Many people may not realize that the Middle Ages was a time of immense creativity and innovation in the arts. From illuminated manuscripts to ecclesiastical architecture, many remarkable works of art emerged during this period.
The Middles Ages span from 500 AD to 1400 AD; the Middle Ages gave us some of our most beloved pieces of artwork that have survived centuries and are still part of our culture today. Many people don’t know much about the art specific to this era. The Middle Ages has about six crucial European art movements that are still vital to us today.
Table of Contents
- When Was The Middle Ages?
- Middle Ages And Art Explored
- 6 Art Movements Of The Middle Ages Art
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Related Questions
When Was The Middle Ages?
The Middle Ages began in Europe around the 5th century and ended in the 15th century. The Middles Ages went from the collapse of the Roman civilization in the 5th century to the Renaissance era.
When exactly the Middle Ages is said to have ended depends upon which part of Europe you are in. For some areas of Europe, it was the 13th and 14th centuries.
Many scholars put the start of the Renaissance in the 13th century when the cultural and economic shift occurred from the eastern Mediterranean to Western Europe, particularly Italy. The Middle Ages was a term given to this era by the Renaissance Humanists. The Humanists under the Renaissance were engaged in a revival of Greek and Rome classical learning and art.
Many historians believe that Renaissance Humanists invented the Middle Ages to distinguish themselves from this era. They wanted to show new enlightenment—a change to what was happening and how it was different from the medieval concept of life.
11 Interesting Facts About The Middle Ages
The Middle Ages were a fascinating historical period with incredible characters and stories. From the Christian Crusades that forever changed Europe to the Vikings invading Europe and beyond.
Here are 11 interesting facts about the Middle Ages.
- Not everything was doom and gloom in the Middle Ages. The Middle Ages was a dynamic era for many, including the arts.
- Europe started to be formed in the Middle Ages, and people were divided into distinct cultural units.
- Roman imperial traditions gave way during this time to those of the Germanic people who were establishing Kingdoms in Europe.
- During the Middle Ages, Western Europe was starting to be Christianized.
- Vikings invaded Europe and beyond.
- This was the era of the Crusades, which was in response to the Muslim wars of expansion.
- The papal monarchy started when the Catholic Church had political roles with the Holy See.
- Universities started in the Middle Ages.
- Marco Polo left on his famous expedition to China during the Middle Ages.
- In 1347, the Black Plague was a terrible disease that killed about half of Europe’s inhabitants.
- French heroine Joan Arc is from the Middle Ages; she was executed in 1431 in England.
Middle Ages And Art Explored
The art produced during the Middle Ages was primarily religious. The Middle Ages art featured biblical scenes, portraits of saints, and illuminated manuscripts. Many art pieces were created to aid worshipers in understanding stories from scripture or aspects of the Christian faith.
Other artworks included depictions of daily life and battle scenes from medieval battles. In addition to paintings, sculptures were highly popular during this era, and many are still preserved in churches today.
Religious art was so important during this era because there was not yet a printed Bible that everyone could read and understand. Churches had art, including stained glass windows, to help their worshippers learn, understand and remember some of the Biblical stories.
6 Art Movements Of The Middle Ages Art
As the Middle Ages spanned such a long time, art historians have tried to categories Middles Eastern Art into different art movements. There are generally accepted six art movements which include:
Early Christian Art And Architecture And The Middle Ages
Early Christian art is also known as Paleo-Christian art. It is an art that Christians produce that renders Christian patronage from the earliest periods of Christianity.
It is usually defined as art produced between 260 and 525. But most of the art that has survived is from the second century onward.

