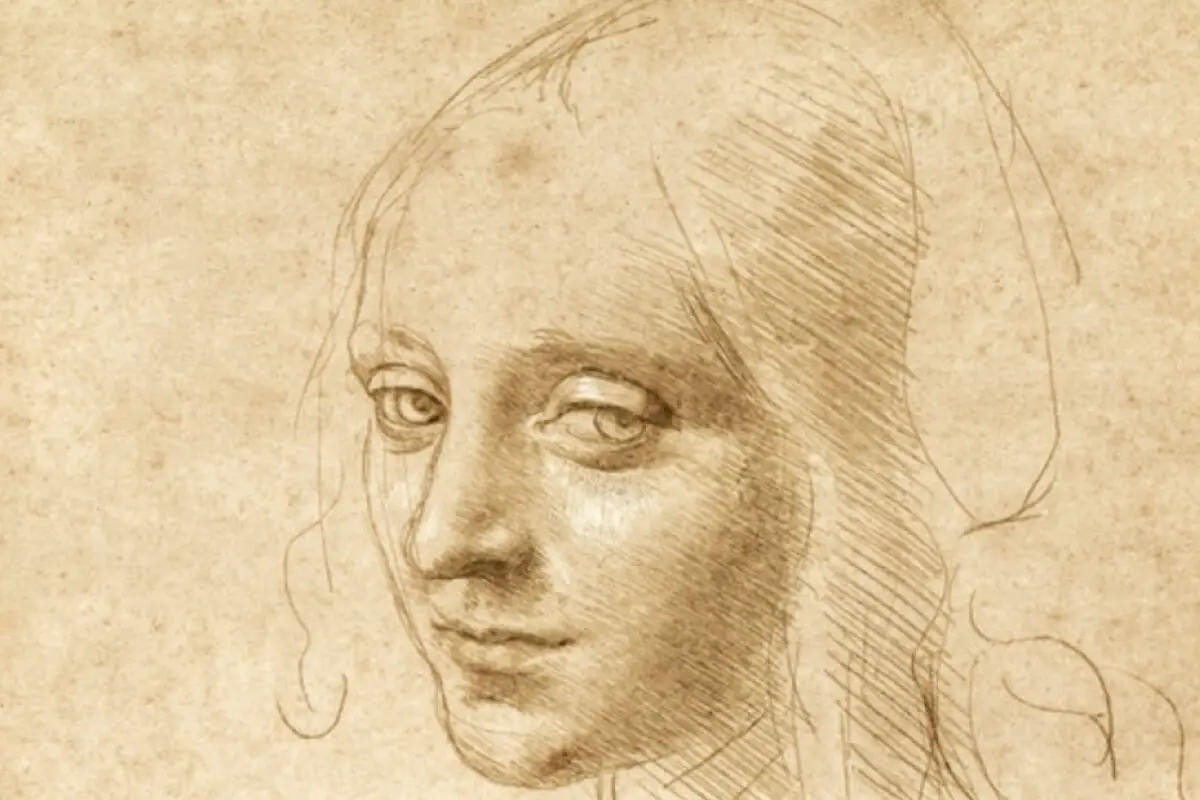
Few figures capture the human imagination as much as Leonardo da Vinci, the quintessential Renaissance man. His intriguing life and unparalleled genius, encapsulated within his profound sketches, reflect the fusion of art and science, painting and engineering, embodying the spirit of an era when boundaries were meant to be dissolved.
Da Vinci’s sketches are not random doodles; they represent a visual diary filled with imaginative experiments, inventions, and detailed studies on various subjects. His drawings’ varied symbolism and styles offer us a glimpse into his ingenious realm.
Table of Contents
- The Life and Times of da Vinci
- Understanding the Purpose of da Vinci’s Sketches
- Examining Specific Sketches By da Vinci
- Related Questions
The Life and Times of da Vinci
Shaping Genius: How Leonardo da Vinci’s Era Influenced His Artistic Output
History has always been indisputable in shaping the lives and careers of great minds. One such individual whose life was indelibly marked by the vibrance of his epoch is Leonardo da Vinci, the epitome of the Renaissance era.
