Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes, more commonly known as Francisco Goya, stands as a towering figure in art. His rich and varied artistic journey traversed numerous stylistic epochs and trends.
While many artists typically resonate with one specific art movement, Goya’s oeuvre and legacy embrace Romanticism, the Renaissance, and Rococo. To grasp the depth and nuances of his craft, it’s essential to explore these periods and discern how Goya seamlessly blended his creations with their distinct aesthetics.
Table of Contents
- Francisco Goya: Spanning The Ages Of Art
- Why Goya Spanned These Movements
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Related Questions
Francisco Goya: Spanning The Ages Of Art
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes, popularly known as Francisco Goya, is considered one of the most prominent figures in art. He was a painter whose illustrious career spanned various stylistic periods and movements.
Although it’s common for artists to be associated with a single art movement, Goya’s works and influence span Romanticism, the Renaissance, and Rococo. To understand the complexity of his artistry, we must delve into each movement and see how Goya intertwined his works within them.
Goya And The Renaissance
The Renaissance was a period from the 14th to the 17th century, primarily recognized for the revival of interest in classical art and learning of Greece and Rome. While Goya lived from 1746 to 1828, placing him well after the pinnacle of the Renaissance, the echoes of this movement profoundly influenced him.
His works, such as “The Family of Charles IV” (1800), showcase a semblance of Renaissance portraiture in composition and the portrayal of royalty, akin to the style of artists like Velázquez.
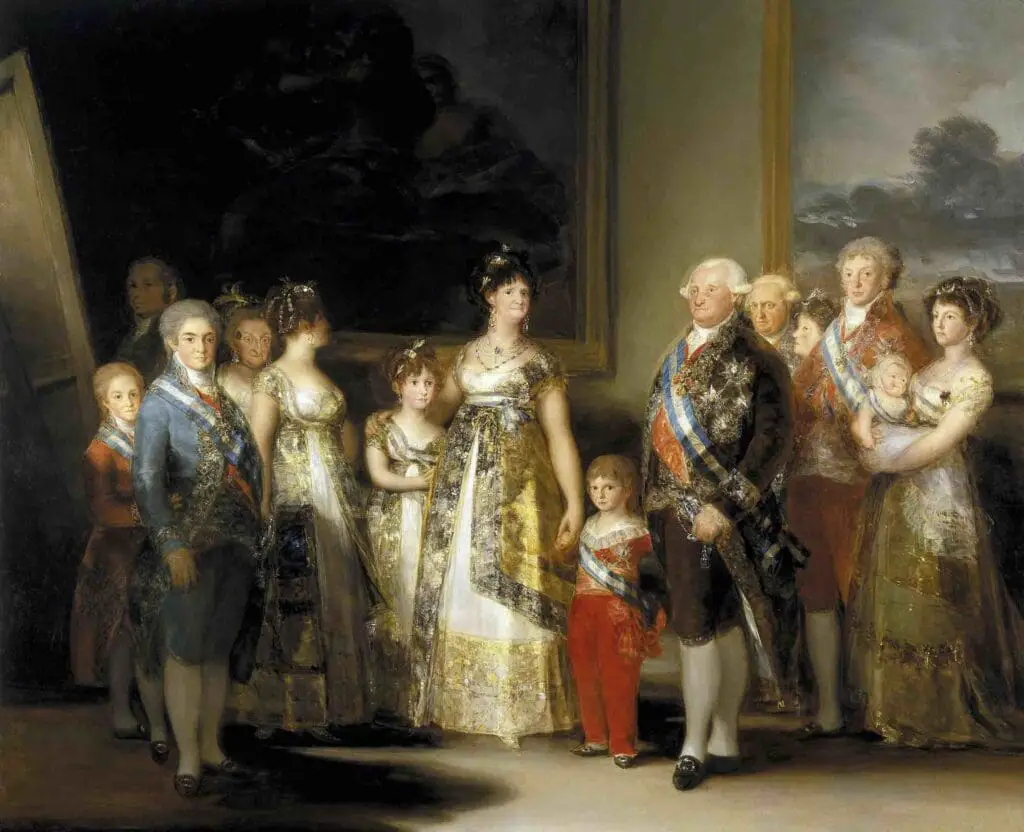

Furthermore, Goya’s interest in meticulous details, human anatomy, and realistic depiction of his subjects showcases a continuation of Renaissance principles. His pursuit of knowledge and understanding of human experience aligns him with the intellectual curiosity of the Renaissance era.
