The Renaissance era is often hailed as a pivotal period in the history of art and culture, mainly because it represented a “Rebirth” of classical ideals. The Renaissance is one of my favorite periods of art as it produced so many great artists.
Art underwent transformative changes during the Renaissance, and philosophy and culture were also significantly impacted. Read on to discover when and where the Renaissance occurred, and learn about the seminal artists who defined this remarkable period.
Table of Contents
- What Is The Renaissance Era? A Deep Dive Into The Rebirth Of Art, Culture, And Thought
- The Italian Renaissance Era (14th To 17th Century
- The Northern European Renaissance (Late 15th To Early 17th Century)
- Related Questions
What Is The Renaissance Era? A Deep Dive Into The Rebirth Of Art, Culture, And Thought
The Renaissance, which means “rebirth” in French, was an unparalleled period in European history that bridged the gap between the Middle Ages and the Modern era. While the Renaissance is known for its artistic achievements, it was also a time of immense growth in literature, philosophy, science, and the rediscovery of classical Greek and Roman ideas.
It was when humans took center stage, and the individual’s potential for greatness was highly celebrated, marking a departure from the more collective ethos of the Medieval period.
Defining The Renaissance Era
The Renaissance era is generally considered to have originated in Italy during the 14th Century and lasted until the 17th Century, gradually spreading across Europe. The epoch is characterized by the revitalization of classical learning and wisdom, hence the term “rebirth.”
People began to develop an intense interest in the achievements of the individual, and a more human-centered view of the world took precedence over the strictly religious perspective of the preceding Middle Ages.
Renaissance Era As A Catalyst for Change
Several critical events laid the groundwork for the emergence of the Renaissance. Here are some of the significant world events that set the stage for the Renaissance era to begin.
- Fall of Constantinople (1453): The fall of this Byzantine capital to the Ottoman Turks led many scholars to flee to Europe, bringing with them valuable manuscripts of classical Greek and Roman literature.
- Discovery of the New World (1492): Christopher Columbus’s discovery opened the doors for exploration, further broadening the European mindset.
- Protestant Reformation: Initiated by Martin Luther in 1517, the Reformation led to a reevaluation of individual faith and interpretation of scripture, greatly influencing art and thought.
- The Invention of the Printing Press (circa 1440): Johannes Gutenberg’s invention made it easier to disseminate information, making knowledge more accessible to the general population.
- Revival of Classical Learning: First seen in Italy and later in Northern Europe, the Renaissance was fueled by a renewed interest in classical Greek and Roman culture.
All of these had a significant impact on culture and life in Europe. These events helped lead to the change of the Renaissance era we know it today.
The Italian Renaissance Era (14th To 17th Century
The Italian Renaissance unfolded between the 14th and 17th centuries, marking a period of intellectual awakening and cultural rejuvenation. Italy became the global epicenter for art, literature, and cultural innovations during this era. Continue reading to delve into the influential artists who shaped this transformative period.
Major Artists Of The Italian Renaissance Era And Their Contributions
Some of the greatest artists who lived created art during the Renaissance era. Below are five of the most essential Renaissance-era artists.
