One of the most influential artists to ever live is Leonardo da Vinci. He continues to be one of the most influential people ever.
Leonardo da Vinci made many contributions to the Renaissance in art, science, engineering, medicine, and architecture. He was a keen observer who wrote down much of what he discovered in his notebooks. His artistic techniques changed how artists painted and influenced many other Renaissance artists.
Table of Contents
- Leonardo da Vinci and the Renaissance
- Leonardo da Vinci, The Renaissance, Science and Engineering
- Leonardo da Vinci: The Renaissance Luminary and His Artistic Prowess
- Leonardo da Vinci: 10 Reasons for His Timeless Significance
- 12 Reasons Why Leonardo da Vinci Stands Out as a Quintessential Renaissance Artist
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Related Questions
Leonardo da Vinci and the Renaissance
Leonardo da Vinci (1452 – 1519) was a significant figure in the Renaissance. Leonardo da Vinci is regarded as one of the greatest artists who ever lived. Still, more than just being an artist, he also made significant contributions to engineering, science, urban planning, philosophy, anatomy, and cartography.

Leonardo da Vinci was a highly prolific artist, scientist, engineer, and philosopher. His work was entirely done secretly, but others, such as his artwork, were done in the open. He was known during this era to be a prominent artist, architect, and engineer.
One of Leonardo’s most important contributions to the Renaissance is the revival and rebirth of learning; Leonardo helped lead the way. He helped to influence the arts, but more than that, he contributed to science and experimented with many avenues in the world of science and nature.
Leonardo was also an inventor, yet his inventions did not have as much impact in his era as his other contributions.
Leonardo da Vinci, His Art, and The Renaissance
Leonardo’s artwork significantly advanced the Renaissance to new heights that had never been seen before. Leonardo was an extremely influential Renaissance artist, but also a revolutionary artist as his artwork was very realistic and expressive.
Leonardo used his extensive anatomical studies to understand the human body to paint realistically. His study of the human body made his paintings also very dynamic with how the emotions were expressed; this type of expressive art was new and modern in his era.
Leonardo’s influence can be seen in other artists who adopted a more realistic and naturalist painting approach. He also wrote a lot about his painting technique so that other artists could study and understand it.
