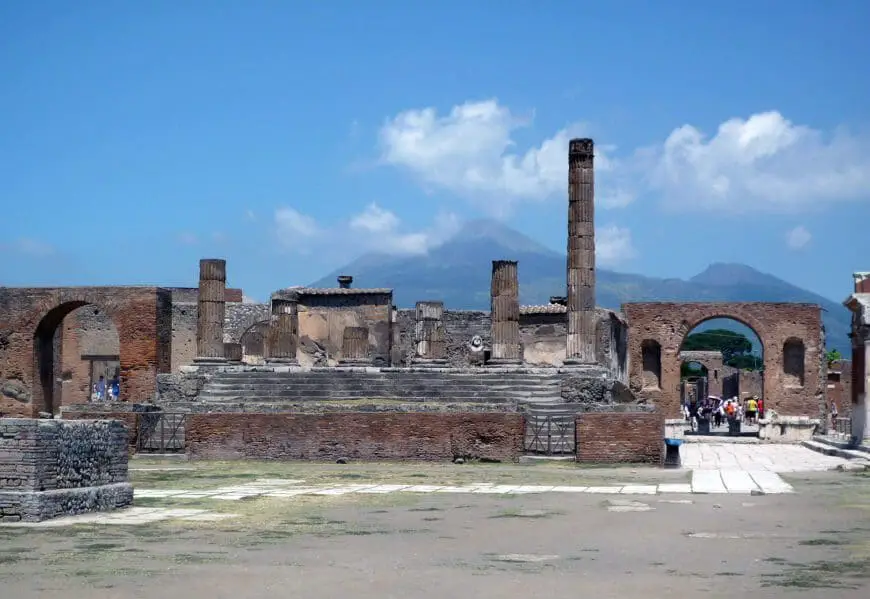
At about noon on August 24, 79 CE, a massive eruption on Mount Vesuvius showered volcanic debris over Pompeii, Italy. Buildings were destroyed, and the city’s population was crushed, fixated, and buried under a blanket of ash and volcanic pumice.
The City of Pompeii is essential for studying and understanding Roman art as it gives us a glimpse into everyday people’s lives, homes, art, and lives. As art is a consistent and intricate part of our lives, Pompeii shows us what was important before and during 79 CE; we get a glimpse into what kind of Roman art was created during that time.
Table of Contents
- Pompeii’s History And Rome
- Pompeii’s Importance To Roman Art
- 12 Reasons Pompeii Stands as a Pillar of Historical Significance
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Related Questions
Pompeii’s History And Rome
The City of Pompeii remained buried under volcanic ash until it was unearthed in the 1700s. The world was astonished at the discovery of a sophisticated Roman city frozen in time.
Before its untimely demise, Pompeii was a thriving Roman city. Before being aligned with the Romans, the city had also been conquered by the Greeks, Etruscans, and Samnites.
Under the care of Rome, Pompeii played an essential role in trade and commerce. It was close to the Mediterranean basin area and strategic roads built by the Romans. The Pompeii area had a lot of fertile farmland.
The discovery of Pompeii showed us the day-to-day life of what was once an ancient Roman City in Campania, Italy. Here are a few facts about Pompeii:
- City Aligned With Rome – Pompeii was aligned with Rome and colonized by Rome in 80 BC. It was located near the coast of the Bay of Naples, once a thriving Roman City.
- Also, Under Greek And Etruscan Influence – Pompeii came under Greek and Etruscan influence before it was aligned with the Roman Empire.
- Damaged By Earthquake – Pompeii was damaged by an earthquake; a significant earthquake struck Pompeii in 63 BC, just a few years before the volcano completely buried the city in 79 BC. The earthquake tremors continued, and historians feel that the earthquake tremors must have become a way of life. Many people lived through the earthquakes only to be buried by volcanic ash.
- Pompeii Was Covered 6 Meters Under Volcanic Ash – When the Volcano erupted, it buried Pompeii under 6 meters of ash and other volcanic debris. This was a rapid and swift burial of an entire city.
