Rembrandt is one of the most famous Dutch artists to have ever lived. Most people have heard about him and his name.
Rembrandt is known to have studied under two leading art masters. The first was Jacob van Swanenburgh, and the second was Pieter Lastman. He could also spend a few months studying under Jakob Pynas. We know that he painted together and was influenced by Jan Lievens.
Table of Contents
Artist Masters That Rembrandt Studied Under
From about 1620 to 1624, Rembrandt studied as an artist, and he had two masters he trained with in succession.
What is unusual about Rembrandt is that, unlike many young artists during his day, he did not go to Italy to study under an Italian master to learn about art. Instead, he chose to do all of his artistic study in Holland.
We do not know the whole reason for this; it could have been because he did not have the money to study in Italy. Some felt that Rembrandt could learn all he needed in Holland without traveling and living in Italy. This makes Rembrandt unique compared to many other artists during his time who traveled and studied under Italian masters in Italy.
Rembrandt’s First Art Master Was Jacob van Swanenburgh

Rembrandt’s frist art master was Jacob van Swanenburgh (1571-1638). It was thought that Rembrandt studied under van Swanenburgh for at least three years. Van Swanenburgh must have taught him the basic skills and the knowledge necessary for his profession.
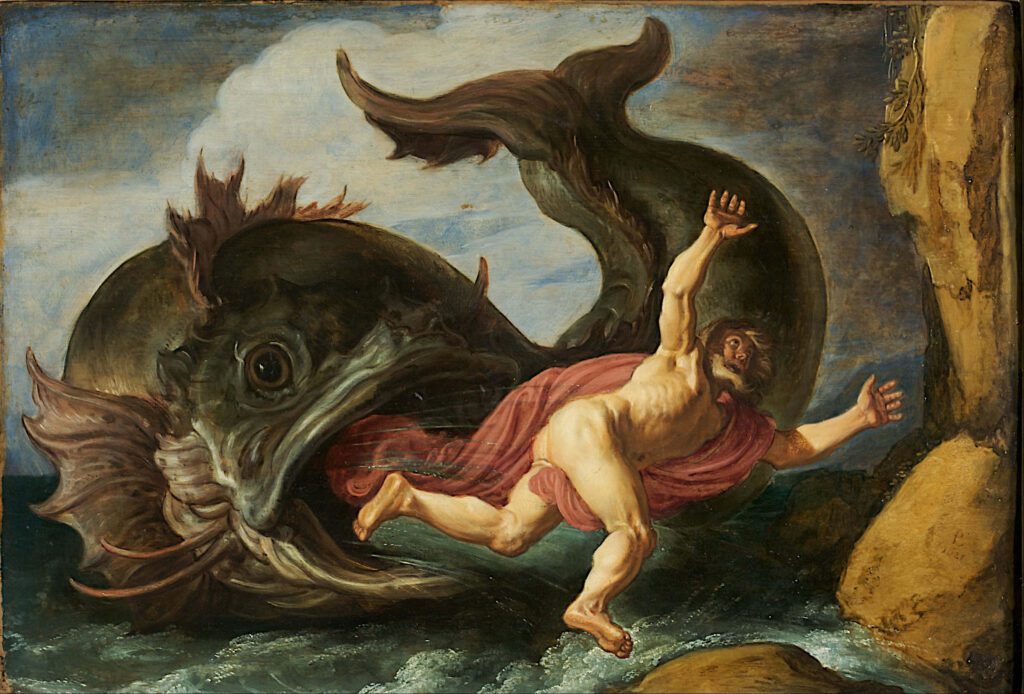
Van Swanenburgh was a specialist in architectural pieces and scenes of hell in the underworld. This type of painting called for skills and painting of fire and its reflection of the surrounding objects. During Rembrandt’s time, knowing how to paint the hell and fire paintings was considered a distinct and demanding skill.
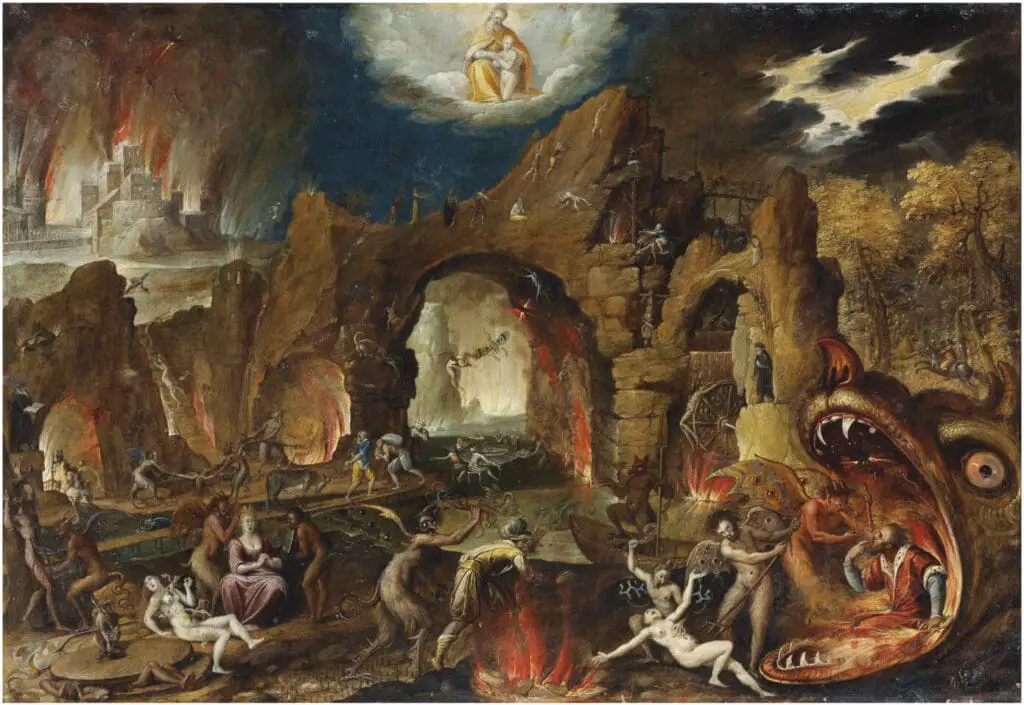