Leonardo was a master of his painting technique, which included his treatment of light and shading, known as chiaroscuro. Leonardo did not invent the chiaroscuro technique, but he helped perfect it. Many other artists followed Leonardo’s techniques and methods.
Leonardo was also a master artist of linear perspective; he developed new ways of looking at perspective. His perspective helped give his artwork more depth and make it appear more realistic.

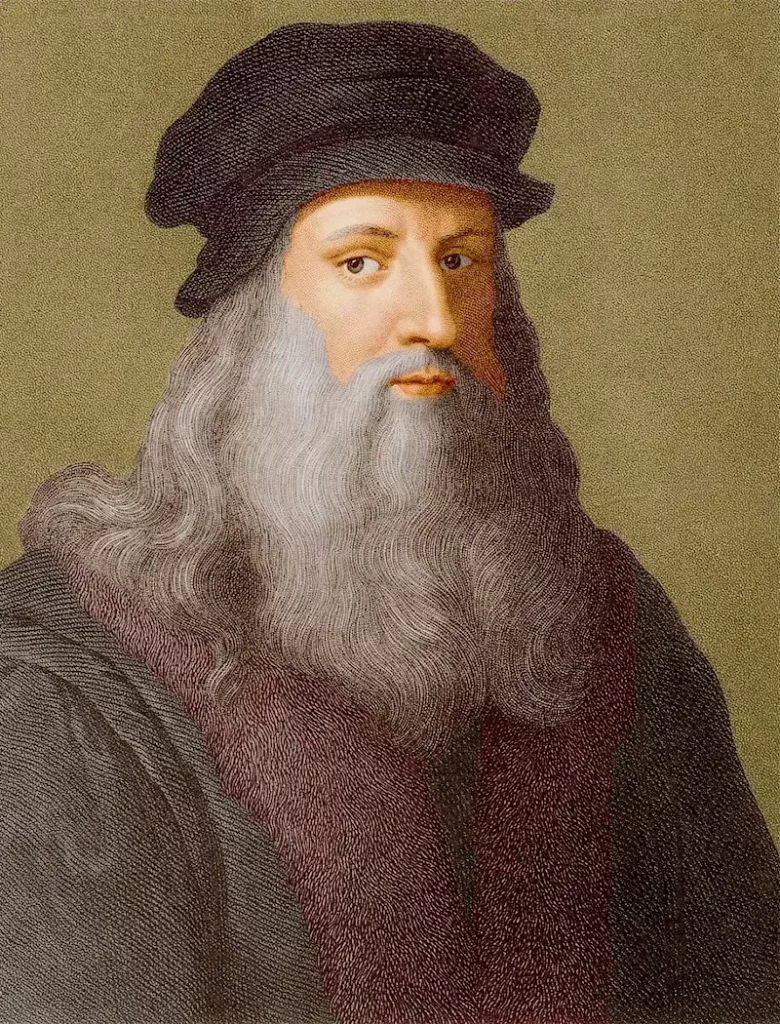
One of Leonardo’s most important contributions to the Renaissance and art is developing the sfumato method, a new method to blend paint and glazes. The sfumato method is the artistic technique that allows tones and colors to shade gradually into one another; this technique helps produce softened outlines or hazy forms, which are most often associated with the painting of a human face in his famous painting Mona Lisa.
Leonardo’s sfumato technique helped make his human subjects look like living and breathing subjects.
Leonardo da Vinci and His Influence On Other Artists
Leonardo and his artistic style influenced a lot of other artists. One artist influenced by this technique and style of Leonardo was Michelangelo. The frescos that Michelangelo created became more dynamic and expressive due to Leonardo’s technique and style. It is interesting to point out that even though Leonardo and Michelangelo were bitter rivals, Leonardo’s art influenced Michelangelo’s art.
Leonardo’s art, technique, and style influenced other Renaissance painters, such as Raphael (1483-1520). Another painter Leonardo influenced was Filippino Lippi (1457 – 1531) and del Sarto (1486-1531).
Leonardo also produced some sculptures, though no longer any left; his sculptures and architectural drawings also greatly influenced the architects of his time.
Leonardo da Vinci, The Renaissance, Science and Engineering
One of the things that are so unique about Leonardo is that he was not only an artist but was also fascinated with science, engineering, and mechanics. He took these subjects very seriously, writing extensively about them in his notebooks.
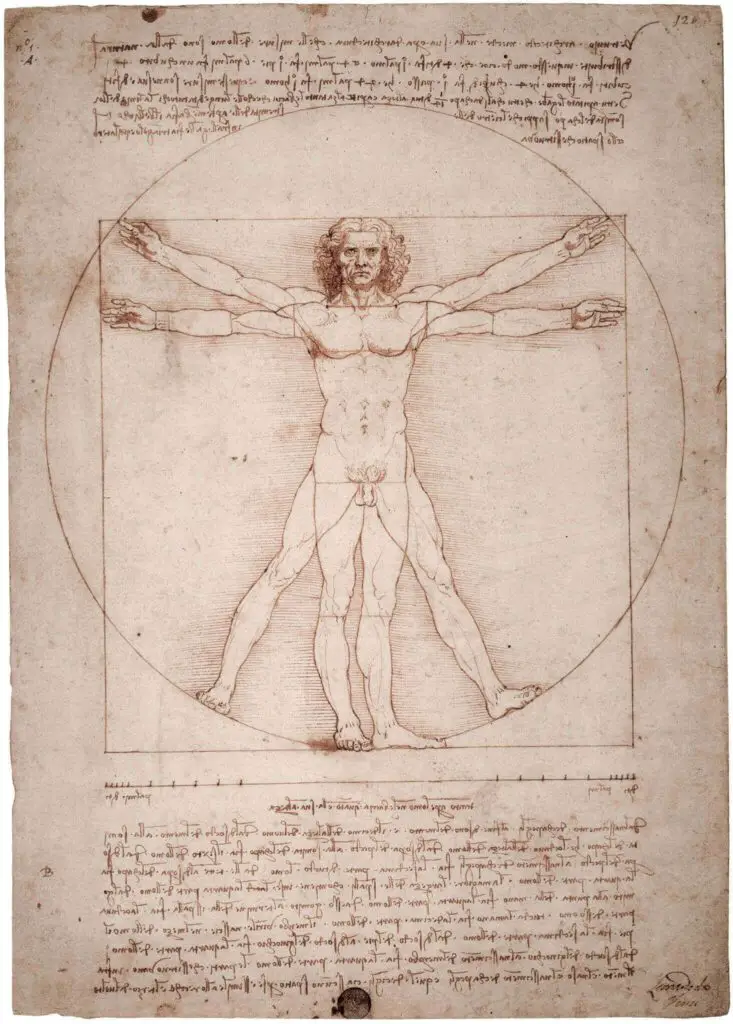
Leonardo’s theory of knowledge was based on his study of nature. He was also intrigued with the human body. It is believed that he dissected up to 30 human bodies and then used a lot of that knowledge to make detailed anatomical drawings.
