Many people can be confused about what the ancient Western classical arts meant. I know that I have also been confused by what period the Western classical arts covered.
The Ancient Western Classical arts cover three main art periods: Minoan Art, Ancient Greek Art, and Ancient Roman Art. Though these arts are similar, they are not all the same. Minoan art was before Greek art and is from present-day Crete (Greece). Ancient Greek Art is one of the best-known Ancient Classical art forms. The Greeks were known for their idealism, form, proportion, and perspective. Roman Art believed in realism in art and received inspiration from Greek Art.
Table of Contents
- What Is Ancient Classical Art?
- Minoan Art
- Ancient Greek Art
- Roman Art
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Related Questions
What Is Ancient Classical Art?
Ancient classical arts are divided into three periods: Minoan, Ancient Greek, and Roman. This period covers a considerable artistic period of thousands of years.
The Ancient Classical Arts encompassed the cultures of Greece and Rome. At the time, both Greek and Roman were the cornerstones of Western civilization. The Ancient Classical Arts include innovations in painting, sculptures, decorative arts, and architecture.
Many ancient classical artists believed in realism and the ideals of beauty, harmony, and proportion. The ancient classical artists thought that the human form was one of beauty so the human form would continue to dominate art for many centuries.
One of the most important things to know about this era of art is that the Ancient Classic Art era would be a foundation upon which art would build for many years to come. Even today, many artists receive inspiration from the Romans or Greek art.
Below is a basic chart showing the three main focuses of the Ancient Classical Arts and the approximate years or timeline.
| Ancient Classical Art Periods | Years (Time) |
| Minoan Art | 2600 to 1100 BC |
| Ancient Greek Art | Around 1050 to 300 B.C. ( flourished around 450 B.C. ) |
| Roman Art | 509 B.C. To about 330 AD (around for about 1,000 years) |
Minoan Art
The Minoan Art that has survived today gives us great insights into the cultures that flourished in Crete (present-day Greece). Minoan’s art speaks of a society that was in touch with the environment and the natural world’s logical order.
The artifacts that have been found reveal people who developed a high degree of self-respect and a keen eye for observing their own physical environment. Sadly not that much Minoan art has survived. The survived art tells us a lot about the people who lived during this period.
The art of the Minoans can be divided up into four main categories 1) pottery 2) jewelry 3) painting and 4) metalwork. Here is a brief summary of each of these.
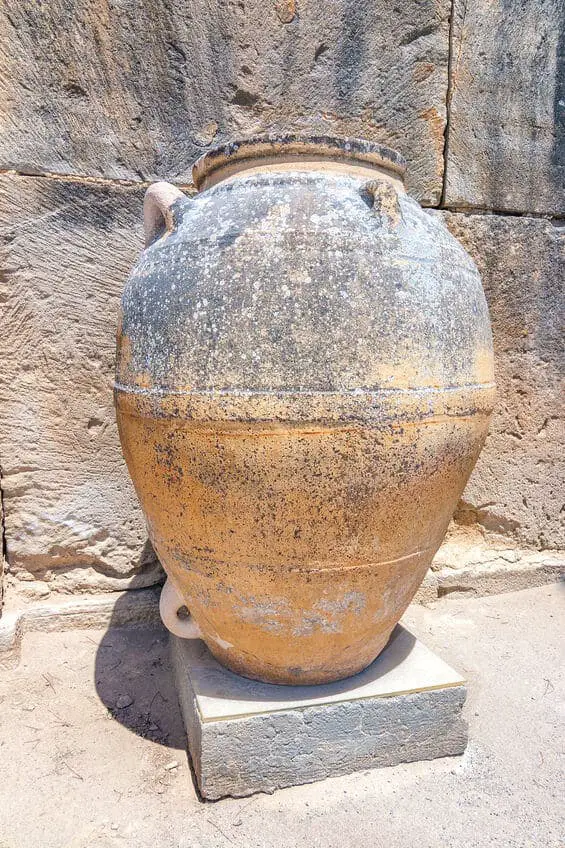

Pottery
The Minoans left us with many kinds of vessels and decorative pottery. Ceramics are characterized by patterns such as spirals, triangles, curved lines, and crosses. All kinds of shapes that they saw from nature were interrupted in their designs.