Rembrandt’s early exposure to this type of hell in fire paintings and the reflection that was needed with the surrounding objects led to his abiding interest in the effects of light on his paintings.
Rembrandt’s Second Master Was Pieter Lastman

Rembrandt’s second teacher or art master that he studied under was Pieter Lastman (1583-1633). Lastman lived in Amsterdam, and we believe that Rembrandt stayed with him and worked underneath him for six months.

During this time, Lastman was well-known as a history painter. He must have helped Rembrandt gain all the knowledge and skills necessary to master historical paintings.
Historical paintings involve placing various figures from biblical, historical, methodological, or allegorical scenes into what could be very complex scenes. These paintings were intricate and required a great deal of skill and knowledge.
In the 17th century, historical painting held one of the highest positions for painters because it required a complex command of all subject matters, from the landscape to the architecture to still life painting to drapery to animals to human figures to all types of different postures and positions expressions and costumes.
In other words, to be a historical painter, you had to master almost all types of art and painting and be able to put them together into one single painting eloquently.
Jakob Pynas As Rembrandt’s Teacher
One biographer, Arnold Houbraken, mentioned in his 18th-century book that Rembrandt also studied under Jakob Pynas (1592 – 1650). Arnold Houbraken (1660 – 1770) was a Dutch painter and writer who is mainly remembered as the biographer of the Dutch Golden Age painters, including a biography on Rembrandt.
This has not been able to be ultimately confirmed, but it is possible that Rembrandt did study some historical paintings under Jakob Pynas.