Leonardo had a keen sense of observation. He observed so many subjects, from hydraulic engineering to town planning. Leonardo was a great believer in empiricism, believing all knowledge comes from our experiences.
Leonardo’s belief in empiricism was considered very radical for the time. This was so radical because the Church and Ancient Classical authors were wholly unchallenged at the time, and people were encouraged to follow the Church and classical thought and not use their experiences to learn outside what was already given to them.
So it can be said that Leonardo was considered a modern thinker during his time, especially concerning his ideas on science and learning. But despite this, his power was still limited due to the political situations of the time or the power of the Church during his era.
Because of the power of the Church during his time, Leonardo was not allowed to publish the anatomical studies he learned through dissecting the bodies. These publications and these findings were considered sinful by the Catholic Church and amounted to hierarchy.
Leonardo was also threatened by persecution from the civil authorities due to his “modern” ideas, research, and findings. Because of this constant threat, he lived under; he kept many of his discoveries, learnings, and ideas secret.
Leonardo was so worried about this threat and being found out and punished that he published his ideas using an uneasily deciphered code that could not readily be broken. Because of the deciphered code for his discoveries, many of his published works on scientific achievements and other observations were not disclosed until a century after his death.
If Leonardo had been allowed to publish his work of science, such as what he discovered about the study of the heart, it would have helped to advance the science of his day by an entire century. It can be said that the Church and political situation of his time held back his scientific discoveries.
One thing that Leonardo did was help to force a change of the intellectual environment of the Renaissance to one that would eventually take on a more modern outlook for the era.
Leonardo da Vinci significantly influenced many aspects of the Renaissance; his art, technique, science, engineering, and learning influenced people in his era and for centuries after. This makes Leonardo one of the most influential people ever to live.
Leonardo da Vinci: The Renaissance Luminary and His Artistic Prowess
Leonardo da Vinci, a polymath of the Renaissance era, holds an unparalleled position in the annals of art history. Renowned as a painter, inventor, scientist, and thinker, da Vinci’s multidisciplinary genius often shone through in his artistic works.

Here are 12 reasons that underscore why Leonardo da Vinci is considered one of the greatest artists in history:
- Mastery of Technique: Leonardo’s technique, especially his use of sfumato (the soft gradation of tones), set new standards in depicting light and shade, adding depth and three-dimensionality to his subjects.
- Unmatched Observational Skills: His keen eye for detail was evident in the anatomical accuracy of his figures. He spent years studying the human body, even dissecting cadavers, to understand its mechanics and representation.
- Innovation in Portraiture: The “Mona Lisa,” with her enigmatic smile and direct gaze, revolutionized portrait painting, challenging the conventions of the time and influencing countless artists thereafter.
- Pioneering Sketches: Leonardo’s notebooks, filled with sketches of landscapes, human figures, and inventions, provide deep insights into his creative and scientific thought processes.