from Roman Catacombs, 300-360 AD
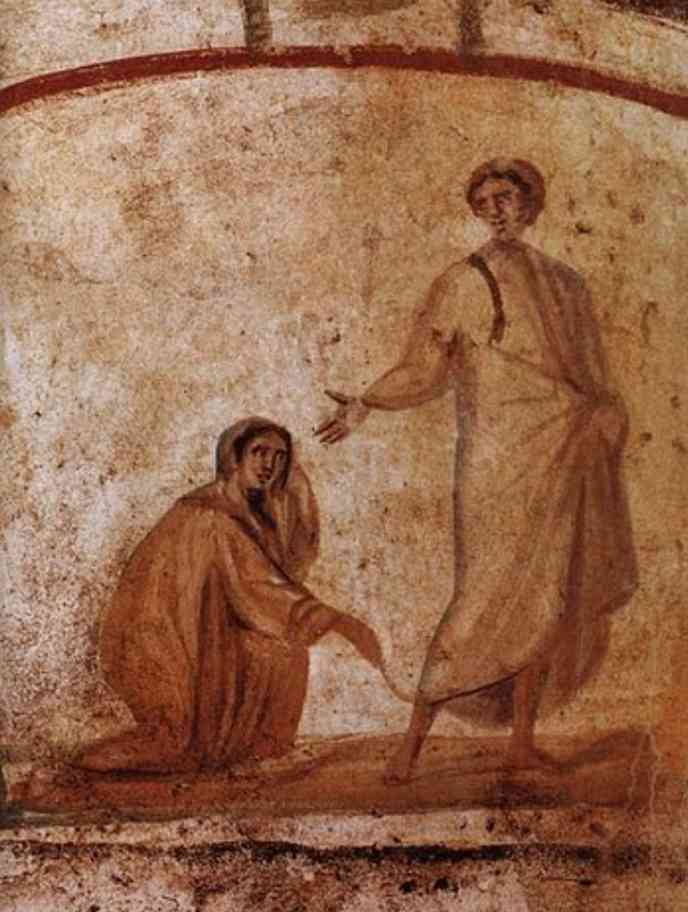
An example of this art would be “Jesus healing the bleeding woman,” from Roman Catacombs, 300-360 AD, or The Good Shepherd from the Catacomb of Priscilla, 250 to 300.
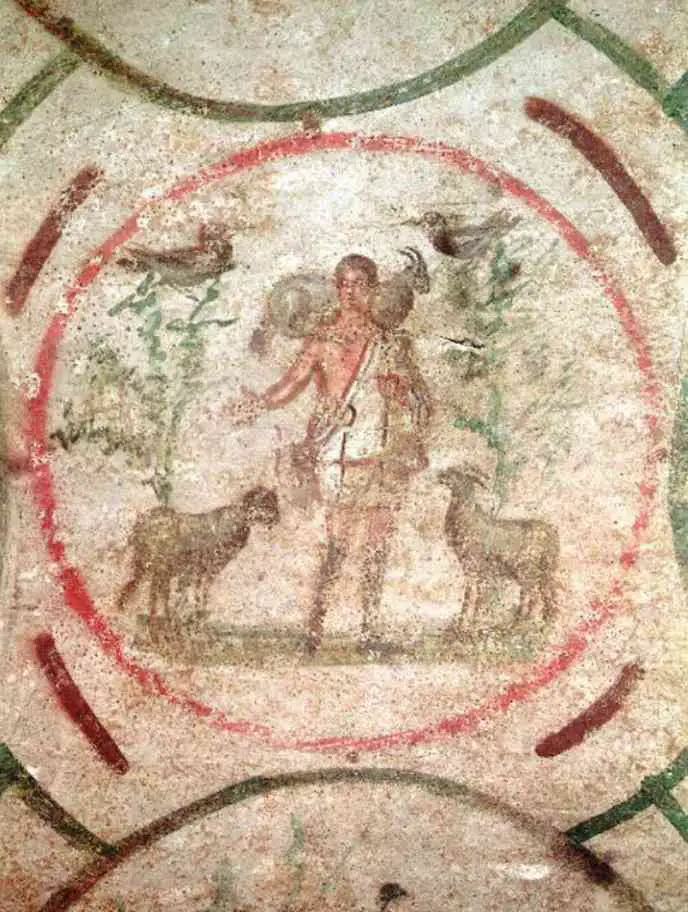

For these art pieces, we do not know the artists’ names or much about their lives.

Listen To Our Podcast About Exploring The Timeless Artistic Treasures Of The Middle Ages by clicking here.
Migration Period Art And The Middle Ages
Migration Art is the artwork of the Germanic people during the migration, which is 300 to 900. Included in the migration art is of the Germanic Tribes in Europe and the start of the Anglo-Saxon and Celtic art in Britain and Ireland.