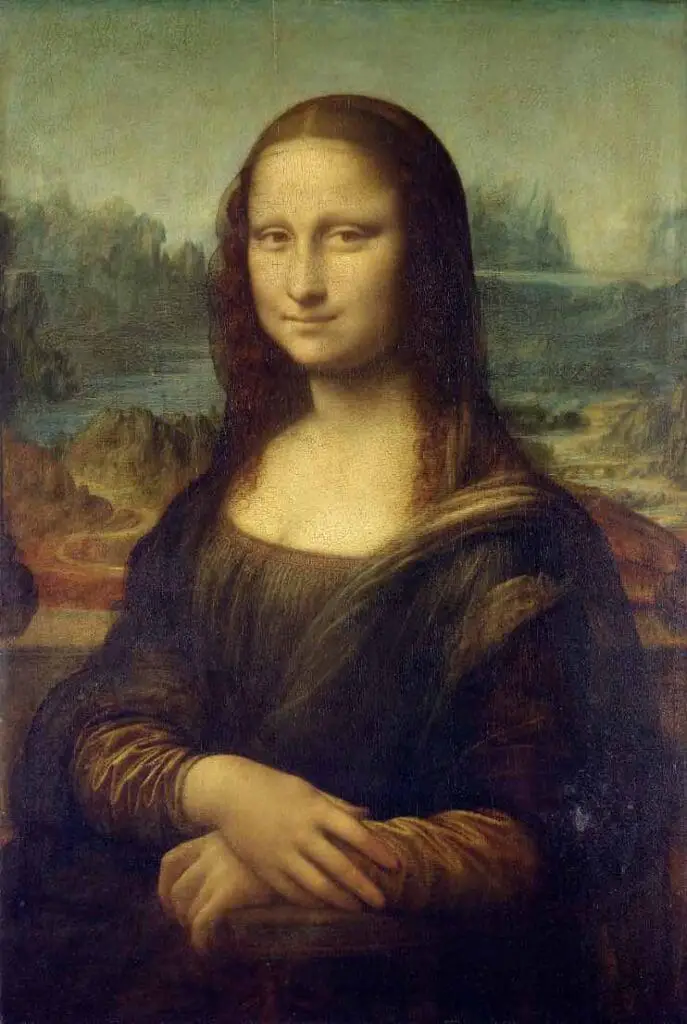
Leonardo da Vinci (1452–1519):
Known for his unparalleled versatility, Leonardo contributed to the arts—evident in masterpieces like the “Mona Lisa” and “The Last Supper”—and in sciences, anatomy, and engineering.