- Composition Mastery: His work, “The Last Supper,” showcases his ability to capture drama and narrative, arranging figures to draw attention to the central character, Jesus, and the apostles’ reactions.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: Leonardo’s varied interests, from anatomy to flight, enriched his artwork. He merged artistic expression with scientific understanding, a combination ahead of his time.
- Enduring Influence: His artworks and techniques have influenced generations of artists, from his contemporaries to modern-day painters.
- Holistic Representation: Leonardo’s works, especially his portraits, captured not just the physical appearance but also the psyche and character of the subjects, making them appear lifelike and relatable.
- Pushing Boundaries: He was unafraid to explore uncharted territories, be it through dissecting human bodies against church norms or envisioning centuries ahead inventions.
- Legacy Beyond Art: While many artists are celebrated for their artworks, Leonardo’s brilliance shines through his inventions, architectural designs, and scientific observations, making him a holistic genius.
- Perfectionist Pursuits: Leonardo’s relentless pursuit of perfection meant that he took years to complete specific works, constantly refining and improving them. Some, like “The Adoration of the Magi,” remained unfinished but are still studied for their innovative techniques.
- Universal Recognition: Centuries after his demise, Leonardo’s works remain some of the most recognized and revered in the world, a testament to their timeless appeal and his unparalleled skill.
Decoding The Genius
Leonardo da Vinci’s impact on art is immeasurable. His works, marked by innovation and an insatiable curiosity, continue to inspire and awe. As we delve deeper into his masterpieces and the techniques he employed, we come to appreciate the depth of thought, precision, and passion that made him a true maestro of the Renaissance and, indeed, of all time.
Leonardo da Vinci: 10 Reasons for His Timeless Significance
Leonardo da Vinci, a polymath of the Renaissance era, is undoubtedly one of the most celebrated figures in art and science. His contributions spanned a range of disciplines, and even today, centuries after his death, he remains an icon of creativity and innovation.
Here are ten reasons why Leonardo’s influence remains unwavering in contemporary times:
- Masterpieces that Resonate: Works like “Mona Lisa” and “The Last Supper” are not just famous, but they continue to inspire debates, studies, and interpretations, captivating audiences worldwide.
- Innovative Techniques: Leonardo’s sfumato technique, where he used thin layers of paint to create soft transitions between colors and tones, revolutionized portrait painting and is still emulated by artists today.
- Integration of Art and Science: Leonardo blurred the lines between art and science as a keen observer of the world. His anatomical sketches, for instance, are as valued for their artistic beauty as they are for their scientific accuracy.
- Journals and Sketchbooks: Leonardo’s copious notebooks, filled with sketches, inventions, and observations, are invaluable resources that offer insights into the workings of a genius mind. They are frequently referenced in various fields, from art to engineering.
- Renaissance Ideals: Leonardo embodies the Renaissance Man’s ideals – someone who pursues knowledge in various fields. His life and work inspire multidisciplinary approaches to education and creativity.
- Inventions Ahead of His Time: While renowned for his art, Leonardo’s sketches also proposed designs like the helicopter, parachute, and scuba gear, showcasing his vision, which was centuries ahead.
- Inspiration for Modern Media: Leonardo’s life and art remain a rich source of inspiration for movies, documentaries, novels, and TV shows, underscoring his enduring cultural relevance.
- A Testament to Lifelong Learning: Leonardo’s insatiable curiosity about the world, from the flow of water to bird flight, encourages the principle of lifelong learning and the relentless pursuit of knowledge.
- Revolutionizing Anatomy: Leonardo’s detailed anatomical drawings, borne from dissecting cadavers, bridged art and medicine. They improved the understanding of the human body and set standards for anatomical illustration.
- A Global Symbol: Beyond specific accomplishments, Leonardo da Vinci stands as a symbol of genius, creativity, and boundless exploration, resonating with anyone aspiring to push the boundaries of what’s possible.
Leonardo da Vinci is not just an artist or scientist; he represents the limitless potential of human ingenuity. His multifaceted legacy serves as a testament to the intersections of art, science, and curiosity, ensuring his significance for future generations.
