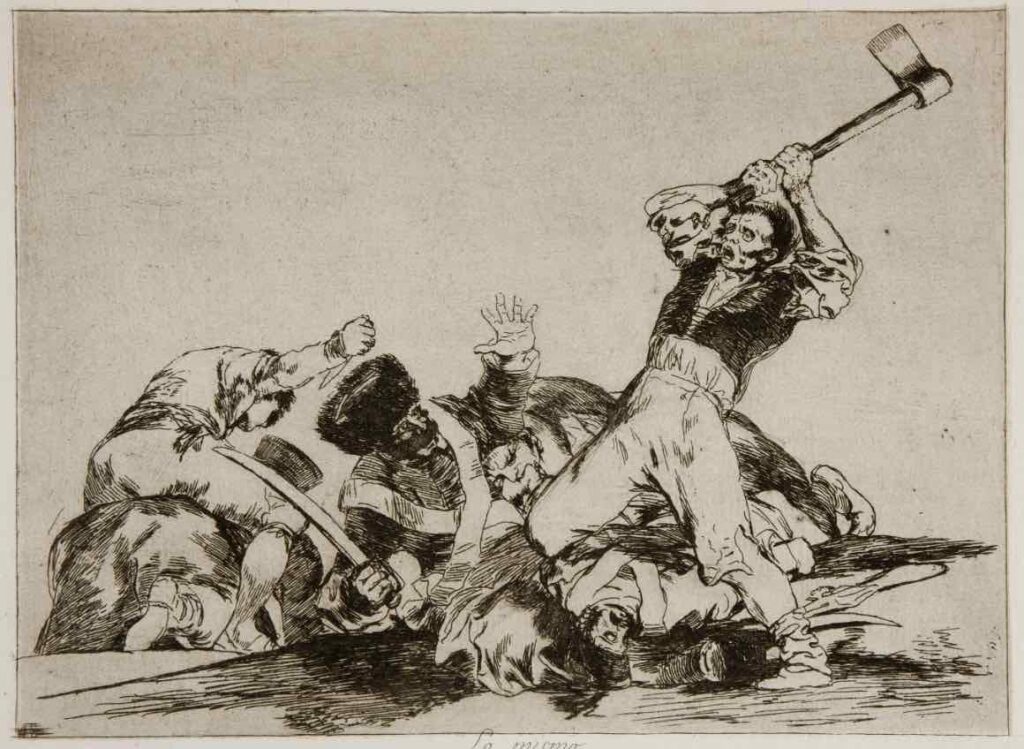

This is one of the example of The Disasters of War By Francisco Goya
Portraits:
Goya’s portraits are celebrated for their psychological depth. He could reveal his subjects’ personalities, aspirations, and vulnerabilities, from the nobility to the ordinary people.
The Black Paintings:
In the latter part of his life, Goya painted a series of murals on the walls of his home, known as the “Black Paintings.” These works are filled with haunting, nightmarish imagery and reflect Goya’s fears, anxieties, and view of the world around him.
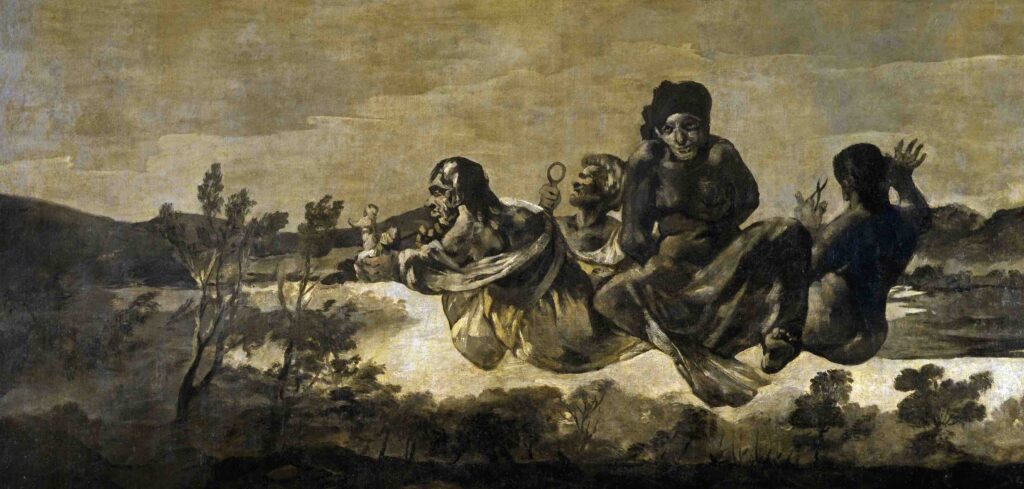

Is an example of the Black Painting of Fransisco Goya
Influence On Modern Art:
Goya is often hailed as a precursor to modern art. His later works demonstrate a loosening of brushwork and a move away from traditional compositional techniques, which would influence future artists such as Édouard Manet and Pablo Picasso.