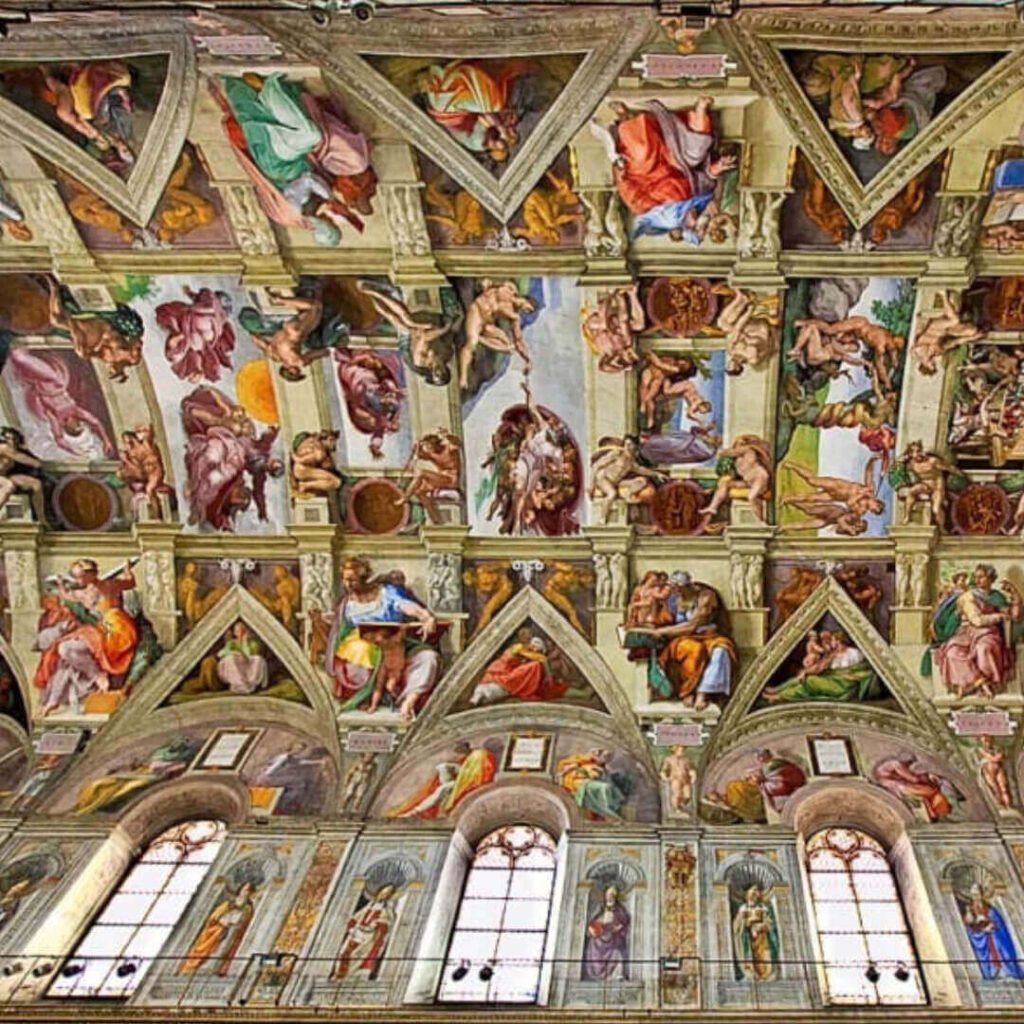
Michelangelo Buonarroti (1475–1564):
Responsible for the magnificent Sistine Chapel ceiling and the statue of David, Michelangelo was an exemplary sculptor, painter, and architect.

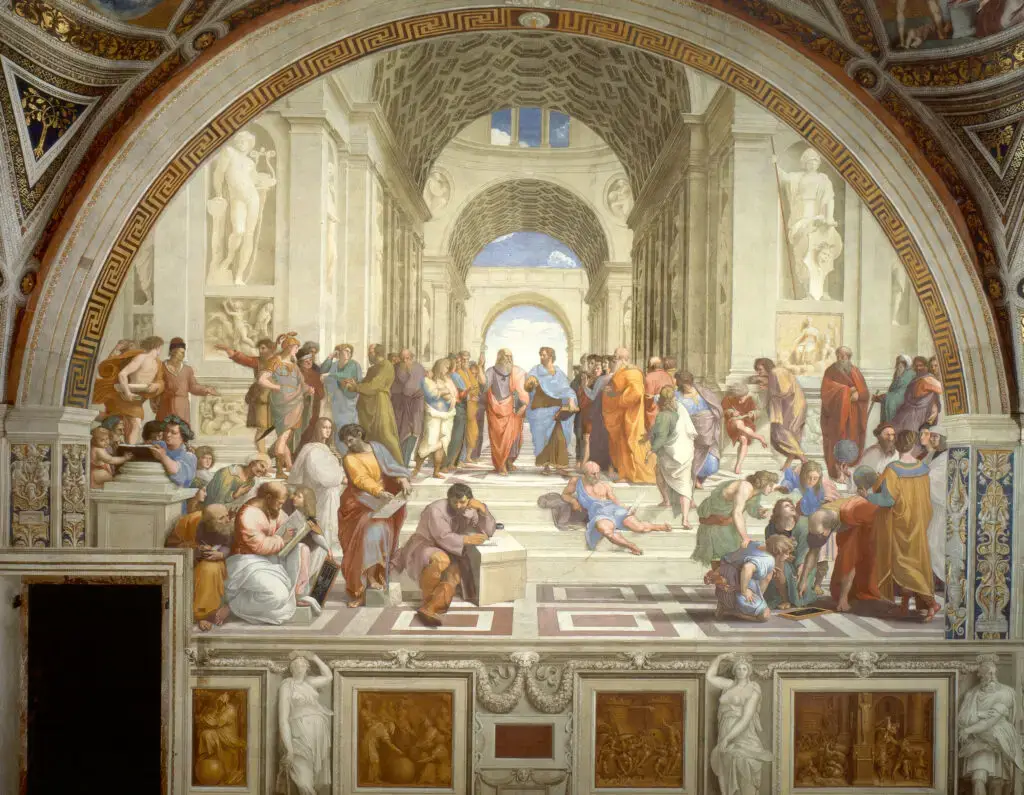
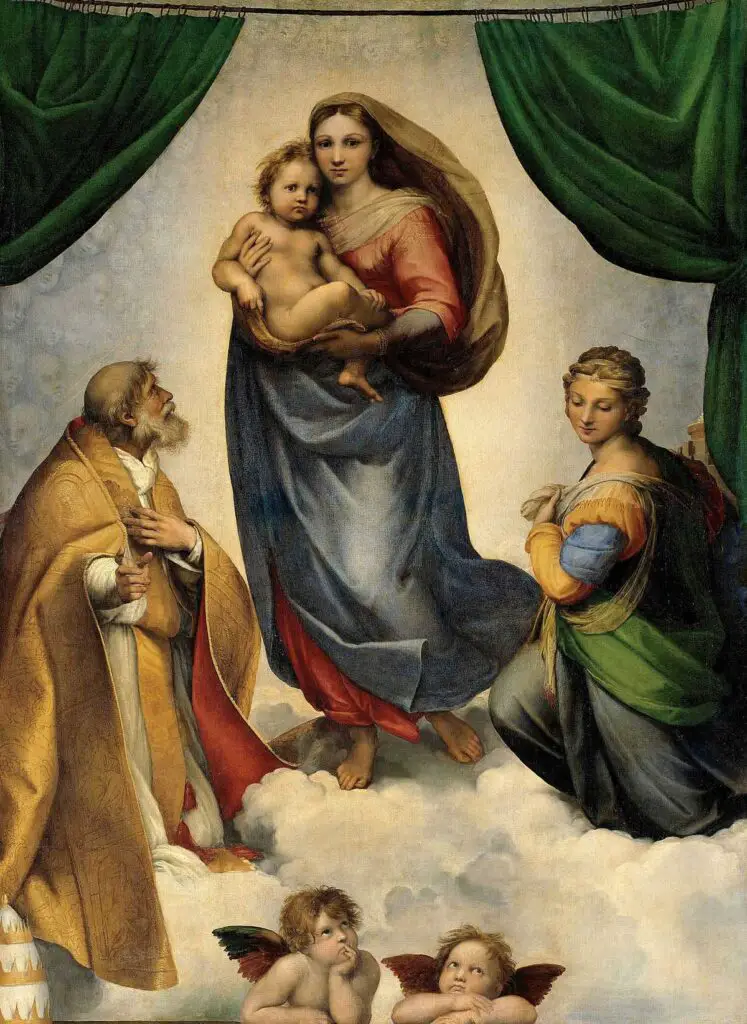
