The Renaissance period in Italy was a time of great cultural and artistic growth, spanning from the 14th to the 17th century. It was a pivotal era characterized by significant advancements in art, science, literature, and philosophy.
It is interesting to explore the world in Italy during the Renaissance era. The Renaissance produced three significant artists, including the iconic figures of the time: Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael. For all those that lived in Italy, the influence of the Catholic Church could be felt with other cultural and social norms prevalent during this extraordinary era.
Table of Contents
- Life In Renaissance Italy – What Life Was Like During The Renaissance Era
- The Power Of The Catholic Church During The Renaissance Era
- Cultural And Social Norms During The Renaissance
- Related Questions
Life In Renaissance Italy – What Life Was Like During The Renaissance Era
Renaissance Italy was a busy period marked by thriving city-states such as Florence, Venice, and Rome. These commerce and intellectual exchange centers provided an ideal environment for artists to flourish.
The wealthy patrons, known as patrons of the arts, commissioned numerous artworks, making it possible for talented artists to pursue their craft. These patrons helped to ensure that the Renaissance became a critical time for the arts.
During the Renaissance, artists enjoyed a higher social standing than other eras. They were often esteemed members of society, receiving support and recognition for their contributions.
The artists during the Renaissance had the opportunity to engage with influential figures, exchanging ideas and collaborating on grand projects. The Renaissance was a great time to be an artist.
The role of artists expanded beyond the realm of painting and sculpture in the Renaissance. The artists were also considered intellectuals, exploring various disciplines, including anatomy, architecture, engineering, and military technology.
This interdisciplinary approach allowed artists to transcend traditional boundaries and develop innovative ideas.
Leonardo da Vinci: The Renaissance Polymath And The Renaissance Man
Leonardo da Vinci, born in 1452 in Vinci, near Florence, epitomized the Renaissance ideal of the “universal man.” That is why even today, Leonardo da Vinci is often called the Renaissance man,
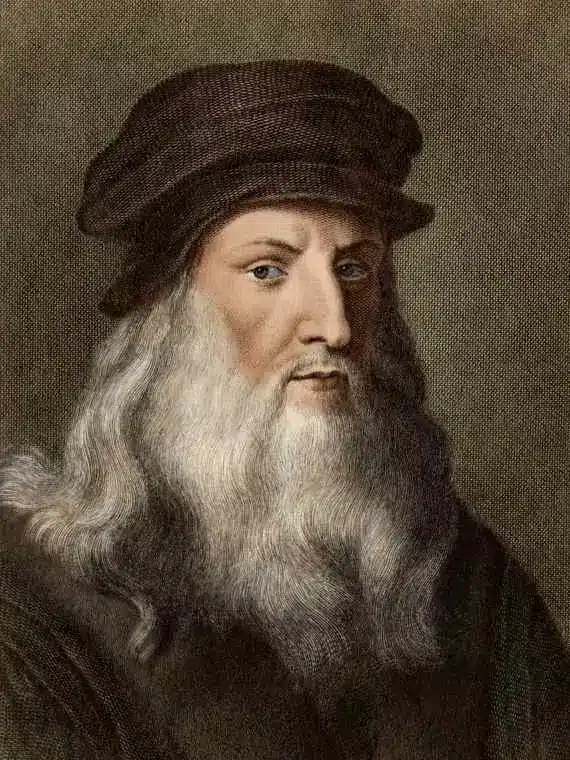

Da Vinci’s insatiable curiosity led him to excel in various fields, including painting, sculpture, architecture, anatomy, engineering, and scientific research. Leonardo’s keen observation and meticulous attention to detail were reflected in his artworks, such as the iconic “Mona Lisa” and “The Last Supper.”