Legacy Of Francisco Goya
Goya’s influence has been enormous. His ability to transition and thrive through various artistic movements and his courage to address the dark side of human nature set him apart from many of his contemporaries.
Today, his works are held in high esteem and are showcased in major museums worldwide.
Francisco Goya is considered an essential artist because of his innovative approach to traditional painting techniques, his brave critique of societal norms and institutions, and his profound influence on the artists who followed him. His rich legacy serves as a bridge between the Old Masters and modern art.
50 Frequently Asked Questions About Francisco Goya
1. Who was Francisco Goya?
Francisco Goya was a renowned Spanish artist known for his paintings, drawings, and etchings. He lived from 1746 to 1828.
2. Where was Francisco Goya born?
Goya was born in Fuendetodos, a small town in Aragon, Spain.
3. What are some of Goya’s most famous works?
Some of his most famous works include “The Third of May 1808,” “The Sleep of Reason Produces Monsters,” and the “Black Paintings” series.
4. What art movements is Goya associated with?
Goya is associated with both the Romantic and the Enlightenment movements in art.
5. Did Goya work in various artistic mediums?
Yes, Goya was a versatile artist who worked in various mediums, including painting, etching, and drawing.
6. What is “The Third of May 1808” about?
“The Third of May 1808” depicts the execution of Spanish citizens by French troops during the Peninsular War. It is a powerful anti-war painting.
7. What is the significance of Goya’s “The Sleep of Reason Produces Monsters”?
This etching is part of his “Los Caprichos” series and explores the theme of reason and imagination.
8. What are the “Black Paintings”?
The “Black Paintings” are a series of 14 dark and intense paintings that Goya created on the walls of his house. They are considered some of his most enigmatic works.
9. Why did Goya paint the “Black Paintings”?
It is believed that Goya painted these works as a form of personal expression and commentary on the darker aspects of human nature.
10. What is the meaning behind “Saturn Devouring His Son”?
This painting from the “Black Paintings” series is a gruesome portrayal of the mythological god Saturn devouring one of his children. It is seen as a reflection of Goya’s inner turmoil.
11. Was Goya a court painter?
Yes, Goya served as a court painter for the Spanish monarchy, producing numerous portraits of royal family members.
12. How did Goya’s style evolve over his career?
Goya’s style evolved from traditional and neoclassical to more emotionally charged and innovative as he grew older.
13. Did Goya experience any significant life events that influenced his art?
Yes, Goya’s life was marked by illness, war, and political upheaval, which had a profound impact on his art.
14. What is the significance of Goya’s series “Los Caprichos”?
“Los Caprichos” is a series of 80 etchings that satirize the social and political issues of Goya’s time, reflecting his critical view of society.
15. How did Goya’s deafness affect his art?
Goya’s gradual deafness led to increased isolation and introspection, which is reflected in his later works, including the “Black Paintings.”
16. What role did Goya play during the Napoleonic Wars?
Goya was appointed as a court painter by Joseph Bonaparte during the occupation of Spain by French forces.
17. Did Goya’s political beliefs change over time?
Yes, Goya’s political beliefs evolved, and he became disillusioned with the monarchy and the French occupation of Spain.
18. Where can one view Goya’s artworks today?
Many of Goya’s works are housed in museums around the world, including the Prado Museum in Madrid and the Metropolitan Museum of Art in New York.
19. How did Goya’s works influence later artists?
Goya’s innovative techniques and exploration of psychological themes influenced many artists, including the Romantic painters and the Surrealists.
20. Did Goya have any significant artistic contemporaries?
Goya’s contemporaries included other notable Spanish artists like Francisco de Zurbarán and Francisco de Goya.
21. Did Goya have a family?
Yes, Goya married Josefa Bayeu, and they had several children together.
22. What is the “Goya Award” in Spain?
The Goya Awards are Spain’s premier film awards, named in honor of Francisco Goya.
23. How did Goya’s health decline in his later years?
Goya’s health deteriorated due to various illnesses, including a severe fever that left him permanently deaf.
24. Did Goya leave behind any autobiographical writings?
Yes, Goya left behind a series of letters and writings that provide insights into his life and thoughts.
25. What is the significance of Goya’s “The Naked Maja”?
“The Naked Maja” is a controversial nude painting that challenged societal norms of the time. It is considered a precursor to modern erotic art.
26. How did Goya’s “The Disasters of War” series come about?
“The Disasters of War” is a series of prints depicting the horrors of war in Spain. Goya created these works as a response to the Peninsular War.
27. What is the “Black Dog” in Goya’s works?
The “Black Dog” is a recurring motif in Goya’s art, often seen as a symbol of his inner demons and mental anguish.