It is thought that Rembrandt studied with Jacob Pynas in his workshop for a few months after his six-month apprenticeship with Peter Lastman ended.
Influence Of Jan Lievens On Rembrandt’s Art

It has felt that the Dutch artist Jan Lieven also impacted Rembrandt and his style during his years of training. Lieven and Rembrandt were contemporaries, but as Lieven was considered a child prodigy, he was already well-established when Rembrandt started his art study and training.
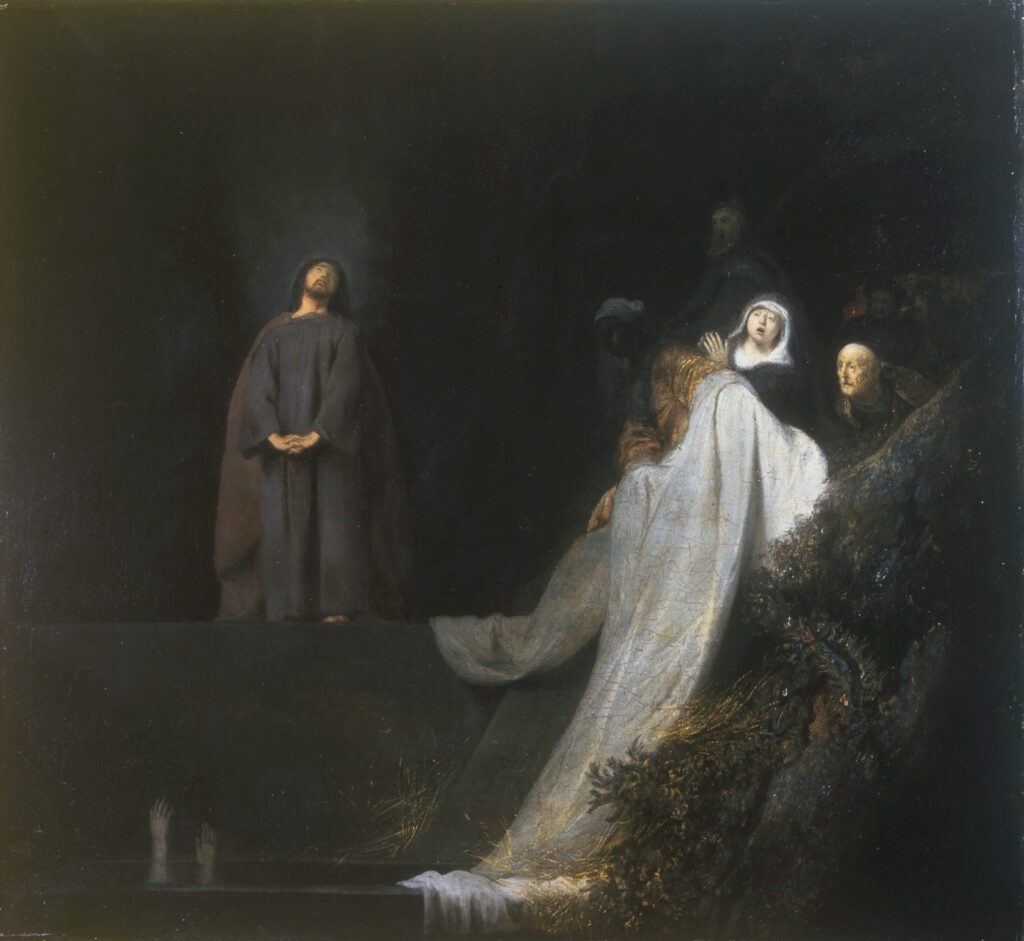