Insular art, also known as Hiberno-Saxon Art, was produced in the Post-Roman Era of Great Britain and Ireland. The term Insular is from insula, which means “island.” Many historians will group Insular art as part of the Migration art movement.
But many also see Insular art as having a unique style from the rest of these kinds of art. Most Insular art is from the Irish movement of Celtic Christianity, which includes some excellent metalwork.

One of the famous artworks from this time is the Book of Kells, which can contain some very lavish text. Many artworks we have left is the art that includes metalwork and stonework.
Byzantine Art And The Middle Ages
Byzantine art emerged from the Christianized Greek cults of the Eastern Roman Empire. The capital of Byzantine art was Constantinople (present-day Istanbul).
Even today, you can find a lot of Byzantine art in Istanbul, Turkey. Some of the most famous Byzantine art include the Byzantine Mosaic of the Hagia Sophia in Constanopole of Christ Pantocrator.
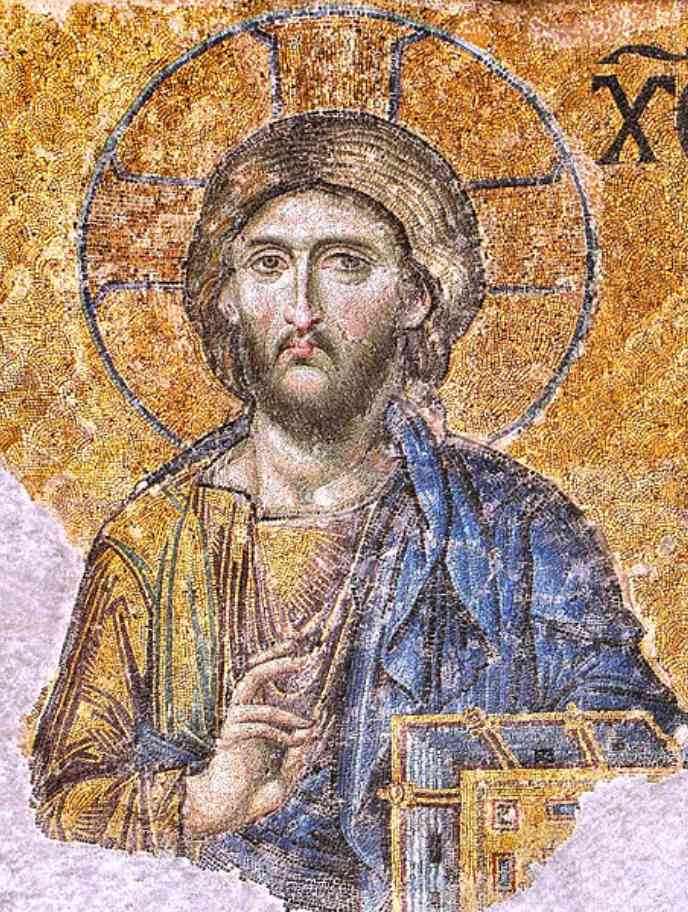

This art is on the walls of the upper southern gallery Hagi-Sophia. The full piece of art also shows Christ flanked by the Virgin Mary and John the Baptist.
Pre-Romanesque Art And The Middle Ages
Pre-Romanesque art is a period used mainly to show this period’s architecture and monumental sculptures. The primary theme during this time was the introduction of the classical Mediterranean and Early Christian art forms.
This art is from the Merovingian Kingdom, about 500 AD, and the Carolingian Renaissance in the late 8th century. The Merovingian Dynasty was the ruling family of the Franks, one of Europe’s most powerful empires.
The Carolingian Renaissance was one of three Medieval Renaissances, including a revival of literature, writing, visual arts, architecture, music, spiritual studies, and other reforms. These movements occurred most during the reign of the Carolingian rulers.
Romanesque Art And The Middle Ages
Romanesque art is the art that includes the architecture of this period. The architecture at this time was before Gothic architecture and had a lot of paintings and sculptures.