I find it very interesting that the artists were sophisticated enough to understand the use of design and color for their pottery during this time. This shows that many of these artists had an innate sense of design and trends for their time.
Paintings and Fresco
Several frescoes have survived at Knossos and Santorini, both in present-day Greece. These sites were unearthed, and the frescos were restored.
From these frescos, we also learn about the artists of this time. The famous bull-leaping fresco depicts people of different sexes. The men have reddish-brown skin, and the women white.
Jewelry
The Minoan artists made jewelry elaborately using gold and copper. Beaded necklaces, bracelets, and hair ornaments are shown in some of the painted frescoes. By all accounts, the Minoan artist became quite adapted to using many kinds of metalwork.
Metal Work and Vessels
Metal vessels have been found from the Minoan period of time. Metal vessels made of some precious metals such as gold have been found. Some unearthed bronze vessels include cauldrons, pans, hydrants, bowls, pictures, basins, cups, vitals, and other artifacts. This shows the sophistication that the Minoans had for these things in their homes.

Ancient Greek Art
When most people think of Ancient Classical art, they think of Greek Art. This is because the Greeks are a significant part of Ancient Classical Arts.
The Greeks built upon the materials used by the Minoan culture, but they also added to it with their own architecture and design. Many Greek artifacts have been found in pottery, jewelry, metalwork, and painting. But they also added to this through their own designs, architecture, and sculptures.
The Greeks believed in idealism and harmony in their art. Their art can best be described as being an idealist. The Greek ideal of beauty was based upon proportions or on the golden ratio of the body parts’ length to each other in their depiction of male and female figures.
Greek Pottery
Greek pottery is different from Minoan art. The Greeks made small terra-cotta figures which they used as gifts to their gods and goddesses, or they would bury them with their dead, or they give them to their children as toys. They would paint religious or mythical figures or scenes on their clay pots.
It can be said that a lot of our knowledge of classical Greek art comes from objects made of stone and clay that have survived thousands of years. With these art objects, you can see how the Greek artist emphasized pattern, order, and proportion. Today, we need to thank the Greek artists for emphasizing this pattern, order, and proportions.
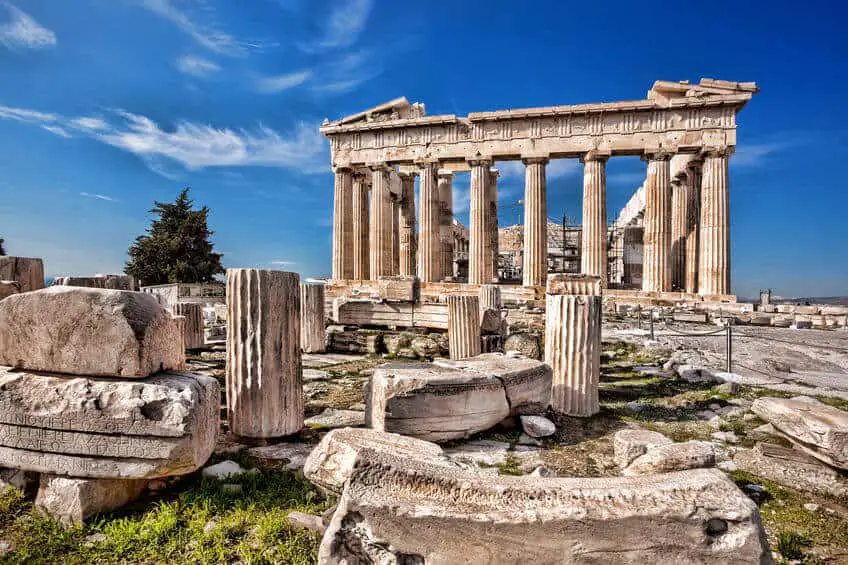
Ancient Greek Architecture
The Greeks gave us all some fantastic architecture. A lot of architecture throughout the centuries has been inspired by the Greeks.