Historians only know that Lieven and Rembrandt worked closely together for some years after about 1625, but many believe their association started much sooner.
No traces of Rembrandt’s student exercises have survived, so we do not have firm documentation if he also studied under other masters.
Rembrandt did not study under any Italian artist or travel to Italy as many artists did during his time. All his artistic training was done in Leiden or Amsterdam.
This makes Rembrandt a truly Dutch artist who is considered to be one of the two greatest artists that have ever come from Holland. The first is Rembrandt, and the second is Vincent Van Gogh.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you want to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. I would be happy to talk to you anytime if you have any questions. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel with great videos and information by clicking here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who were Rembrandt’s main art mentors?
Rembrandt studied under two prominent artists: Jacob van Swanenburgh and Pieter Lastman. These masters played crucial roles in shaping his early artistic development.
Why did Rembrandt choose Jacob van Swanenburgh as his first mentor?
Jacob van Swanenburgh was known for his expertise in history painting, a genre Rembrandt was interested in. Under Swanenburgh’s guidance, Rembrandt honed his skills in depicting historical and biblical scenes.
Tell me more about Rembrandt’s time with Pieter Lastman.
Pieter Lastman, a renowned history painter in Amsterdam, influenced Rembrandt with his narrative style. Rembrandt’s exposure to Lastman’s work added depth and storytelling elements to his own paintings.
Did Rembrandt study under anyone else besides Jacob van Swanenburgh and Pieter Lastman?
Yes, Rembrandt also spent a short period studying under Jakob Pynas. Although the duration was brief, this experience likely contributed to the diverse influences in Rembrandt’s early works.
How did Rembrandt’s collaboration with Jan Lievens impact his art?
Rembrandt and Jan Lievens, both young and aspiring artists at the time, collaborated on several projects. This partnership allowed them to share ideas and techniques, influencing each other’s artistic styles.
What specific techniques did Rembrandt learn from his mentors?
From Jacob van Swanenburgh, Rembrandt learned the technical aspects of painting, including composition and brushwork. Pieter Lastman’s influence is evident in Rembrandt’s narrative skills and ability to convey emotion.
Were there any notable differences in Rembrandt’s style after studying under different mentors?
Yes, Rembrandt’s early works reflect the diverse influences of his mentors. From Swanenburgh, he gained a classical foundation, while Lastman’s influence brought a more dramatic and narrative quality to his paintings.
How long did Rembrandt study under each mentor?
Rembrandt spent a few years with Jacob van Swanenburgh and a shorter period with Pieter Lastman. The exact duration may vary, but these experiences were crucial in shaping his artistic journey.
Did Rembrandt’s style evolve over time, moving away from his early influences?
Yes, as Rembrandt matured as an artist, he developed a distinctive style that moved beyond the influences of his mentors. His later works are characterized by a unique use of light and shadow, known as chiaroscuro.
Did Rembrandt’s early mentors continue to influence his later works?
While Rembrandt’s early mentors laid the foundation for his artistic skills, his later works demonstrate a departure from their direct influence. However, the lessons learned from Swanenburgh and Lastman undoubtedly contributed to the depth and complexity of his art.
Related Questions
What Are The Characteristics Of Mannerism Art?
Mannerism was an art movement filled with elongated bodies, tiny heads, and human figures in twisted forms. Perspective and proportion were unnecessary, but colors, contrasts, virtuosity, and agitated compositions were essential.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Are The Characteristics Of Mannerism Art?
What Was The Focus Of Renaissance Art?
Renaissance art focused on the classics of Greek and Rome, humanist philosophy, and the study of the human figure. Realism was also an essential part of renaissance art. The great artists of the Renaissance also became great anatomists and studied human beings.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Was The Focus Of Renaissance Art?.
What Are The Major Periods In Western Art History?
The significant Western art history periods are defined as Prehistoric Art, Ancient Art, Medieval Art, the Renaissance, Mannerism, Baroque, Rococo, Neoclassicism, Romanticism, Realism, Art Nouveau, Impressionism, Post-Impressionism, Fauvism, Expressionism, Cubism, Surrealism, Abstract Expressionism, Op Art, Pop Art, Arte Povera, Minimalism, Conceptual Art and Contemporary Art.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Are The Major Periods In Western Art History?.