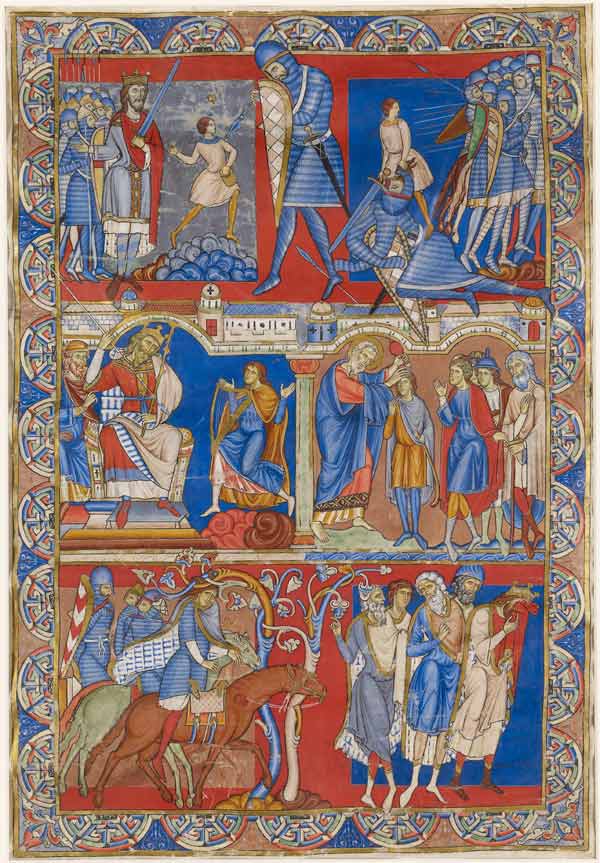

Some well know Romanque art include works such as The Morgan Leaf from the Winchester Bible in 1160-75 that had scenes from the life of David.
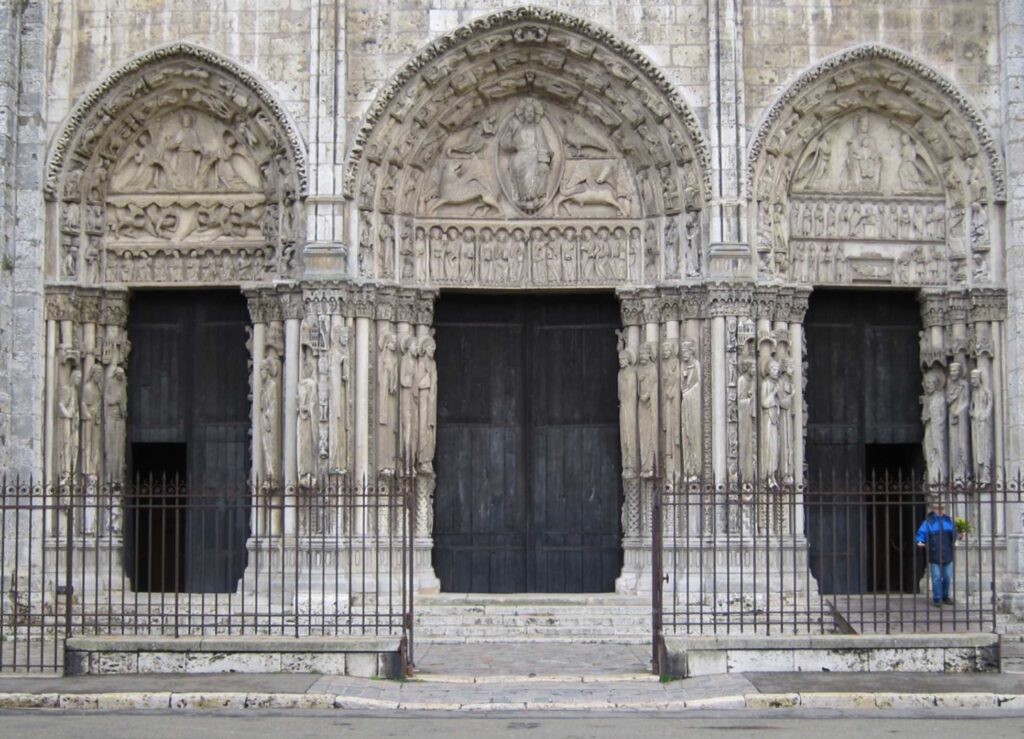
Gothic Architecture And Art And The Middle Ages
Gothic art is Medieval art developed in Northern France from Romanesque Art. Gothic art is probably the most famous and well know of all the Middle Ages art.