Raphael Sanzio (1483–1520):
Renowned for the “School of Athens” and the “Madonna” series, Raphael’s works epitomize the ideals of clarity, harmony, and balance.


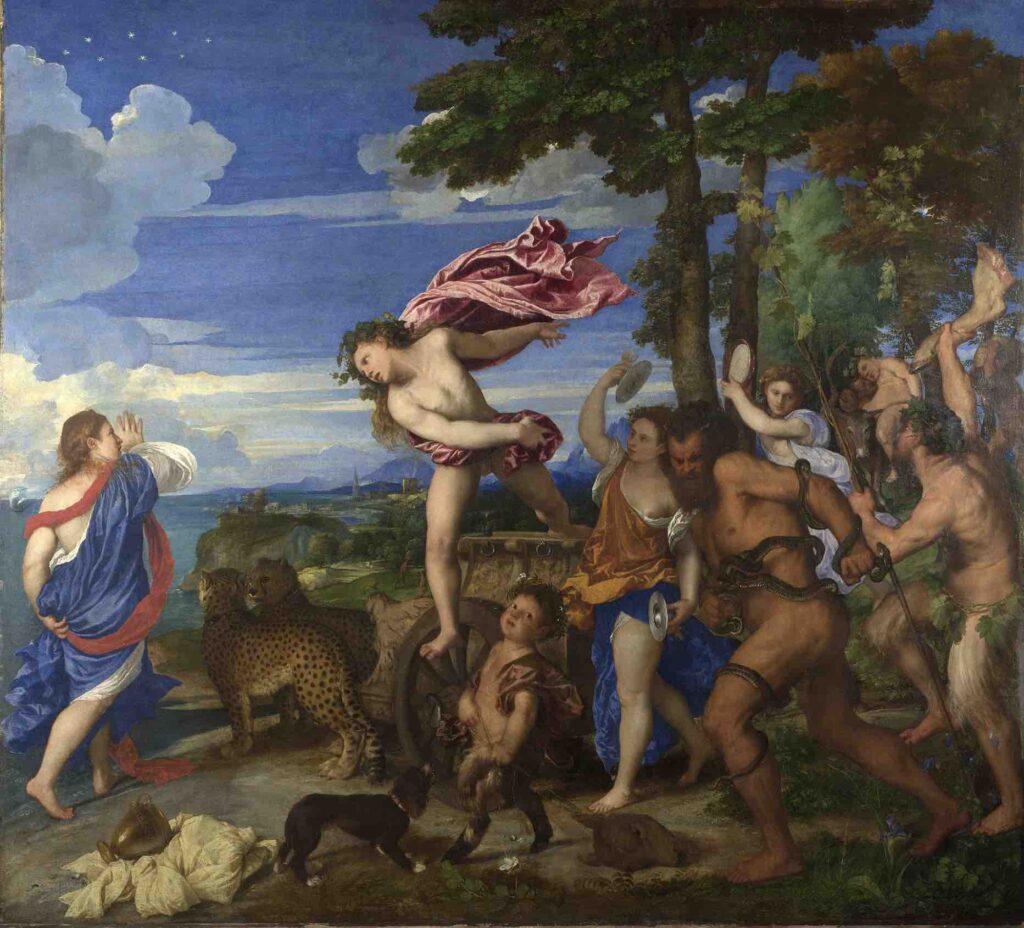
Titian (c.1488–1576):