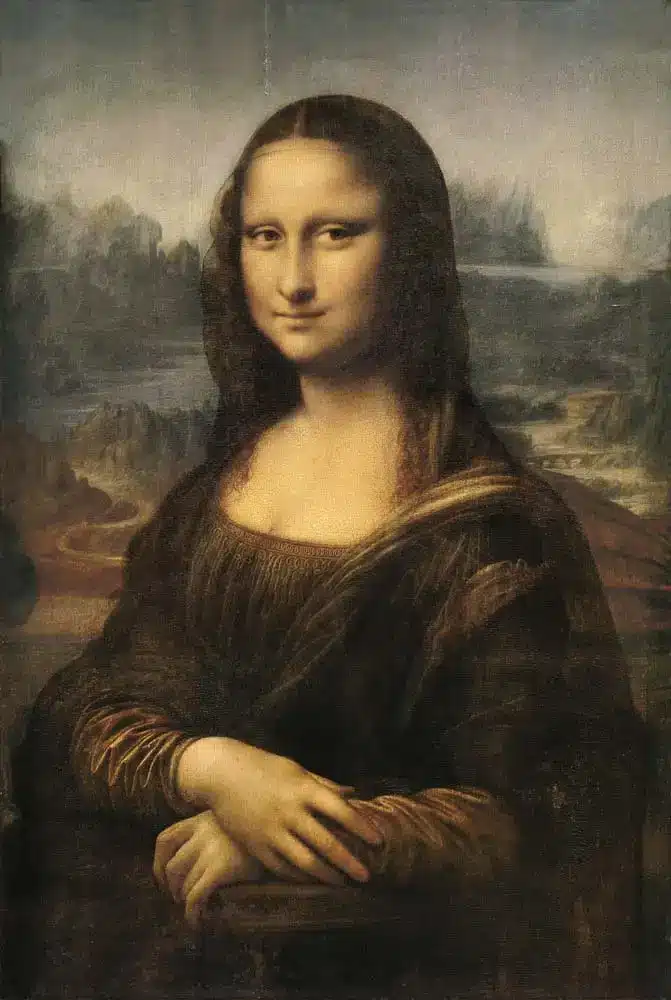


Leonardo struggled to complete many of his projects despite his wide range of talents. He often became absorbed in his quest for knowledge and would abandon works or leave them unfinished.
This characteristic, however, did not diminish his influence. His innovative techniques, such as sfumato (the delicate blending of colors and tones), revolutionized the art world and became synonymous with the Renaissance style.
