The Italian Renaissance is a pivotal art movement shaped by many factors that culminated in this extraordinary era.
The Italian Renaissance period is renowned as a significant epoch in art, with numerous elements contributing to its emergence and significance. The Renaissance’s prominence in art history is attributed to various reasons, each crucial in defining this transformative period. Below is a brief and concise history of how the Renaissance began.
Table of Contents
- Why Did The Italian Renaissance Begin? A Deep Dive Into The Roots Of A Cultural Epoch
- Related Questions
Why Did The Italian Renaissance Begin? A Deep Dive Into The Roots Of A Cultural Epoch
- The Renaissance, a term that means ‘rebirth,’ marks a period of profound cultural, artistic, and intellectual awakening in Europe, particularly Italy. This era, transitioning from the Middle Ages to modernity, has been celebrated for its groundbreaking advancements in various fields.
- Understanding the origins of the Renaissance is crucial, as it reveals how a unique confluence of historical circumstances paved the way for this era of extraordinary human achievement.
- This exploration is not just about mapping a timeline; it’s about appreciating the dynamic interplay of social, economic, political, and cultural forces that nurtured the Renaissance spirit.

Historical Context: The Middle Ages
- The Feudal System: The gradual unraveling of feudalism, characterized by a rigid hierarchical structure, set a shift towards a more fluid social and economic system in motion. This transformation was crucial for developing a societal framework supporting Renaissance ideals.
- The Crusades: These military campaigns were more than just religious wars; they connected the Western world to the East’s riches, knowledge, and ideas. The influx of Eastern goods and philosophies stimulated an appetite for European exploration and discovery.
- Conclusion: The Middle Ages, often viewed as a period of stagnation, ironically sowed the seeds for the Renaissance through social evolution and cross-cultural interactions.

Economic And Social Foundations
- The Growth of City-States in Italy: Italy’s city-states, such as Florence, Venice, and Milan, emerged as thriving centers of trade and commerce. Their wealth and independence created an environment where arts and new ideas could prosper without feudal constraints.
- The Rise of the Merchant Class: This emerging class, enriched by trade, sought to demonstrate their status through wealth and cultural patronage. Their investment in the arts was a significant driver for the Renaissance.
- The Black Death: The Black Death’s sweeping impact led to a drastic reduction in the population, resulting in labor shortages, higher wages, and a challenged status quo. This upheaval created conditions where new ideas could take root.
- Conclusion: Economic prosperity and social upheaval in Italy laid the groundwork for a fertile environment where the Renaissance could flourish.

Cultural And Intellectual Precursors
- Classical Antiquity’s Rediscovery: The reawakening interest in Greek and Roman culture and philosophy provided a treasure trove of inspiration for Renaissance thinkers and artists. This revival led to a new appreciation for humanist principles.
- Humanism: This philosophical stance puts a premium on human values and potential, leading to a shift from theocentric (God-centered) to anthropocentric (human-centered) perspectives in art and science.
- The Byzantine Influence: The fall of Constantinople in 1453 and the resulting exodus of Greek scholars to Italy brought a wealth of classical knowledge, further fueling the Renaissance’s intellectual hunger.
- Conclusion: The rediscovery and infusion of classical and humanist ideas were central to the cultural and intellectual bloom of the Renaissance.
Artistic Developments
- Technological Innovations: Technological advancements in art, such as perspective, oil paints, and anatomical studies, revolutionized how artists depicted the world, leading to more realistic and expressive works.
- Patronage System: The support of influential patrons, like the Medici family in Florence, was vital in empowering artists to pursue their creative visions. This patronage was a cornerstone for many of the era’s artistic achievements.
- Conclusion: Artistic innovation, supported by patronage, was a vital component of the Renaissance, leading to some of the most enduring works of Western art.