An extraordinary Venetian painter, Titian was known for his expertise in color and texture, evident in works like “Bacchus and Ariadne.”

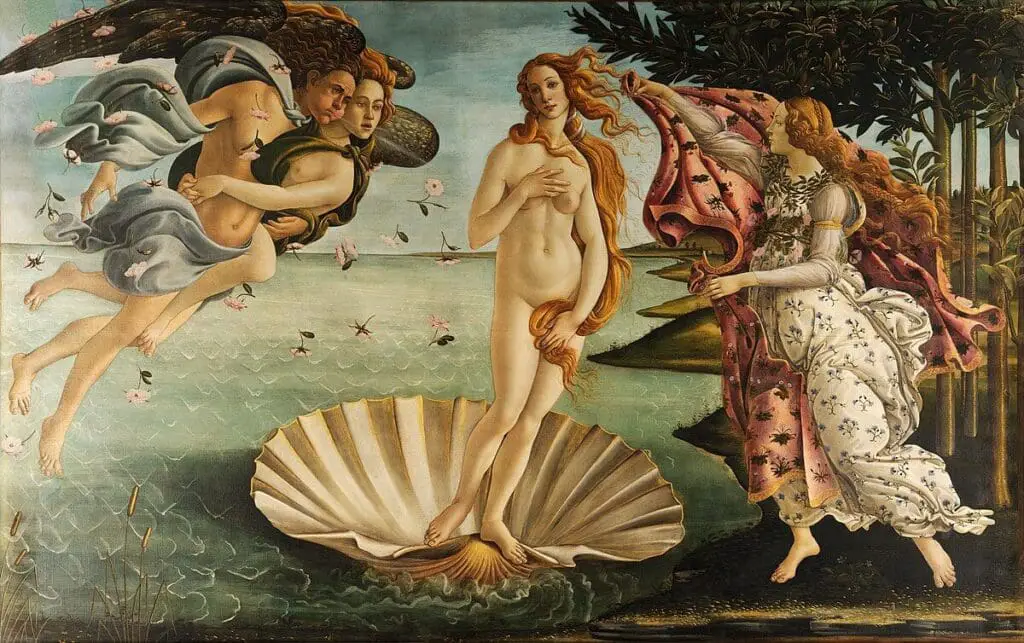
Sandro Botticelli (1445–1510):
Known for “The Birth of Venus,” Botticelli’s paintings are rich in allegory and classical elements.