Michelangelo: The Master Of Sculpture And Frescoes
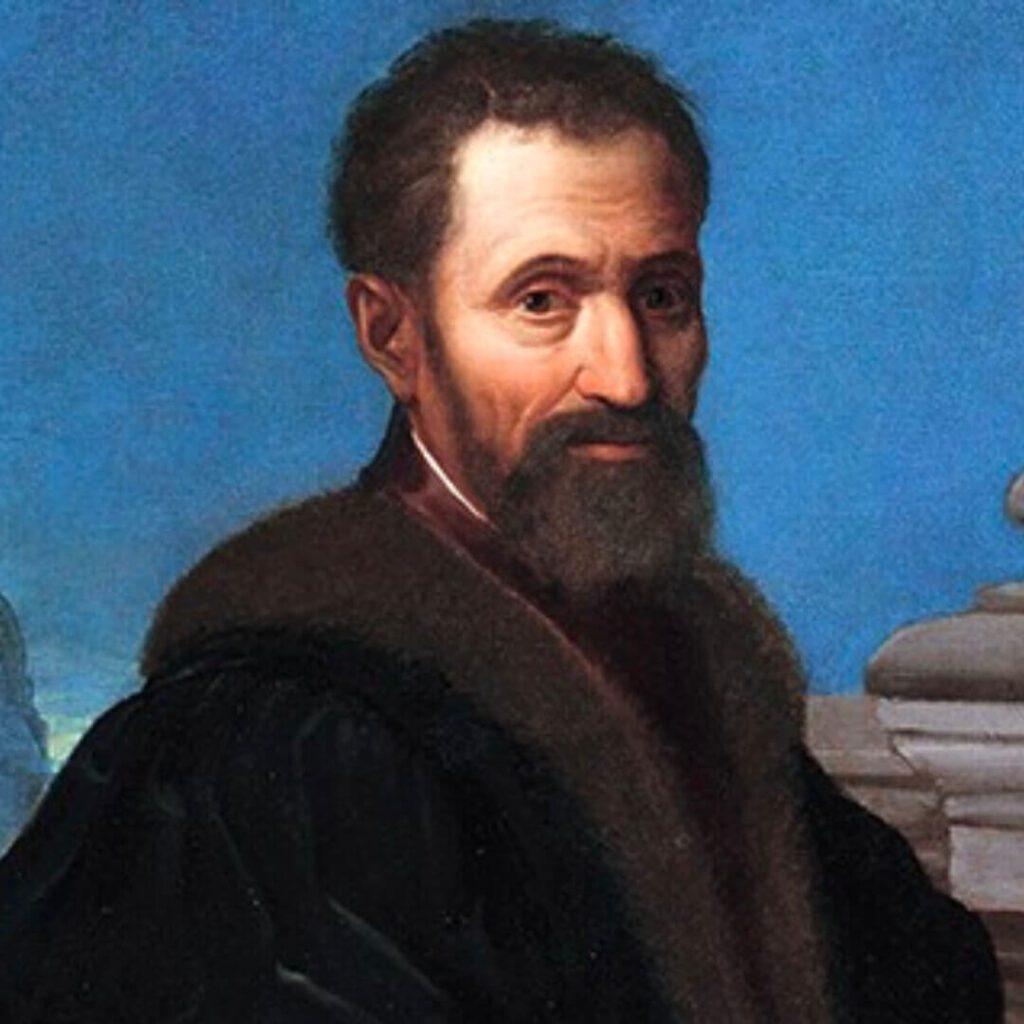

Michelangelo Buonarroti, born in 1475 in Caprese, displayed an exceptional talent for sculpture from a young age. His awe-inspiring works, including the renowned statue of David and the breathtaking ceiling of the Sistine Chapel, firmly established his reputation as one of the Renaissance’s greatest artists.
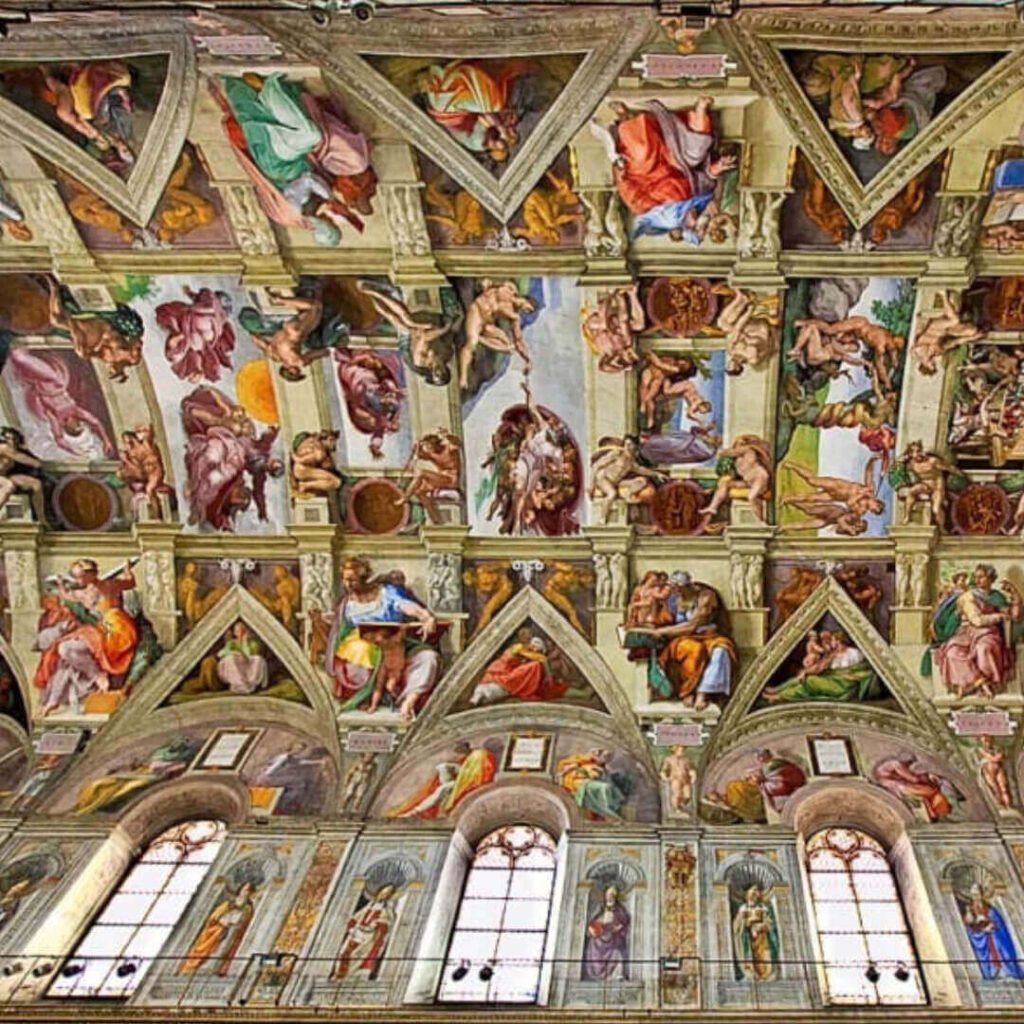
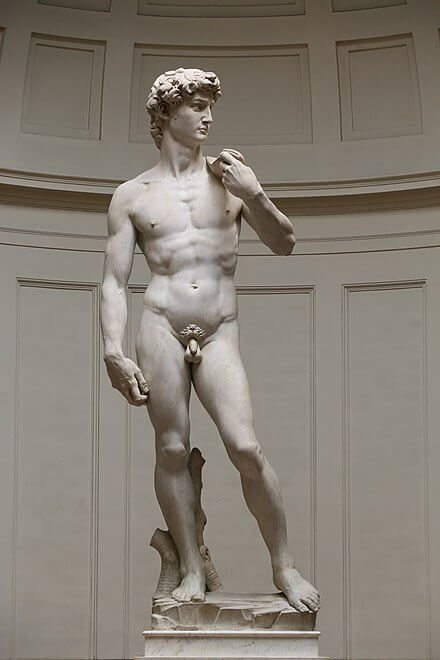