The Greeks help give us the proportion and perspective. They had perfectly even buildings. This gave the Greek buildings a flawless and majestic look.
Greek Sculptures
The ancient Greeks idealized the human body form. This was depicted mainly with nude male figures.
Unfortunately, not many Greek statues have survived today as the stone statues were easily broken, and the metal ones were melted down for reuse. So we do not have so many existing Greek sculptures and statues, but the ones that did survive, we can clearly see the Greek idealism of the human body form.

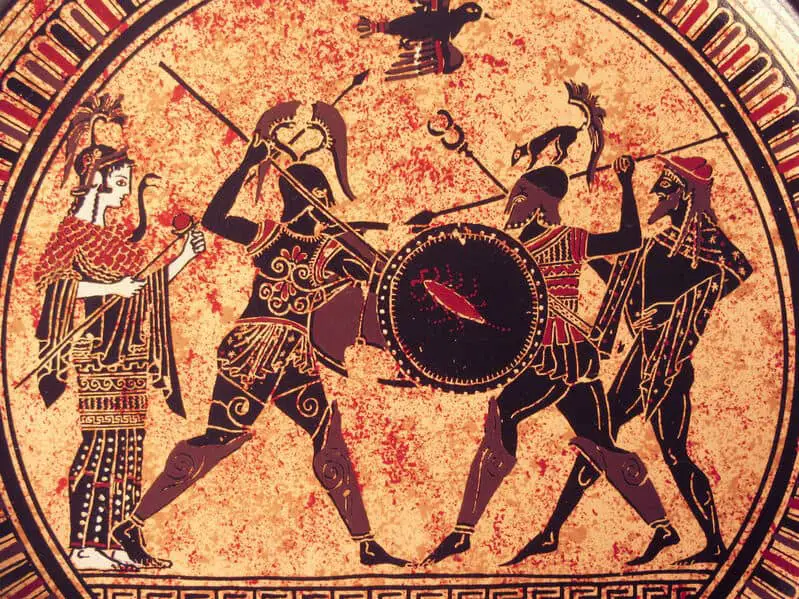
Roman Art
Many historians tend to see Roman art as a copy of Greek art. But this is not true; the Romans had their own art form. The Romans did take inspiration from Greek art.
For the Ancient Greeks, their art was almost always a form of religious expression. On the other hand, the Romans saw their art as more of a commodity.
Because the Romans saw art as a commodity, some Roman art may not be as impressive as Greek art. Roman art was in demand by the Rome elite and others. This huge demand, of course, was how art was viewed.
No doubt, the Romans owe a lot of their artistic achievements to the Greeks. This is because the Greek artisans have long mastered creating some of the greatest masterpieces ever.
Roman Portrait Sculptures
The Romans loved their portrait sculptures. The portrait sculptures stretch way to the early part of Rome’s history.
When a Roman man died, his family created a wax sculpture of his face, which they kept at home to record a person’s existence. The emphasis for these sculptures was placed more on realism than on artistic beauty
Roman sculptures were not just for the deceased but also honored important living personalities. Influential Romans were rewarded by having their statue put on public display.
Mosaics
The Roman artists also gave us some intricate mosaics. The mosaics were used a lot in public and private buildings.
The mosaics were very intricate and were influenced by many of the Greek mosaics. As in keeping with their portraits, the Roman mosaics would often include famous figures and some figures from mythology.

Paintings
In keeping with decorating their building and other spaces, the Romans also used paintings. A few of these paintings have survived today.
Most paintings had themes such as animals, still life, scenes from everyday life, portraits, and some mythological subject matter.
The Romans also brought to us the Gold Glass technique, which was having a layer of gold leaf with a design between two layers of glass. Many of these have survived today and show how talented many of these artists were.