- Important Archeological Site – Pompeii is an important archaeological site as it gives us a glimpse into ancient Rome’s life, culture, religion, and political life.
- Do Not Know How Many Died – We do not know how many of the 20,000 residents of Pompeii and 4,000 residents of Herculaneum and other areas died, but we know a lot about how they lived. The volcano eruption covered not only Pompeii but also a nearby city known as Herculaneum, Oplontis, and Stabiae. The city is so well preserved that we can learn much from them about life and art in ancient Rome.
- Preservations Of Organic Materials – What is very interesting about the volcanic eruption is that the ash in some areas is carbonized, preserving the wood, beds, doors, and even some organic materials as food.
Pompeii’s Importance To Roman Art
Pompeii was a Roman city that showed us Roman art, including frescoes, architecture, and other significant construction projects. The city buried under the ashes had everything from an amphitheater to an aqueduct. These significant projects give us a glimpse into life in ancient Rome.
The importance of Pompeii to Roman art is that life, art, architecture, and the city was frozen in time. So Pompeii today shows us what life was once like in ancient Rome. In particular, Roman artwork such as frescoes and mosaics were well preserved, which helped to give us a glimpse into what life was like in this Roman city.
We also learned from Pompeii that art was essential to the residents there. Villas had frescoes and mosaics covering the walls and floors. We understand that in ancient Rome, art was not just a way of life but also a status symbol and a way to decorate one’s interior.
Here are some of the significant works of art that have been preserved and found in the city of Pompeii.
The Villa Of Mysteries
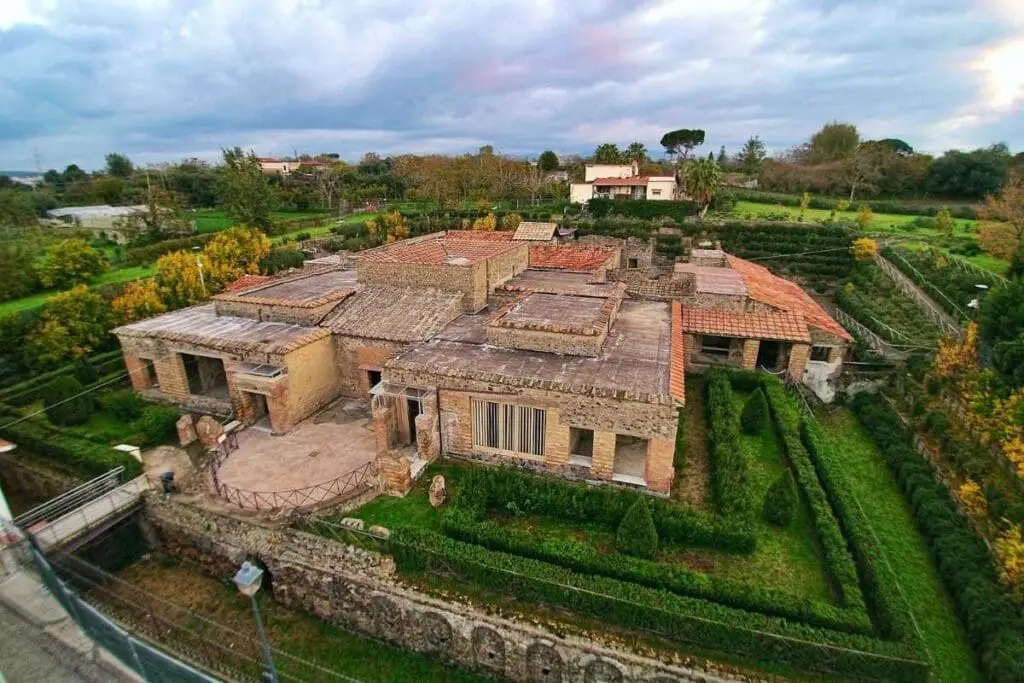

The Villa of Mysteries is a well-preserved ancient Roman Villa on the outskirts of Pompeii. What is unique about this villa is the series of exquisite frescos in some rooms. These frescoes were thought to show the initiation of a young woman into a Grieco Roman mystery cult.