Goya And Rococo
Rococo, originating in early 18th-century France, is characterized by ornate detail, pastel colors, and playfulness or whimsicality. It was the primary style when Goya began his art career, and it’s no surprise that his early works reflected Rococo’s aesthetics.
For instance, his tapestry cartoons for the Spanish monarchy capture Rococo’s playful and light-hearted spirit. Take “The Parasol” (1777) as an example; it portrays a young couple, with a woman holding a parasol to shade herself, set against a light and airy backdrop. The soft color palette and the relaxed composition are unmistakably Rococo.
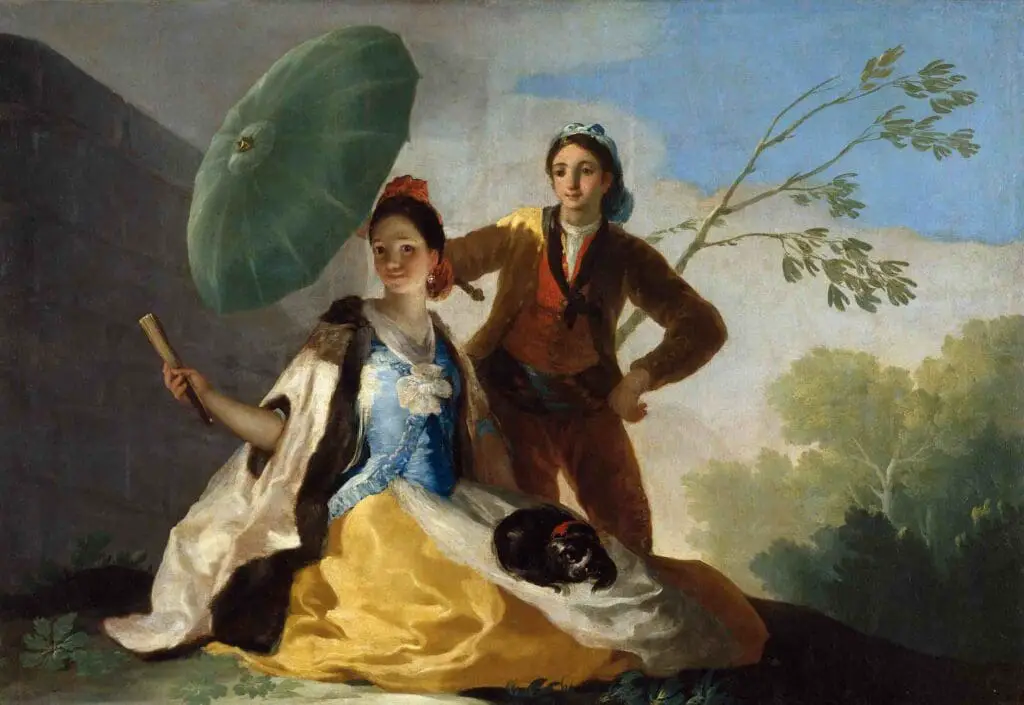

However, as Goya matured, so did his style. He never fully committed to the frills and frothiness of Rococo. Instead, his work began reflecting deeper and more somber themes, foreshadowing his alignment with Romanticism.
Goya And Romanticism
Romanticism emerged in the late 18th century as a reaction against the Enlightenment’s rationalism and the Neoclassical period’s stark classicism. It emphasized emotion, individualism, and nature’s awe-inspiring and sometimes terrifying beauty.
Goya’s shift to Romanticism is palpable in his later works. As he faced personal challenges, including a mysterious illness that left him deaf, and as he bore witness to the turbulent sociopolitical changes in Spain,
Goya’s artistry evolved. His “Black Paintings,” a series of dark and haunting frescoes, perfectly encapsulate the essence of Romanticism.
Works like “Saturn Devouring His Son” (1819-1823) are a visceral expression of raw emotion, a far cry from his earlier, light-hearted Rococo pieces.