Ancient Classical Art is important for us to learn about as they are still a foundation upon which many artists still build today. This is why it is interesting to study these ancient artists, as we can learn from them. Today, we can discover how they were able to build upon another civilization’s art and create their own unique art.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you are interested in seeing any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you at any time. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel filled with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend just 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the Ancient Western Classical Arts?
The Ancient Western Classical Arts refer to the artistic expressions that emerged during three key periods: Minoan Art, Ancient Greek Art, and Ancient Roman Art. These periods showcase the cultural and artistic achievements of ancient civilizations in the Western world.
What distinguishes Minoan Art from Ancient Greek and Roman Art?
Minoan Art predates Ancient Greek and Roman Art and originates from the island of Crete. It is characterized by vibrant frescoes, intricate pottery, and a focus on nature
What defines Ancient Greek Art?
Ancient Greek Art is renowned for its idealism, emphasis on form, proportion, and perspective. This period produced iconic sculptures, pottery, and architecture, with a strong emphasis on portraying the human body in its most perfect and harmonious form.
How does Ancient Roman Art differ from Ancient Greek Art?
While Ancient Roman Art drew inspiration from Greek Art, it had a distinctive focus on realism. Roman artists aimed to capture the everyday life and achievements of their society, leading to the creation of detailed sculptures, mosaics, and architectural wonders.
Were the Ancient Western Classical Arts limited to visual arts?
No, the Ancient Western Classical Arts encompassed a broad range of artistic expressions, including sculpture, painting, pottery, architecture, literature, and performing arts. Each period contributed significantly to the cultural heritage of the Western world.
How did Ancient Greek Art influence Roman Art?
Ancient Roman Art borrowed heavily from Ancient Greek Art, adopting their techniques, styles, and subject matter. However, Romans added their touch by incorporating a more realistic approach and focusing on depicting historical events and individuals.
What role did idealism play in Ancient Greek Art?
Idealism in Ancient Greek Art involved portraying subjects in their perfect, idealized forms. Artists aimed to capture not only physical beauty but also the essence of virtue, creating works that celebrated the human potential for greatness.
How does Ancient Western Classical Art continue to influence modern art?
The principles of balance, proportion, and perspective established in Ancient Western Classical Art continue to inspire modern artists. Elements of classical aesthetics are often incorporated into contemporary art, architecture, and design, showcasing the enduring impact of these ancient traditions.
Did Ancient Roman Art focus solely on realism?
While realism was a significant aspect of Ancient Roman Art, it also embraced symbolism, mythological themes, and idealized portraits. Roman artists displayed versatility, adapting their styles to various contexts and subjects.
Why is the study of Ancient Western Classical Arts important?
Studying Ancient Western Classical Arts provides insights into the cultural, social, and philosophical aspects of ancient civilizations. It allows us to understand the evolution of artistic expression and appreciate the timeless beauty and craftsmanship that continue to influence our cultural heritage.
Related Questions
How Do You Identify A Japanese Artist’s Signature on Woodblock Prints?
The signature on a Japanese woodblock print is the Japanese characters above or near the red artistic seal or chop. Sometimes, the artist would add words behind their own name, such as “designed by.” Other times, the artist would use different chops or seals during different periods of their life. Many times, the actual artist’s signatures are complicated to read.
You can discover more by reading our blog How Do You Identify A Japanese Artist’s Signature on Woodblock Prints? by clicking here.
Who Was the Chinese Painter 八大山人 Bada Shanren (1626-1705)?
Bada Shanren was born in 1626 as a Ming Dynasty Prince in Jiangxi Province, China. When the Ming Dynasty lost power, he went into hiding for over 40 years at a Buddhist Monastery. When he left the monastery, he was in his 60s, and he became a professional artist. Bada Shanren made strong sounds and loud noises while he painted, so many people thought he was mad.
You can learn more by reading our blog post Who Was the Chinese Painter 八大山人 Bada Shanren (1626-1705)? by clicking here.