Critical Philosophers And Writers Of The Italian Renaissance Era
In addition to groundbreaking artists, the Renaissance era was prosperous with influential philosophers and writers whose works continue to be cited today. Like the artists of the time, these thinkers made enduring contributions to the intellectual and cultural landscape.
Petrarch (1304–1374):
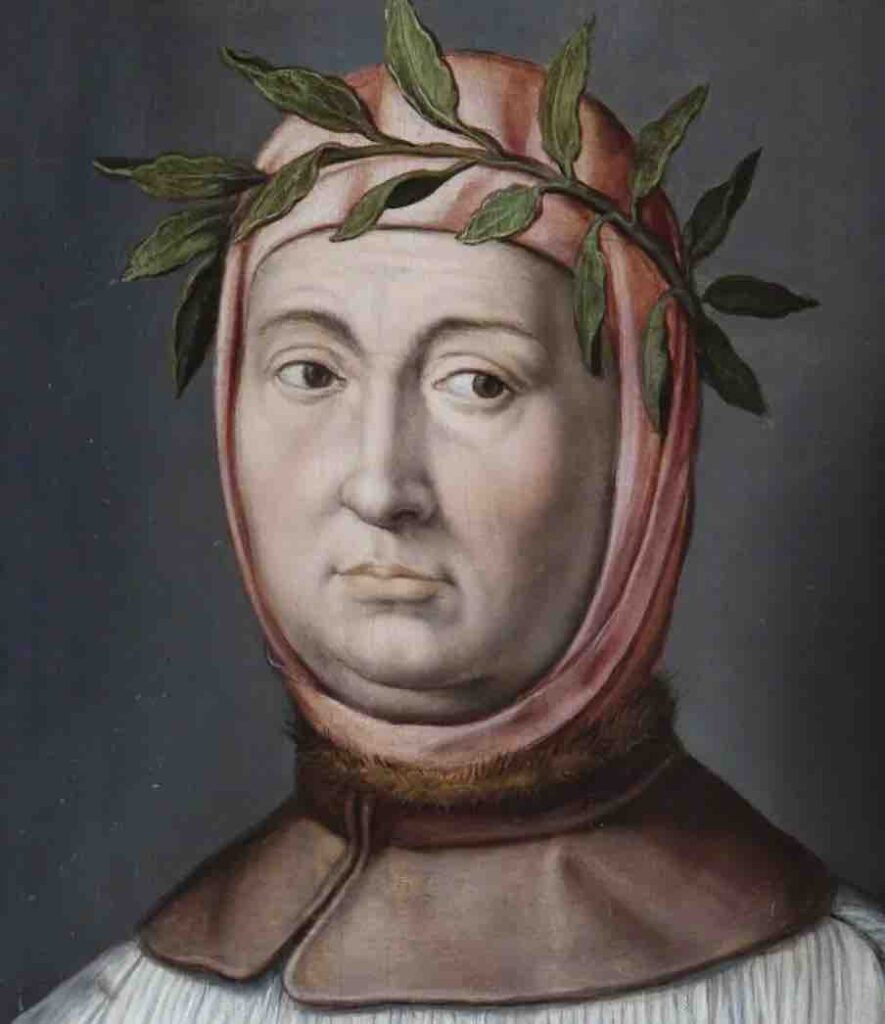

Often called the “Father of Humanism,” Petrarch laid the intellectual foundations for the Renaissance by rediscovering and championing classical texts.
Machiavelli (1469–1527):

A political theorist, Machiavelli’s “The Prince” offered a realistic, if not cynical, approach to politics, a departure from the ideological perspectives of the Middle Ages.