The frescoes are vital because they are well-preserved and give us a glimpse into the art of ancient Rome. The frescoes paintings are thought to be from the first century BC.
The Villa is named the Villa of Mystery because of the beautiful Roman-style Frescoes dating from 70 to 60 BC. There are several murals today that have survived.
The Alexander Mosaic

The Alexander mosaic depicts a battle between Alexander the Great and King Darius II of Persia. This wonderful mosaic was discovered in 1831 during the evacuations of Pompeii.
The right-hand side of the mosaic is well preserved as it shows Darius and Persians. On the left hand, which is poorly perceived, shows Alexander and his army. Some historians say the depicted battle goes back as far as 331 BCE.
The Cave Canem Mosaic

Another important mosaic is the Cave Canem mosaic, also known as the “Beware of the dog” mosaic. The mosaic of a dog is located at the entrance of the House of the Tragic Poet.
The dog on the mosaic looks ready to pounce on any unwelcome visitor that comes into the home. We learn much about Rome and its dogs from this mosaic: the dog has teeth and a chain around its neck.
The phrase “Cave Canem” is written in Latin, which translates to “Beware of the dog.”
House Of Menander

The House of Menander shows us a home of a typical high-ranking family. The home was filled with art, particularly frescoes from the Illiad and Odyssey.
The home received its name because of a picture of Menander, an Athenian playwright, placed in the entrance. Artifacts such as silverware as been found in the house.
The House Of Vettii

Another important series of frescoes in Pompeii is at the House of Vettii. The dining room has a fresco displaying a series of cupids.
The importance of the House of Vettii is that it shows us some of the important design and interior design trends of the final years of Pompeii’s existence. The home shows us some key elements of Roman art and architecture.
Compared to many other houses in Pompeii, The House of Vettii gives us a glimpse into the direction that Roman art was going before Pompeii was covered by volcanic ash.
Pompeii gives us an essential glimpse into ancient Roman life and art. What is so unique about Pompeii and makes it so important is that Roman life, culture, and art were frozen in time under the volcanic ash. Because of Pompeii, we can discover the art and culture of ancient Rome.
12 Reasons Pompeii Stands as a Pillar of Historical Significance
The ancient city of Pompeii, frozen in time by the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in 79 AD, offers an unparalleled window into Roman life. Its haunting and fascinating remains have made Pompeii one of the most important archaeological sites in the world.
Here are 12 compelling reasons why:
- Preservation: The volcanic ash from Vesuvius’ eruption acted as a preservative, sealing the city and its contents, providing a snapshot of daily Roman life that’s rare in the archaeological record.
- Daily Life Insights: Unlike many ancient sites that focus on temples or palaces, Pompeii showcases homes, shops, and streets, offering insights into the everyday lives of its inhabitants, both rich and poor.
- Art and Architecture: Pompeii houses an array of well-preserved frescoes, mosaics, and architectural structures, reflecting the artistic and architectural sensibilities of its era.
- Civic Structures: The city’s amphitheater, basilica, and public baths highlight the Roman emphasis on communal and social activities, showcasing the importance of public spaces in Roman culture.
- Written Records: Graffiti and inscriptions found on walls provide first-hand accounts of social interactions, politics, and even humor of the time.
- Economic Insights: Shops, markets, and the remains of food and produce offer a unique perspective on the commerce and diet of a typical Roman city.
- Cultural Melting Pot: Artifacts and architectural styles indicate that Pompeii was a cosmopolitan city with influences from various cultures, reflecting the diversity of the Roman Empire.
- Religious Practices: Temples dedicated to different deities, alongside shrines and household gods, provide insights into its residents’ spiritual life and religious practices.
- Vivid Human Tragedy: The plaster casts of voids left by decomposed bodies give a poignant, tangible connection to the people who perished, making the past deeply personal.