Da Vinci’s artistic prowess assumes a significant relevance when we draw upon historical, cultural, and political factors during his time.
The Renaissance period, spanning the 14th to the 17th century, marked a genuine revival of interest in classical learning, values, and art forms. In response to this societal voltage, da Vinci developed and advanced his artistic style and approach to sketches.
Many art historians argue that the societal yearning for classical learning during the Renaissance stirred da Vinci’s insatiable curiosity and fostered his scientific approach to art. Leonardo’s sketches reflect this thirst for knowledge.
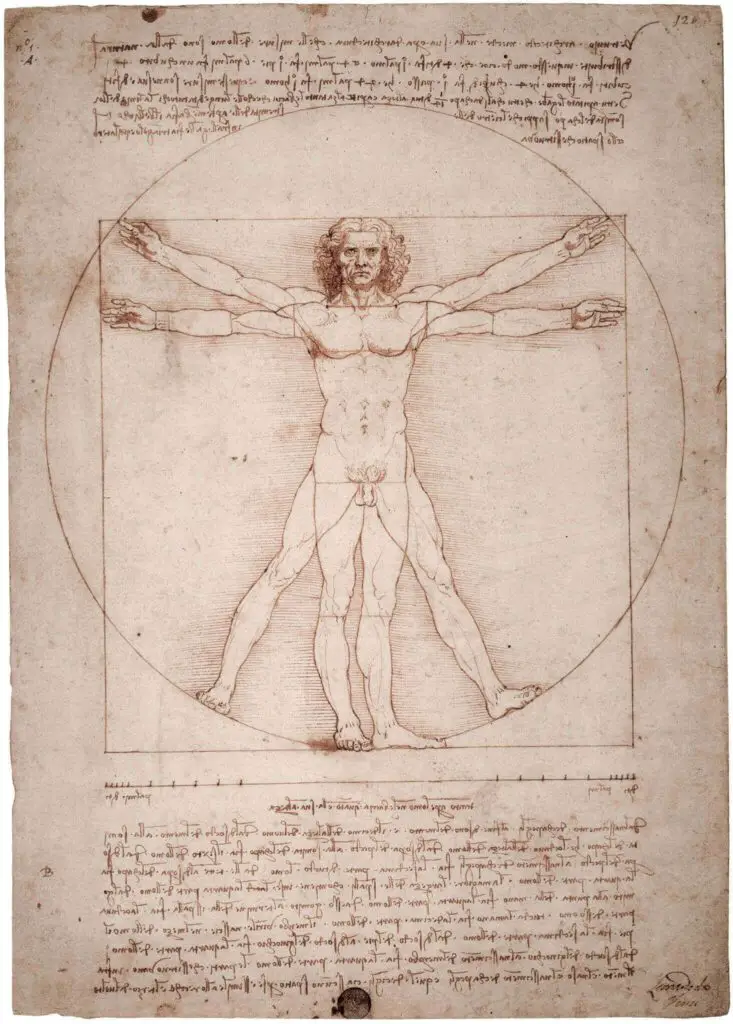
They intimate a meticulous study of empirical data – a hallmark of the period’s intellectual norms. For instance, his anatomical drawings, like the “Vitruvian Man,” speak of a detailed examination of the facets of nature and human anatomy.
Politically, intense rivalry between Florence, where da Vinci began his career, and other city-states resulted in patronage of artists by wealthy sponsors. This sponsorship pattern compelled artists like da Vinci to portray their sponsors favorably, inadvertently weaving a theme of political power into their works. Herein lies the subtle brushstrokes of politics visible in da Vinci’s tableaus.
Moreover, da Vinci’s iconic chiaroscuro technique, characterized by shadowy figures emerging from misty landscapes, might well reflect the period’s uncertainties.