Michelangelo’s immense skill in capturing and imbuing the human form with emotion elevated his sculptures to unprecedented realism. His contributions to architecture, notably the design of St. Peter’s Basilica in Rome, further cemented his status as a visionary artist.
Raphael: The Master Of Harmony And Beauty

Raphael Sanzio, born in 1483 in Urbino, was celebrated for his ability to infuse his works with a sense of harmony and beauty. His paintings, characterized by their graceful figures, serene expressions, and vibrant colors, captured the essence of the Renaissance spirit.
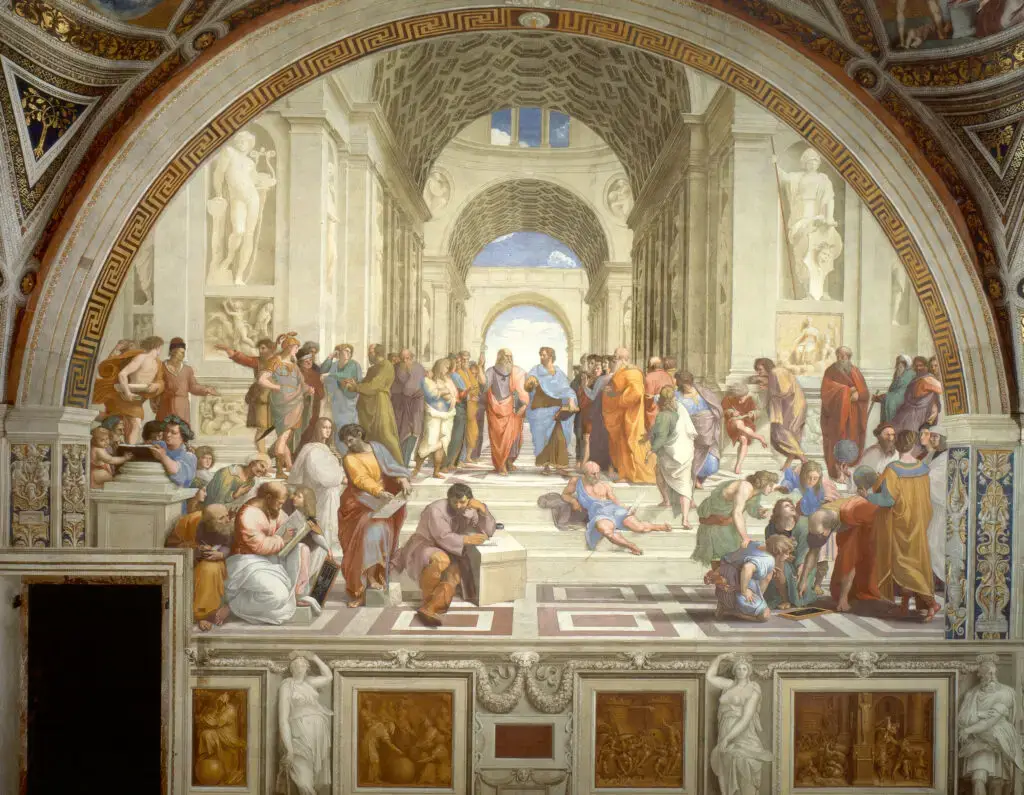
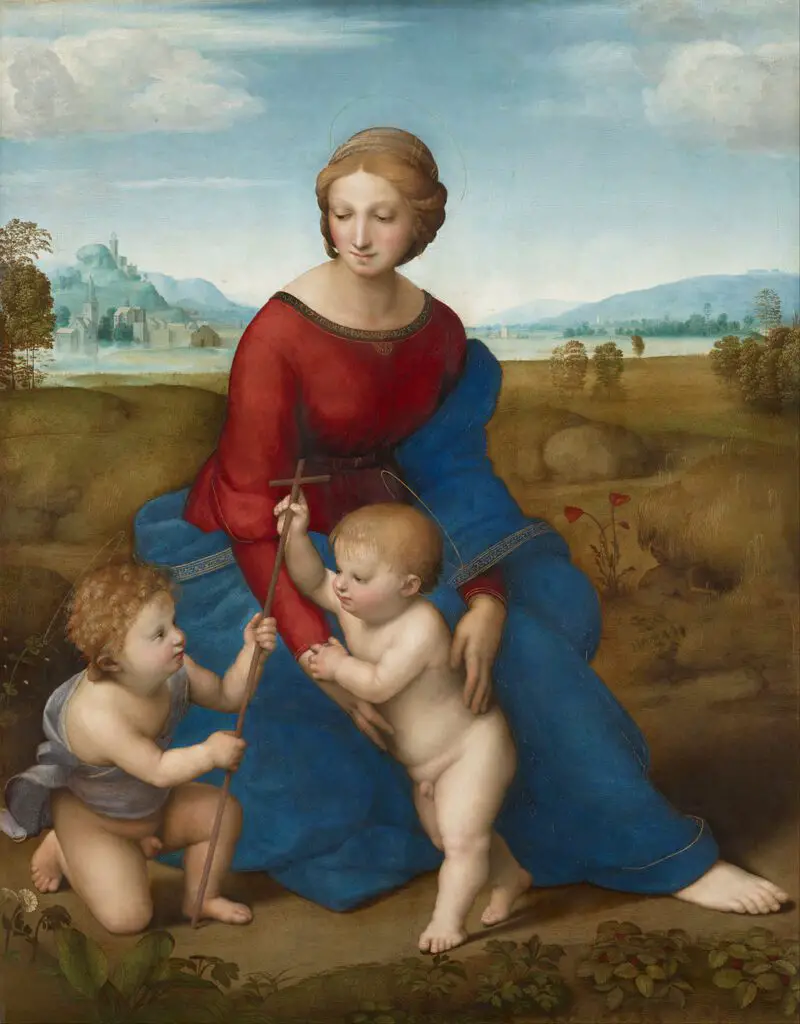


Raphael’s most famous works, such as “The School of Athens” and “Madonna of the Meadow,” exemplify his exceptional talent for composition and portraying human emotions. His artistry greatly influenced subsequent painters, and his legacy remains integral to art history.