Political And Religious Factors
- Papal Influence: The Papacy played a dual role as a religious authority and a significant patron of the arts. This dual role significantly influenced the cultural and artistic landscape of the time.
- Decline of Church Authority: The weakening of the Catholic Church’s authority, exemplified by events like the Avignon Papacy and the Great Schism, allowed for the growth of secular ideas and a more human-centered worldview.
- Conclusion: The shifting political and religious landscape provided an opening for Renaissance ideas to emerge and flourish.
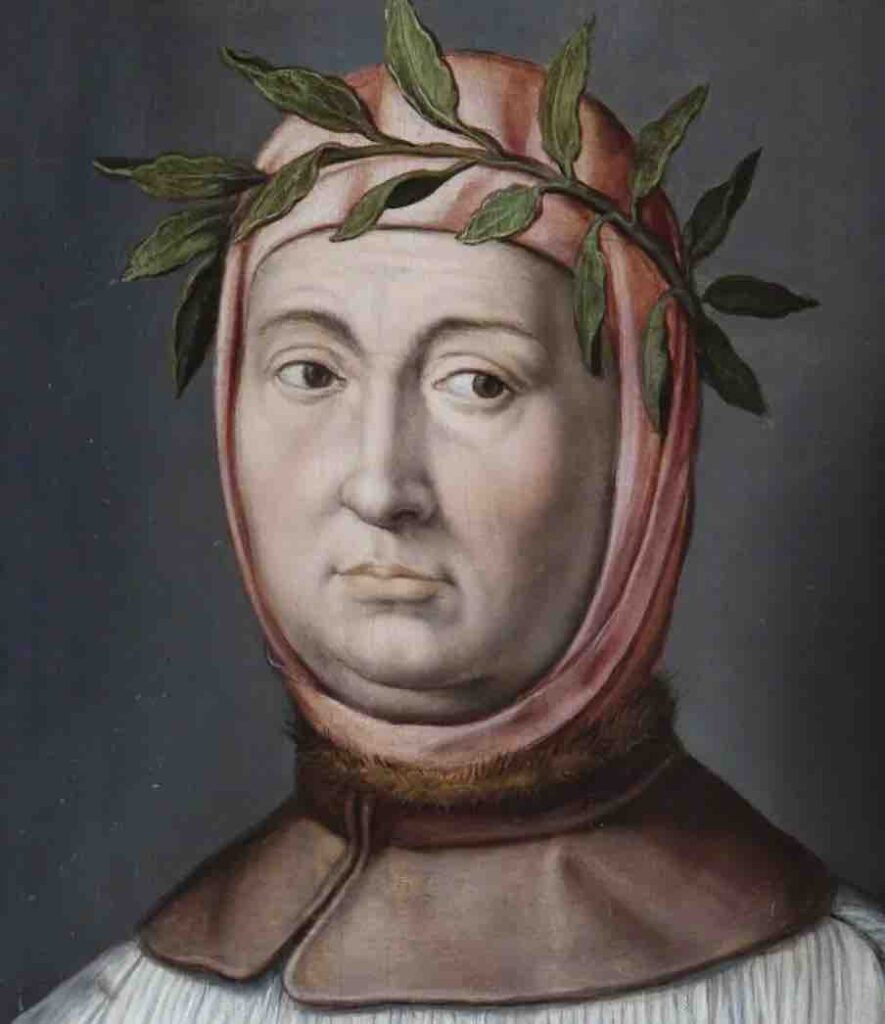

Renaissance Precursors And Thinkers
- Petrarch: Often referred to as the ‘Father of Humanism,’ Petrarch’s works laid the groundwork for Renaissance humanism, inspiring a shift towards classical learning and individual expression.
- Giotto: As a precursor to Renaissance art, Giotto’s move towards realism and away from the Byzantine style heralded the artistic transformations of the Renaissance.
- Conclusion: Early thinkers and artists like Petrarch and Giotto set the intellectual and aesthetic tone defining the Renaissance.
The Spread Of Ideas
- The Printing Press: The invention of the printing press by Gutenberg around 1440 was revolutionary, allowing ideas to be disseminated more widely and quickly than ever before, spreading Renaissance thought across Europe.
- The Role of Universities: The burgeoning of universities and the reform in education they underwent played a crucial role in fostering and disseminating Renaissance humanism and scientific inquiry.
- Conclusion: The spread of ideas through new technology and educational reform was instrumental in extending the influence of the Renaissance beyond Italy’s borders.
The Italian Renaissance was not an isolated phenomenon; it resulted from a complex interplay of historical forces. Economic growth, social change, intellectual curiosity, and artistic expression converged to create unparalleled creativity and innovation.
The legacy of the Renaissance is still evident today, not only in the arts and literature but in the very fabric of Western thought and values.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you want to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you anytime. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend just 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Related Questions
Where Did The Renaissance Begin? Why It Was Essential
The Renaissance began in Florence, Italy in the 14th Century. Florence was essential for the Renaissance because of its location, wealth, and many other factors. As we explore the Renaissance and Florence, this vital movement started.
You can read more by reading our blog, Where Did The Renaissance Begin? Why It Was Essential by clicking here.
Italy – Renaissance Art Defined And Explored
Originating in Florence, Italy, the Italian Renaissance is pivotal in shaping this transformative era, laying the artistic foundations we continue to admire today. Celebrated for its revival of classical ideals and introduction of innovative artistic techniques, the period also stands as a staunch advocate of humanistic values. Join us as we delve deeper into this fascinating Italian Renaissance art history chapter.
By clicking here, you can discover more by reading Italy – Renaissance Art Defined And Explored.
24 Important Artworks Of The Renaissance
The Renaissance period is indispensable for anyone delving into art history. The era stands as one of the most pivotal and transformative phases in the artistic landscape, characterized by a profound reawakening of classical ideals, unprecedented innovation in techniques, and a focus on human experience and emotion.
You can learn more by reading 24 Important Artworks Of The Renaissance by clicking here.