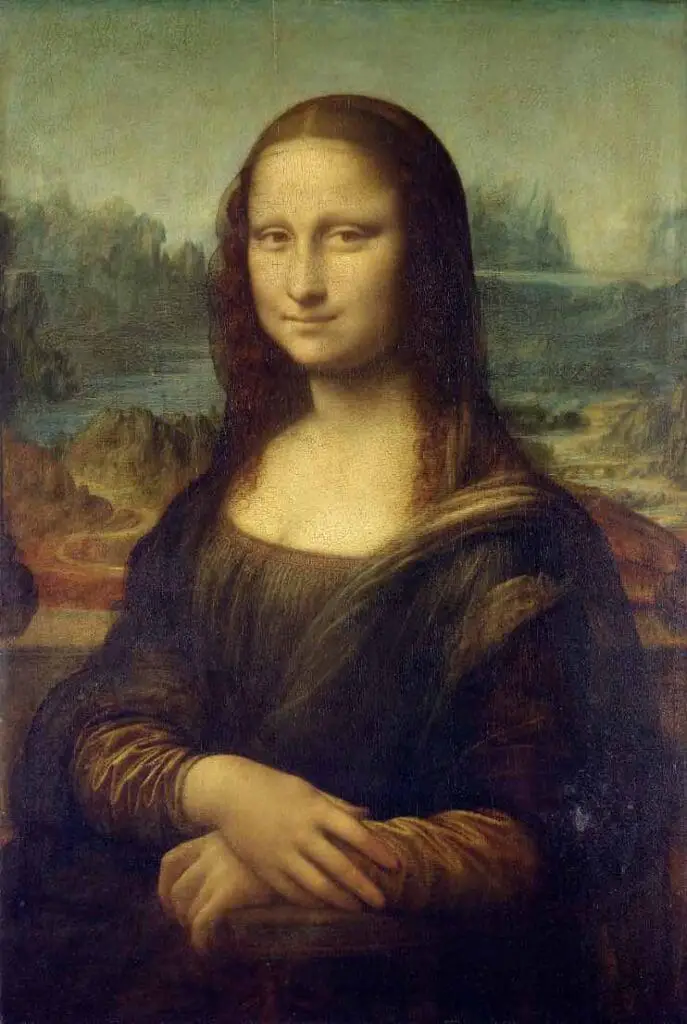
The era was a time of enlightenment and revival and was born out of political instability and war. This duality of the time underscored his technique, creating a palpable sense of mystery that consequently became a signature in his paintings such as “Mona Lisa” and “The Last Supper.

Turning to religion, da Vinci, being commissioned by religious figures and institutions, was inevitably influenced by the religious ethos of his era. His religiously-themed paintings like “The Annunciation” and “The Last Supper” showcase a fusion of bold naturalism with divine symbolism, underscoring his ingenuity and the religious tenets of the era.
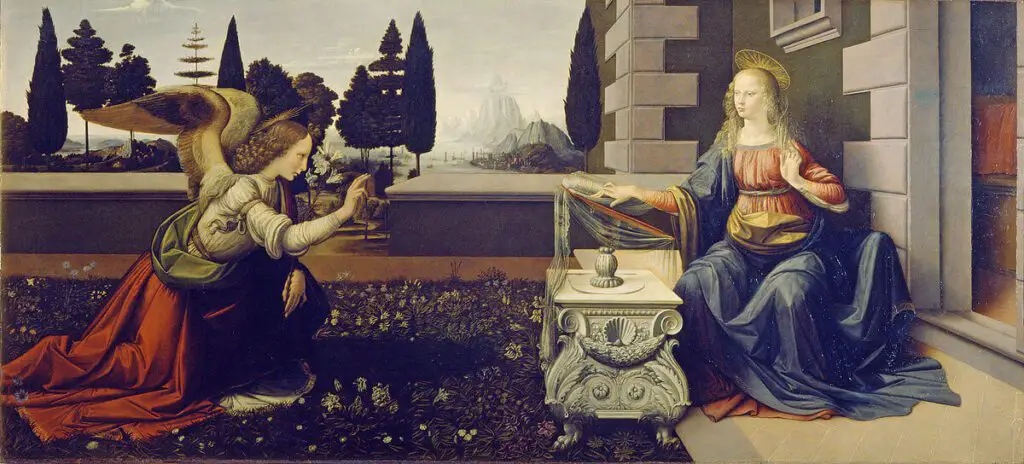

Ultimately, Leonardo da Vinci’s artistic style and approach to sketches must be evaluated within the context of his time. This holistic approach unearths and uncovers the influences that shaped his work.