Gothic art quickly spread from architecture to all art forms, including sculptures, textiles, paintings, frescos, stained glass windows, panel paintings, mosaics, and manuscripts.
Some famous Gothic art includes the Western Royal Portal of Carter’s Cathedral from 1145 to the Wilton Diptych from 1395 to 1459.

The art produced during the Middle Ages influenced the culture of Europe and has been admired for centuries. It continues to inspire people today.
The Middle Ages was a significant development period for European art. Art in this era has been celebrated for its skillful craftsmanship, beauty, and ability to tell stories about the people and times of the period.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you want to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you anytime. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Frequently Asked Questions
When were the Middle Ages, and why is it considered a significant period for art?
The Middle Ages spanned from 500 AD to 1400 AD, and it is considered significant for art due to the emergence of various artistic movements and the creation of enduring masterpieces during this time.
What were the key artistic movements during the Middle Ages?
The Middle Ages witnessed several important artistic movements, including Byzantine, Carolingian, Romanesque, Gothic, International Gothic, and Gothic Revival.
How did illuminated manuscripts contribute to Middle Ages art?
Illuminated manuscripts were intricately decorated manuscripts, often religious texts, with elaborate illustrations and designs. They were a significant form of artistic expression during the Middle Ages, showcasing exquisite craftsmanship and attention to detail.
What role did ecclesiastical architecture play in the art of the Middle Ages?
Ecclesiastical architecture, particularly Gothic cathedrals, was a prominent feature of Middle Ages art. These structures were characterized by pointed arches, ribbed vaults, and flying buttresses, creating awe-inspiring spaces for religious worship.
Were religious themes predominant in Middle Ages art?
Yes, religious themes were predominant in Middle Ages art, reflecting the strong influence of the Catholic Church. Biblical narratives and saints’ lives were common subjects, serving both religious and educational purposes.
How did the Black Death impact art during the Middle Ages?
The Black Death, a devastating pandemic in the 14th century, had profound effects on Middle Ages art. Themes of mortality and the transience of life became prevalent, influencing artistic representations such as the “Dance of Death.”
What is the significance of stained glass windows in Gothic art?
Stained glass windows were a hallmark of Gothic art, serving as a way to illuminate sacred spaces with vibrant colors and tell biblical stories to an often illiterate congregation. The intricate designs showcased the technical skill of medieval artisans.
How did the Middle Ages contribute to the development of portraiture in art?
During the later Middle Ages, the development of portraiture became more prominent. While earlier medieval art focused on symbolic representation, portraiture began to capture individual likeness, paving the way for later Renaissance portraiture.
What was the impact of the Renaissance on Middle Ages art?
The Renaissance, which followed the Middle Ages, marked a shift in artistic styles and techniques. However, the Middle Ages laid the groundwork for many artistic concepts and skills that were further developed during the Renaissance.
How does Middle Ages art continue to influence contemporary culture?
Many aspects of Middle Ages art, including Gothic architecture and illuminated manuscripts, continue to influence contemporary culture. Elements of medieval art often appear in literature, film, and popular culture, showcasing the enduring impact of this historical period on artistic expression.
Related Questions
How Did Mannerism Become An Offshoot Of The Works Of The Renaissance?
Mannerism is the art movement that emerged after the High Renaissance era. Mannerism art is an offshoot of the Renaissance; Renaissance artists such as Michelangelo and Raphael adopted mannerism techniques. Mannerism art exaggerated and distorted elements of Renaissance art while creating a sense of imbalance in their art.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading How Did Mannerism Become An Offshoot Of The Works Of The Renaissance?
What Did Leonardo da Vinci Contribute To The Renaissance?
Leonardo da Vinci made many contributions to the Renaissance in art, science, engineering, medicine, and architecture. He was a keen observer who wrote down much of what he discovered in his notebooks. His artistic techniques changed how artists painted and influenced many other Renaissance artists.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Did Leonardo da Vinci Contribute To The Renaissance?
Meaning Of “Art Speaks Where Words Are Unable To Explain”
“Art speaks where words are unable to explain” means that words, even though very powerful and pcannot alwayss able to convey the messagegetan convey. Words are powerfulimage or piece of art can be much more potent than the spoken or written word.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading the Meaning Of “Art Speaks Wher.Words .Are Unable To Explain”