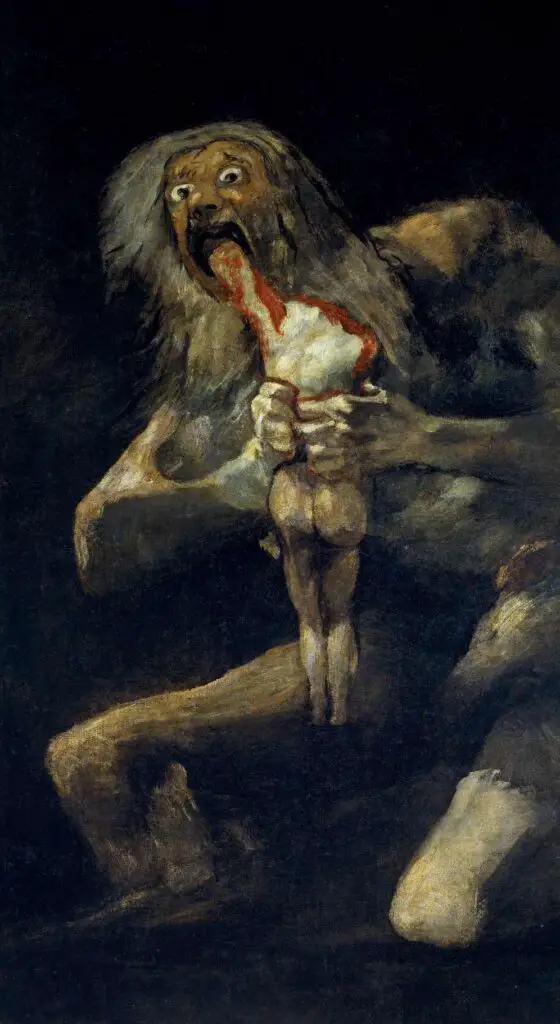

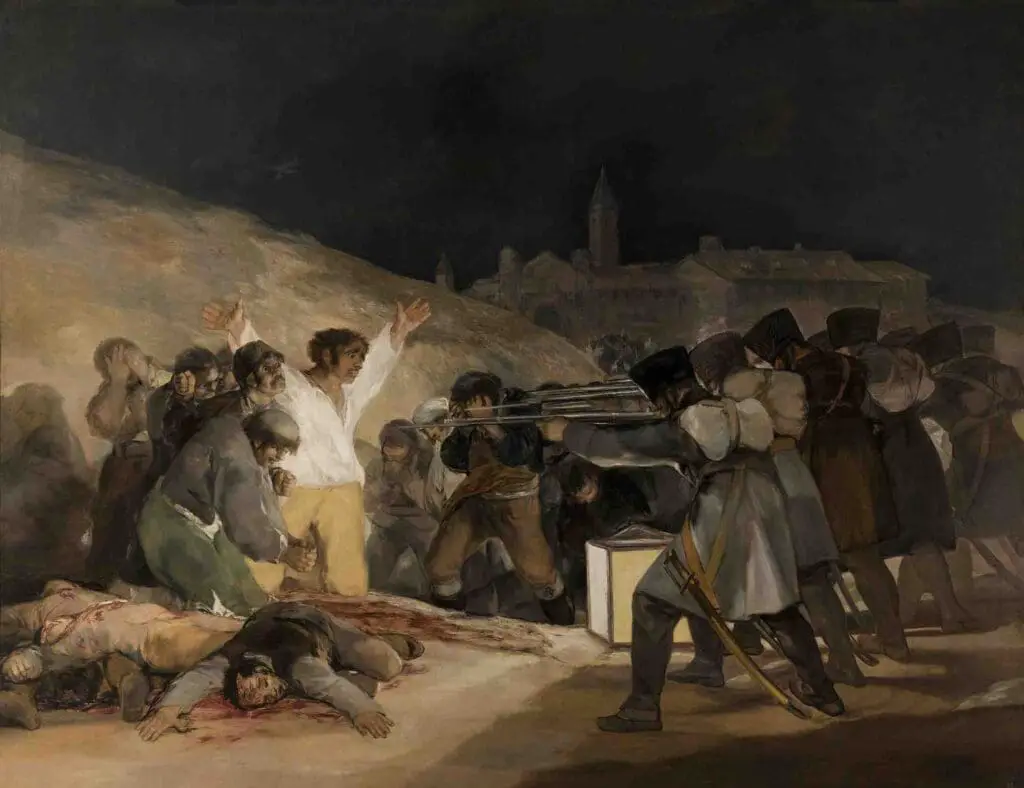
Moreover, “The Third of May 1808” (1814) is a testament to Goya’s Romantic sensibilities. The painting, which depicts the execution of Spanish civilians by Napoleon’s troops, is not just a historical record but a powerful emotional statement on the horrors of war and the plight of innocent victims.