- Ongoing Discoveries: A significant portion of Pompeii remains unexplored despite extensive excavations. Each new discovery adds layers to our understanding of the ancient world.
- Educational Value: As one of the most visited archaeological sites globally, Pompeii serves as an outdoor museum, educating millions about ancient history, archaeology, and volcanology.
- Warning from History: Pompeii’s fate is a stark reminder of nature’s power. Modern understanding of volcanic activity, risks, and the importance of preparedness is, in part, shaped by studying the Vesuvius eruption.
Pompeii is not just an archaeological site; it’s a time capsule. The city, with its streets, buildings, and artifacts, tells a story of a vibrant society, its way of life, its achievements, and its sudden, tragic end.
This narrative makes Pompeii an invaluable treasure for historians, archaeologists, and the world at large.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you want to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel filled with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend just 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why is Pompeii important for the study of Roman art?
Pompeii is a vital source of information on Roman art because it was preserved almost intact by the volcanic ash from Mount Vesuvius’s eruption in 79 AD. The city provides a unique opportunity to see Roman art and architecture as it was at the time of the eruption.
What types of Roman art can be found in Pompeii?
Pompeii is rich in various types of Roman art, including mosaics, frescoes, statues, architectural designs, graffiti, and everyday objects that reflect the aesthetic tastes of the Romans.
How do the frescoes of Pompeii contribute to our understanding of Roman art?
The frescoes in Pompeii provide valuable insights into Roman painting styles, themes, and techniques. They depict a range of subjects, including mythological scenes, landscapes, and daily life, showing how Romans decorated their homes and public buildings.
What can the architecture of Pompeii tell us about Roman art?
The preserved architecture in Pompeii, from public buildings to private homes, allows us to understand Roman architectural styles, construction techniques, and the use of space in urban planning.
Why is Pompeii considered a ‘time capsule’ of Roman art?
Pompeii is often called a ‘time capsule’ because the volcanic ash from Mount Vesuvius preserved the city and its art just as they were in 79 AD. This offers a snapshot of Roman life and art at a specific point in history.
What can the art of Pompeii tell us about Roman society and culture?
The art of Pompeii reflects the values, beliefs, and lifestyles of its inhabitants. It depicts subjects from mythology, history, and daily life, revealing aspects of Roman religion, social hierarchy, leisure activities, and more.
How does the art in Pompeii compare to other Roman cities?
While there are similarities between the art in Pompeii and other Roman cities, the exceptional preservation of Pompeii provides a uniquely complete and detailed record of Roman art.
Are there still ongoing discoveries in Pompeii that impact our understanding of Roman art?
Yes, despite centuries of excavations, Pompeii continues to yield new discoveries that refine our understanding of Roman art, its techniques, themes, and cultural context.
Related Questions
What Are The Major Periods In Western Art History?
The major Western art history periods are defined as Prehistoric Art, Ancient Art, Medieval Art, the Renaissance, Mannerism, Baroque, Rococo, Neoclassicism, Romanticism, Realism, Art Nouveau, Impressionism, Post – Impressionism, Fauvism, Expressionism, Cubism, Surrealism, Abstract Expressionism, Op Art, Pop Art, Arte Povera, Minimalism, Conceptual Art and Contemporary Art.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Are The Major Periods In Western Art History?.
The Important Role Of Art Museums In The Art World
An art museum will help to collect and preserve works of art. They also interpret the art and help to educate us all about art. Many art museums will have programs that will allow you to experiment with different types of art. The core role of an art museum is to inspire us about art.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading The Important Role Of Art Museums In The Art World.
Greek And Rome’s Influence On Renaissance Art
The Renaissance, a period of rebirth, was greatly influenced by the classical ancient arts of Greece and Rome. During this period, many Greek and Roman works of art were also rediscovered; this helped rediscover realism, symmetry, and harmony in the arts. Greek and Roman art also influenced the subject matter of many of the Renaissance artists.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading about Greek And Rome’s Influence On Renaissance Art.