This multi-faceted perspective pays homage to the genius artist Leonardo da Vinci and highlights the inextricable link between art and the societal forces that shape its manifestations. Art, in its essence, is a mirror of the times, and Leonardo da Vinci serves as a testament to this timeless truth.
Understanding the Purpose of da Vinci’s Sketches
The Impetus Behind da Vinci’s Scribbles: A Delve into the Renaissance Master’s Doodles
Often viewed as a master of all trades, Leonardo da Vinci, a timeless Renaissance painter, sculptor, scientist, and architect, has made numerous contributions that have profoundly marked art history. Yet, one might be entranced by his less-noted yet equally captivating scribbles and sketches.
These visually articulate doodles are a tangible testament to da Vinci’s sense of naturalistic and anatomical observation, suggesting an underlying motivation steered by tireless exploration and profound comprehension.

Behind the multiple layers of paint in his illustrious masterpieces, these meandering explorations on paper hold the key to understanding da Vinci’s relentless pursuit of knowledge.
Often overshadowed by his grand coups, such as ‘Mona Lisa’ or ‘The Last Supper,’ these sketches serve as a pivotal framework, yielding fascinating insights into da Vinci’s work methods and cognitive processes.
Ever the perpetual learner, da Vinci used his sketches as visual notations, enabling him to translate his observations into rhythmic arrangements of lines and forms that reflected the actual workings of nature. His anatomical sketches, for instance, are a testament to his meticulous emphasis on observation and analysis, which was at the heart of his method.
Similarly, the minutiae of the natural world were not lost on da Vinci. His sketches of plants, water movements, and even the flight patterns of birds underscore his deep commitment to understanding the intricacies of the world around him, manifesting an unbroken liaison between art and science. This single-minded focus governing da Vinci’s sketches reveals their fundamental role inin-depth comprehension and actualization of the larger natural world.
Troubling for more than aesthetics, da Vinci’s usage of sketches extended to their function as communication and pedagogical tools. For instance, his ‘Vitruvian Man’ embodies the harmonious intersection of art and mathematics and serves as instructional material, simplifying complex theoretical concepts into comprehensible visual narrations.
Offering a window into his creative pipeline, da Vinci’s preparatory sketches for his painting, the ‘Battle of Anghiari,’ exemplify his consideration of different figural compositions, movements, and expressions. His incessant sketching practice was thus shaped by a need to explore varied possibilities before embarking on a grand-scale artistic project.
Far from being trivial or haphazard scribbles, Leonardo da Vinci’s sketches were pivotal components of his artistic endeavor. Not only did they capture the workings of his mind, but they also reflected his primary motivation: decipher the world’s complexities, represent them visually, and advance the human comprehension of nature.
The sketches are a testament to his ceaseless curiosity, providing the world with a trail of breadcrumbs leading to the inner workings of his genius mind. Untangling the web of da Vinci’s motivations behind his sketches sheds light on his tremendous value on observation, learning, and visual storytelling, shaping his artistic legacy’s profound scope, depth, and multidimensionality.
Examining Specific Sketches By da Vinci
Renowned for bridging the gap between art and science, Leonardo da Vinci’s sketches provide us with a glimpse into the mind of a polymath, evidencing his unparalleled ability to see and record the world around him.