12 Reasons Why Leonardo da Vinci Stands Out as a Quintessential Renaissance Artist
Leonardo da Vinci, a name that evokes reverence and awe, is undeniably one of the most celebrated figures of the Renaissance period. His multi-faceted genius spanned art, science, and numerous fields of study, making him a true polymath.
Here are twelve compelling reasons why Leonardo is considered the embodiment of Renaissance brilliance:
- Master of Multiple Disciplines: While primarily celebrated as an artist, Leonardo was also an inventor, scientist, mathematician, and writer. This ability to excel in diverse domains epitomizes the Renaissance Man ideal.
- Iconic Masterpieces: Works like the “Mona Lisa” and “The Last Supper” aren’t just famous landmarks in art history. Their innovative techniques, deep emotions, and compositional brilliance set new standards.
- Innovative Techniques: Leonardo introduced the technique of sfumato – a soft, gradual transition between colors and tones. This added depth and three-dimensionality to his paintings.
- Detailed Anatomical Studies: Leonardo’s keen interest in human anatomy led him to produce detailed sketches based on dissections. These studies greatly enhanced the accuracy and lifelike quality of his figures.
- Notebooks and Sketches: His voluminous notebooks, filled with sketches, ideas, and observations, provide insights into his inquisitive mind. From flying machines to studies of water flow, these pages reveal a restless intellect.
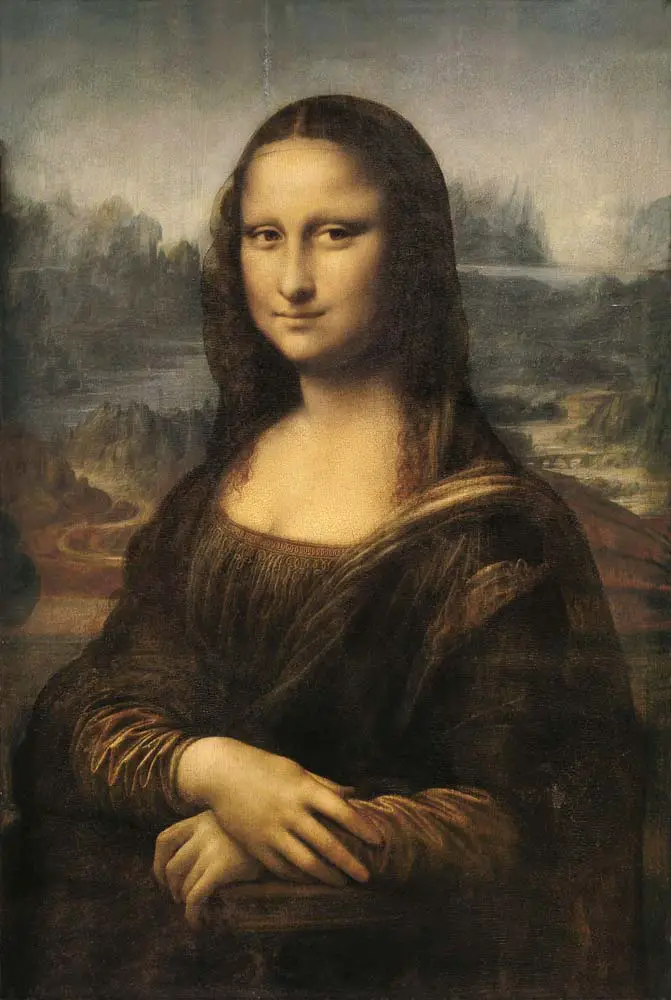
- Exploration of Movement: In paintings like “Vitruvian Man”, Leonardo explored human proportion and movement, merging art and science in a harmonious blend.
- Pioneering Portraiture: Leonardo transformed portrait painting. In “Mona Lisa”, he introduced a dynamic three-quarter pose, a departure from the traditional profile view.
- Landscape as Narrative: In many of his works, landscapes aren’t mere backdrops but crucial narrative elements. The distant mountains and winding rivers in the “Mona Lisa”, for instance, add depth and mystery.