28. Did Goya’s works receive recognition during his lifetime?
Yes, Goya was a respected artist during his lifetime, but his later works were not as widely appreciated as his earlier portraits.
29. Did Goya have any artistic apprentices or students?
Goya’s studio had several students, including the painter Vicente López y Portaña.
30. How did Goya’s work evolve during his time in France?
During his exile in France, Goya continued to paint and evolved his style, producing works like “The Milkmaid of Bordeaux.”
31. What is the “Pinturas Negras” in Spanish?
The “Pinturas Negras” is the Spanish term for Goya’s “Black Paintings.”
32. Was Goya’s work influenced by Spanish folklore?
Yes, Goya’s interest in Spanish folklore and superstitions is evident in some of his works, such as “Witches’ Sabbath.”
33. What is Goya’s connection to the Royal Tapestry Factory?
Goya worked as a designer for the Royal Tapestry Factory, creating designs for tapestries.
34. Did Goya have any patrons who supported his art?
Yes, Goya had various patrons, including the Duke of Osuna and the Spanish royal family.
35. How did Goya’s political satires impact his career?
Goya’s political satires in “Los Caprichos” led to his temporary exile from Madrid as they offended powerful individuals.
36. What is the meaning behind Goya’s “The Colossus”?
“The Colossus” is an allegorical painting with interpretations ranging from a depiction of war to a representation of the Spanish people rising against tyranny.
37. What artistic techniques did Goya use in his etchings?
Goya employed a range of etching techniques, including aquatint, to achieve various
38. How has Goya’s reputation evolved over time?
Goya’s reputation has grown over time, and he is now considered a seminal figure in art history.
39. Did Goya receive any honors or awards during his lifetime?
Yes, Goya was awarded the Order of Charles III by the Spanish king for his artistic contributions.
40. What is the “Red Boy” painting by Goya?
“Red Boy” is a portrait of a young boy painted by Goya.
41. How did Goya’s paintings capture the essence of Spanish life and culture?
Goya’s portraits and genre scenes often depicted the people and customs of Spain, offering a window into Spanish society.
42. Did Goya ever collaborate with other artists?
Goya collaborated with other artists on various projects, including tapestry designs.
43. What is the legacy of Goya’s “La Tauromaquia” series?
“La Tauromaquia” is a series of prints depicting bullfighting scenes. It contributed to the romanticization of bullfighting in Spain.
44. How did Goya’s works reflect his views on religion?
Goya’s works often conveyed his complex relationship with religion, with some pieces expressing skepticism and others reverence.
45. Did Goya’s works have a significant impact on Spanish culture?
Goya’s art played a pivotal role in shaping Spanish culture and influencing subsequent generations of Spanish artists.
46. What is the controversy surrounding Goya’s painting “La Maja Vestida”?
“La Maja Vestida” is a clothed version of “The Naked Maja” that was created to hide the nude figure. It remains controversial due to its association with censorship.
47. How did Goya’s experiences during the Inquisition influence his art?
Goya’s experiences during the Spanish Inquisition influenced his critical view of authority and power, which is evident in some of his works.
48. What is the significance of Goya’s self-portraits?
Goya created several self-portraits throughout his life, providing insights into his changing appearance and state of mind.
49. Did Goya’s art influence other forms of media, such as literature and film?
Yes, Goya’s art has inspired various literary works and has been referenced in films and other forms of popular culture.
50. How is Goya remembered in modern times?
Francisco Goya is remembered as a visionary artist who pushed the boundaries of artistic expression and made lasting contributions to the world of art. His works continue to inspire and provoke thought today.
These frequently asked questions provide a comprehensive overview of Francisco Goya’s life, art, and impact on the world of art and culture.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you want to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel with great videos and information.
Related Questions
Did Michelangelo And Leonardo Know Each Other?
Michelangelo and Leonardo da Vinci knew each other but were considered bitter rivals. Leonardo da Vinci and Michelangelo knew each other, but they did like each other. They were both asked to do a commission on the Council Hall of the Palazzo Vecchio and were supposed to work side-by-side; the project was never completed.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Did Michelangelo And Leonardo Know Each Other?.
Michelangelo’s Method To Paint The Sistine Chapel Ceiling
He built a large scaffolding structure that could move around the chapel to paint the ceiling; the painting of the Sistine Chapel was an extremely strenuous work that was a huge personal cost both physically and mentally to Michelangelo.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Michelangelo’s Method To Paint The Sistine Chapel Ceiling.
Michelangelo’s Sistine Chapel And His Payment
Michelangelo was paid 3200 gold ducats for his work on the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel, which would have been a very lucrative commission. We know that he stopped work on the ceiling for a while due to his not being paid by the Vatican. Michelangelo liked to give the impression that he was a very poor artist, but records have shown that he died an extremely wealthy man.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Michelangelo’s Sistine Chapel And His Payment.