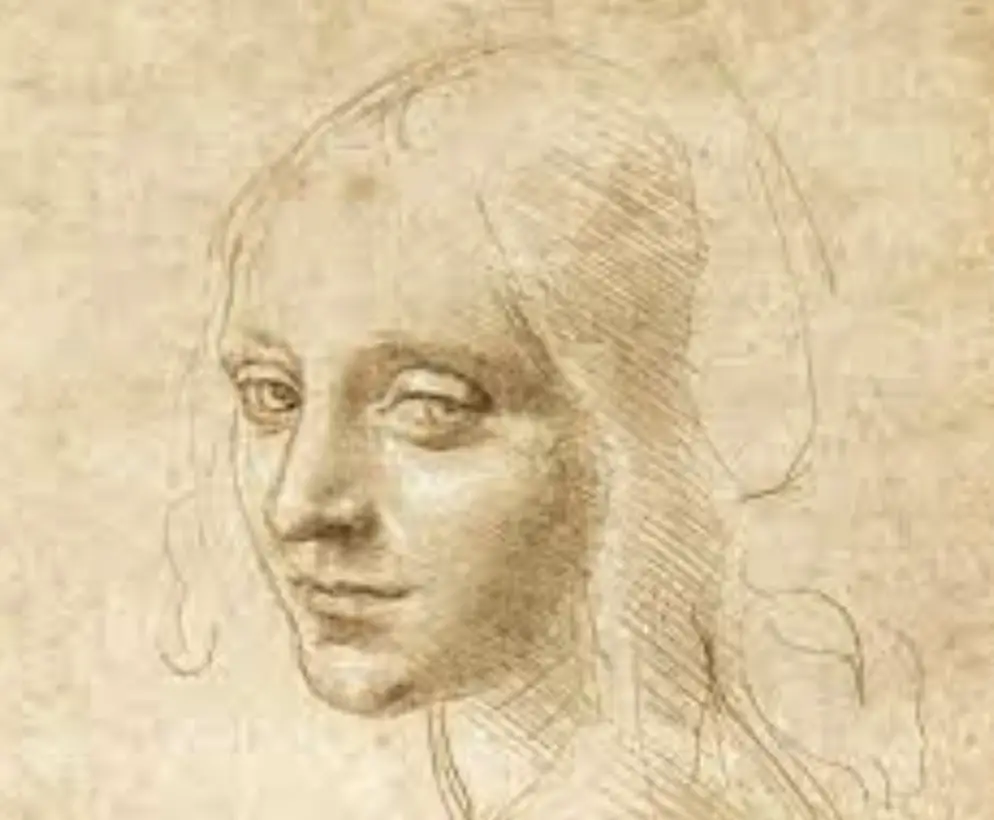

These sketches resonated with da Vinci’s understanding of ‘il disegno,’ which, in the broadest sense, encapsulates both the act of drawing and the intellectual activity of design.
One of the most celebrated of da Vinci’s sketchbook compilations is the Codex Atlanticus, housing a vast array of sketches, from birds in flight to intricate geometric patterns. These sketches capture da Vinci’s fascination with flight, striving to understand its mechanics, symbolic of his broader interest in studying the natural world.
Similarly noteworthy are da Vinci’s anatomical sketches, a testament to his unique style of observing and portraying the human body. His rendition of the Vitruvian Man is a convergence of art and mathematics, encapsulating the belief in the proportionality of the human figure. His detailed sketches of the human heart, bones, and muscles display an acute understanding of biology, intertwining scientific facts with artistic rendering.
A compelling interplay between shadow and light in da Vinci’s sketches creates three-dimensionality. This engagement with chiaroscuro allows the subjects of his sketches to take on a roundness, a depth, which reveals da Vinci’s acute sensitivity to the natural world’s intricacies.
One can’t discuss da Vinci’s sketches without mentioning his study for The Last Supper or his sketches envisioning The Battle of Anghiari. They illustrate da Vinci’s mathematic precision and ability to imbue narrative tension, masterfully using light and perspective to convey space and depth. These sketches are not just preparatory studies but a visual language mapping ideas and possible narratives.