- Scientific Precision: Leonardo’s artistic endeavors were deeply intertwined with scientific observation. Whether studying bird flight or the play of light, his art was enriched by his scientific pursuits.
- Enduring Mysteries: Works like the “Mona Lisa” still spark debates and theories, from her enigmatic smile to her true identity, ensuring Leonardo remains a focal point in cultural discussions.
- Influence on Successive Generations: Leonardo’s techniques, principles, and works have inspired countless artists over the centuries. His influence permeates the realms of art, science, and design.
- Archetypal Thinker: More than his individual achievements, Leonardo represents the ideal of the Renaissance – a period of rebirth, exploration, and the confluence of art and science. His boundless curiosity and relentless pursuit of knowledge embody the spirit of the age.
Leonardo da Vinci wasn’t just a product of the Renaissance; he was one of its defining forces. His legacy transcends time, and his works remain touchstones of human achievement. Such is the genius of Leonardo – a beacon of inspiration for all eras.
Listen To Our Podcast About exploring Da Vinci’s Enduring Influence On The Renaissance Below or By clicking here.

Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you want to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel filled with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend just 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Frequently Asked Questions
What were Leonardo da Vinci’s contributions to the Renaissance?
Leonardo da Vinci made significant contributions to the Renaissance through his art, science, and engineering works. He was known for his innovative ideas, including his designs for flying machines, anatomical studies, and his iconic paintings such as the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper.
What role did Leonardo da Vinci play in the Renaissance?
Leonardo da Vinci was a prominent figure in the Renaissance as an artist, inventor, and scientist. His contributions to art, engineering, and science helped shape the period and influenced later generations.
How did Leonardo da Vinci influence Renaissance art?
Leonardo da Vinci’s art was revolutionary for its time, and his use of techniques such as chiaroscuro and sfumato helped define the Renaissance style. His works inspired other artists and helped elevate art to a new level of beauty and realism.
What was Leonardo da Vinci’s influence on science during the Renaissance?
Leonardo da Vinci’s contributions to science during the Renaissance were significant. He conducted groundbreaking research on anatomy, optics, and mechanics, and his works paved the way for further scientific advancements.
What was Leonardo da Vinci’s greatest contribution to the Renaissance?
Leonardo da Vinci’s greatest contribution to the Renaissance was likely his art, specifically his painting techniques and masterpieces such as the Mona Lisa and The Last Supper. However, his engineering, science, and anatomy innovations were also significant.
How did Leonardo da Vinci’s inventions impact the Renaissance?
Leonardo da Vinci’s inventions, such as his flying machines and hydraulic pumps, were groundbreaking and influenced later inventors. His works showed that technology could be beautiful as well as functional and helped spur further innovations in engineering and design.
How did Leonardo da Vinci’s anatomical studies impact medicine during the Renaissance?
Leonardo da Vinci’s anatomical studies were groundbreaking and influenced the field of medicine during the Renaissance. His accurate depictions of the human body helped doctors better understand anatomy, and his works inspired further scientific inquiry into the human body.
What was Leonardo da Vinci’s influence on painting during the Renaissance?
Leonardo da Vinci’s influence on painting during the Renaissance was significant. His techniques, such as sfumato and chiaroscuro, helped define the Renaissance style, and his works inspired other artists to push the boundaries of art and experiment with new techniques.
Related Questions
Mona Lisa Painting And The Paris Louvre Museum
The Mona Lisa is one of the key paintings of the Louvre Museum. It is one of the most visited paintings in the world. The Mona Lisa is a painting studied, sang, written, and spoken about. There is still a mystery surrounding exactly who the Mona Lisa is and why Leonardo da Vinci painted it. This mystery adds to the allure of the painting.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Mona Lisa Painting And The Paris Louvre Museum.
Why is the Louvre Called the Louvre?
It isn’t easy to see all the exhibitions at the Louvre in just one day. This is because the museum has so much to see and some exhibitions. The Louvre is also one of the most visited museums in Paris and worldwide. Each year, millions of people go through the doors of the Louvre to visit its many exhibitions.
You can learn more about Why is the Louvre Called the Louvre? by clicking here.