Dante Alighieri (1265–1321):
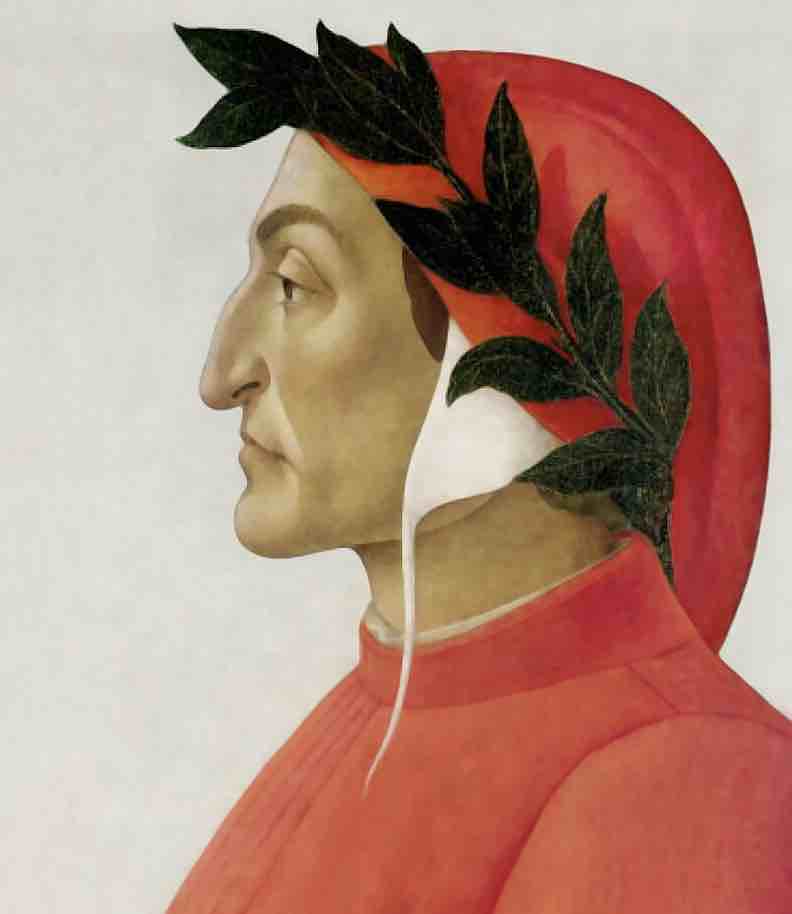


She is known for “The Divine Comedy,” Dante’s work is considered a masterpiece of world literature and a prelude to the Renaissance.
The Northern European Renaissance (Late 15th To Early 17th Century)
While the Italian Renaissance focused more on the achievements of the individual and the beauty of life, the Northern Renaissance was influenced heavily by the Reformation and thus had a more religious tone.
Major Artists And Their Contributions
Even though the Northern Renaissance followed its Italian counterpart, it, too, gave rise to an array of exceptional artists who made significant contributions to the art world. Some of the most notable artists from the Northern Renaissance include the following:
Albrecht Dürer (1471–1528):

Known as the “Leonardo of the North,” Dürer was a master of printmaking, painting, and theory. His works like “Melencolia I” combined Italian artistry with Northern realism.