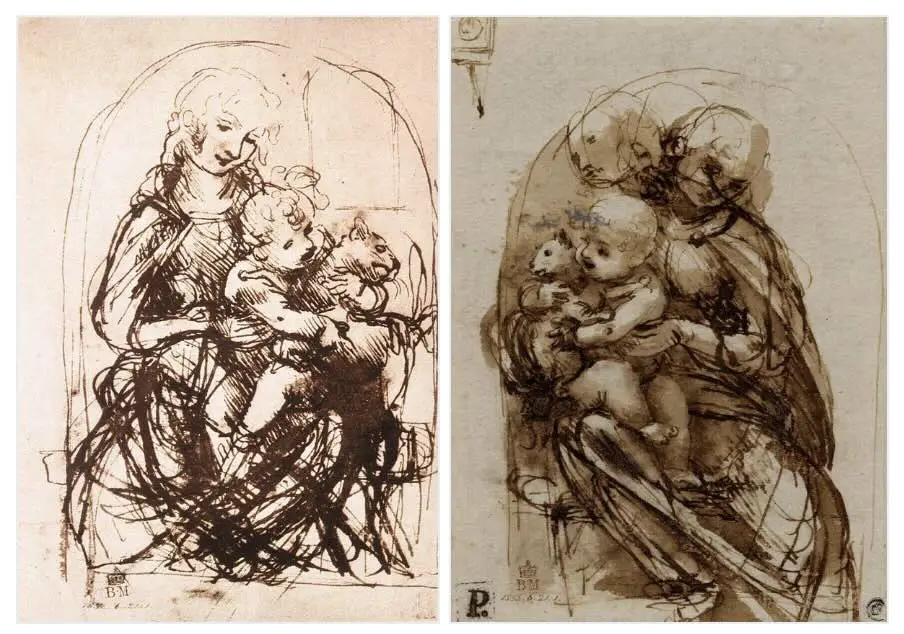

Symbolism is another striking aspect of da Vinci’s work, as seen in his sketch, The Madonna of the Cat (Madonna del Gatto). A seemingly simple domestic scene betrays a wealth of symbolic meaning that aligns with his scientific outlook, exploring the divine geometry in nature and humanity.
The value and process of creation in Leonardo da Vinci’s sketches are inseparable. Each line and stroke is integral, harboring the seeds of the final artwork and encapsulating theories, observations, and projections. His scribbles and plans reveal his iterative process and dedication to constant learning, making his sketches an artistic echo of his mind.
Centuries later, Leonardo da Vinci’s sketches still captivate and inspire. They remain an enduring testament to a mind relentlessly pulled by an insatiable curiosity and demonstrate his enduring dedication to understanding and innovating.
The legacy of Leonardo da Vinci is encapsulated in the narrative of his sketches, a testament to an artistic genius whose career was fueled by intellectual inquiry and constant observation. They represent an essential art history component, roughly outlined in charcoal and ink but ultimately painted in brilliance.
Da Vinci’s sketches remain an alluring testament to his ceaseless curiosity and innovative approach, as they illustrate his ability to blend art and science seamlessly. From revealing intricate aspects of his formative years and personal life to exposing the substantive purpose of his sketches, his symbolic language and style, and the exploration of individual sketches, we can witness the grandeur of his vision and the breadth of his genius.
As we pull back the layers of Leonardo’s works, it becomes evident that they are time capsules transcending historical and cultural barriers, resonating even today with their immense depth and universal appeal.
Sifting through the veil of historical antiquity, we continue unraveling the mystery of Leonardo da Vinci, appreciating how truly ahead of his time he was: a man who painted not just on canvas but on the fabric of human consciousness.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you are interested to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. I would be happy to talk to you if you have any questions. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel filled with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Related Questions
How Was Leonardo da Vinci Able To Master So Many Different Professions?
Leonardo da Vinci is a man known to have had many different titles and professions during his lifetime. He was able to master this profession because he was a genius. But more than just being a genius, Leonardo is also self-educating and never stops learning. He had an insatiable amount of curiosity about all kinds of subjects.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading How Was Leonardo da Vinci Able To Master So Many Different Professions?
What Can We Learn From Leonardo Da Vinci?
Leonardo da Vinci was a philosopher; being a philosopher means that you want to seek wisdom. Leonardo was one person who tried to seek knowledge or enlightenment in his life. Leonardo was an active observer and learner of the human body, human behavior, and nature.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Can We Learn From Leonardo Da Vinci?
Was Leonardo da Vinci A Philosopher?
Leonardo da Vinci was a philosopher; being a philosopher means that you want to seek wisdom. Leonardo was one person who wanted to seek wisdom or enlightenment in his life. Leonardo was an active observer and learner of the human body, human behavior, and nature.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Was Leonardo da Vinci A Philosopher?