Why Goya Spanned These Movements
Goya’s ability to be part of multiple movements is not merely coincidental. It reflects his versatility as an artist and his keen sensitivity to the changing world.
His early career, influenced by the light-heartedness of Rococo, was dominated by portraits of the nobility and tapestry designs. However, personal experiences and Spain’s tumultuous history pushed him into Romanticism’s deep, emotional recesses.
His transition between these periods wasn’t abrupt. Goya took the realist tenets from the Renaissance, the lightness and ornateness of Rococo, and fused them with the emotional intensity of Romanticism. This blend created a unique style that, while rooted in existing movements, was unmistakably Goya’s own.
Francisco Goya’s art is a testament to an artist’s ability to evolve and reflect the changing times. While his works can be categorized under various movements, trying to box him into a single one would be an oversimplification.
Instead, by appreciating his journey across the realms of the Renaissance, Rococo, and Romanticism, we can truly understand the genius and versatility of Goya. In doing so, we’re reminded that art isn’t static; it’s ever-evolving, much like the artists who bring it to life.
Frequently Asked Questions
What art movements influenced Francisco Goya’s early works?
Goya’s early works were influenced by the Rococo style, a movement characterized by ornate and playful compositions that were prevalent in the 18th century.
How did Francisco Goya contribute to the Romantic movement in art?
Goya is considered a precursor to Romanticism. His later works, like the “Black Paintings” and “Saturn Devouring His Son,” exhibit a darker and more emotional tone, aligning with the Romantic emphasis on individual expression and intense emotions.
In what ways did Goya’s art reflect the socio-political context of his time?
Goya’s “The Third of May 1808” is a poignant example of his engagement with socio-political issues. This painting captures the brutality of war and oppression during the Peninsular War.
Can Goya be associated with the Renaissance art movement?
Although Goya lived well after the Renaissance period, his works show some influence from Renaissance techniques. His skillful use of chiaroscuro, for instance, reflects Renaissance principles of light and shadow.
What are the key characteristics of Goya’s “Black Paintings”?
The “Black Paintings” are a series of murals created by Goya in his later years. They are characterized by their dark and somber tones, depicting themes of fear, insanity, and mortality.
How did Francisco Goya’s personal life impact his artistic evolution?
Goya’s personal experiences, including his illness and deafness, had a profound impact on his later works. These challenges are thought to have influenced the themes and emotions in paintings like “Self-Portrait with Dr. Arrieta.”
Did Francisco Goya’s art undergo a significant evolution throughout his career?
Yes, Goya’s art underwent notable changes. His early works were influenced by the Rococo, while his later works, especially the “Black Paintings,” demonstrated a shift towards a more introspective and emotional style.
How did Goya’s approach to printmaking contribute to his artistic legacy?
Goya’s innovative techniques in printmaking, especially in the series “Los Caprichos” and “The Disasters of War,” showcased his ability to communicate powerful social and political commentary through visual storytelling.
Was Francisco Goya recognized and appreciated during his lifetime?
Yes, Goya achieved recognition during his lifetime, serving as a court painter to the Spanish crown. However, his later works, which delved into darker and more critical themes, were not fully appreciated until after his death.
How does Francisco Goya’s art continue to influence contemporary artists?
Goya’s exploration of human emotions, societal critique, and innovative techniques continue to inspire contemporary artists. His ability to transcend specific art movements makes his work relevant and influential across different artistic styles.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you want to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. I would be happy to talk to you if you have any questions. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend just 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Related Questions
What Was The Focus Of Renaissance Art?
The focus of Renaissance art was on the classics of Greek and Rome, humanist philosophy, and the study of the human figure. Realism was also an essential part of renaissance art. The great artists of the Renaissance also became great anatomists and studied human beings.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Was The Focus Of Renaissance Art?.
What Is The Importance Of Art From The Renaissance Period?
Renaissance art is essential as it was a time of rebirth and discovery. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael were at the forefront of that change, creation, and discovery. Renaissance art has influenced art and artists for many centuries and continues to influence artists today.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Is The Importance Of Art From The Renaissance Period?.
Early Renaissance Vs. High Renaissance Art Explained
Early Renaissance and High Renaissance are both periods of the art of the Renaissance era. The entire Renaissance era shared a lot of the same characteristics. The High Renaissance was dominated by three major artists: Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Early Renaissance Vs. High Renaissance Art Explained.