Jan van Eyck (c.1390–1441):
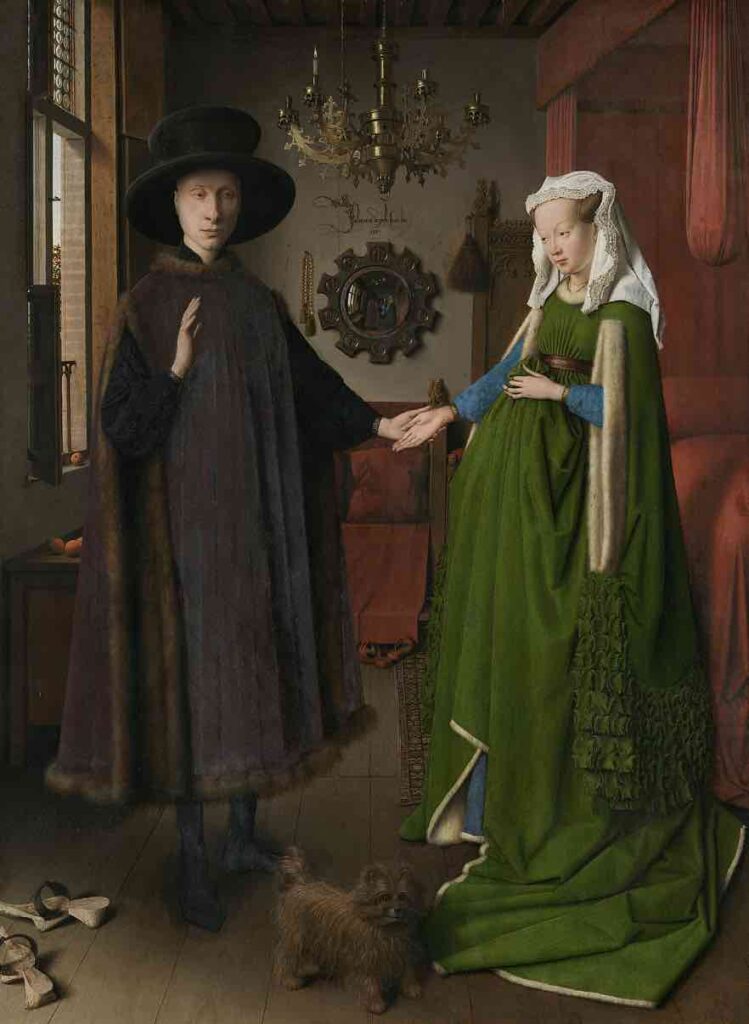

A pioneer in oil painting, van Eyck was known for his attention to detail and works like “The Arnolfini Portrait.”
Hans Holbein the Younger (c.1497–1543):

Famous for portraits of English royalty, including Henry VIII, Holbein’s works are exceptional examples of Northern Renaissance art.
Key Philosophers And Writers
Alongside the celebrated artists of the Northern Renaissance, this period was also marked by the emergence of influential philosophers and writers who left an indelible impact on intellectual history. Some of the most prominent thinkers to arise from the Northern Renaissance include:
Erasmus (1466–1536):

Known for “The Praise of Folly,” Erasmus laid the egg that Luther hatched, criticizing the Catholic Church and advocating for reform.
Sir Thomas More (1478–1535):

Known for “Utopia,” More’s works critiqued European society and presented an idealized vision of communal living.
The Renaissance was a “rebirth,” a transformative period that left an indelible mark on European history. It redefined the limits of individual capabilities and transformed art, science, and thought. Its legacy persists today, serving as a testament to the unquenchable human thirst for knowledge and excellence.
In its broad spectrum of innovation, the Renaissance fundamentally altered the course of European history, laying the foundation for modern Western culture. With its contributions spanning from the mesmerizing art of Leonardo and Michelangelo to the groundbreaking ideas of Petrarch and Erasmus, the Renaissance Era stands as one of the most astonishing epochs in the history of human civilization.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you are interested to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you any time. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel filled with great videos and information by clicking here.
Related Questions
What Did Leonardo da Vinci Contribute To The Renaissance?
Leonardo da Vinci made many contributions to the Renaissance in art, science, engineering, medicine, and architecture. He was a keen observer who wrote down a lot of what he discovered in his notebooks. His artistic techniques changed how artists painted and influenced many other Renaissance artists.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Did Leonardo da Vinci Contribute To The Renaissance?.
What Technique Did Leonardo da Vinci Add To The Painter’s Toolbox?
Leonardo da Vinci added the Sfumato technique to the painter’s toolbox. The Sfumato technique is about an artist using a soft transition between the different colors and tones that the artist is using. Many artists, including Leonardo, use this technique on the faces they are painting to give them a more realistic feel.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Technique Did Leonardo da Vinci Add To The Painter’s Toolbox?
What Are The Characteristics Of Mannerism Art?
Mannerism was an art movement filled with elongated bodies, tiny heads, and human figures in twisted forms. Perspective and proportion were unnecessary, but colors, contrasts, virtuosity, and agitated compositions were essential.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Are The Characteristics Of Mannerism Art?