The Power Of The Catholic Church During The Renaissance Era
During the Renaissance, the Catholic Church held immense power and influence over Italy’s cultural, social, and political landscape. The Church was central in commissioning artworks, particularly in Rome and Florence, where the Papal Court and influential families provided substantial support.
Artists often received commissions from the Church to create religious-themed artworks, such as altarpieces, frescoes, and sculptures. These artworks adorned churches, cathedrals, and other religious buildings, serving to communicate the teachings of the Church and evoke devotion among the faithful.

The Catholic Church also controlled artistic expression, imposing specific guidelines and restrictions. The Council of Trent, held between 1545 and 1563, sought to address the issues raised by the Protestant Reformation and reaffirm the Church’s authority.
As a result, there was a shift towards more conservative and didactic art, emphasizing the clarity of religious imagery and avoiding excessive ornamentation.
Despite these influences of the Catholic Church, artists such as Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael could navigate the Church’s demands while still expressing their creative genius. They incorporated religious themes into their works and brought forth their unique artistic styles and interpretations, contributing to the development of Renaissance art.
Cultural And Social Norms During The Renaissance

Beyond the influence of the Catholic Church, Renaissance Italy was characterized by a distinctive set of cultural and social norms.
Humanism, a philosophical and intellectual movement that focused on human potential and the study of classical antiquity, greatly impacted the cultural atmosphere of the time. The Renaissance humanists valued education, knowledge, and the pursuit of individual excellence.
They believed in the importance of a well-rounded education encompassing the liberal arts, sciences, and humanities. This emphasis on education led to establishment of humanist schools and academies, which fostered intellectual growth and exchanging ideas.
Society was organized into hierarchical structures, with the aristocracy and wealthy merchant classes occupying the highest positions. Artists, while enjoying higher social status, were still subject to the patronage system, relying on the financial support of the elite for their livelihood.
For instance, the Medici family of Florence played a significant role as patrons of the arts, supporting numerous artists and scholars.
During the Renaissance, we also witnessed scientific advancements, with figures such as Galileo Galilei and Nicolaus Copernicus challenging traditional beliefs and paving the way for the scientific revolution. The study of anatomy, fueled by the curiosity of artists like Leonardo da Vinci, contributed to breakthroughs in understanding the human body.
Moreover, the Renaissance saw the rise of independent city-states with distinct cultures and political structures. This fostered competition and rivalry between city-states, leading to an atmosphere of artistic innovation and progress. Artists often sought to outdo each other, resulting in a vibrant art scene and the creation of iconic masterpieces.
The Renaissance in Italy was a transformative period characterized by remarkable artistic achievements and cultural advancement. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael left an indelible mark on the world of art, and their masterpieces continue to inspire and captivate audiences today.
The Catholic Church held significant power during this era, commissioning and influencing artistic expression. However, artists balanced religious themes with their artistic visions, pushing the boundaries of creativity and leaving an enduring legacy.
The cultural and social norms of the time, including the influence of humanism, the patronage system, and the pursuit of knowledge, shaped the Renaissance in Italy into a period of intellectual and artistic reawakening. It was a time when artists thrived, society flourished, and the foundations for modern Western civilization were laid.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you want to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel filled with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend just 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Related Questions
What Was The Focus Of Renaissance Art?
The focus of Renaissance art was on the classics of Greek and Rome, humanist philosophy, and the study of the human figure. Realism was also an essential part of renaissance art. The great artists of the Renaissance also became great anatomists and studied human beings.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Was The Focus Of Renaissance Art?.
What Is The Importance Of Art From The Renaissance Period?
Renaissance art is essential as it was a time of rebirth and discovery. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael were at the forefront of that change, creation, and discovery. Renaissance art has influenced art and artists for many centuries and continues to influence artists today.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Is The Importance Of Art From The Renaissance Period?.
Early Renaissance Vs. High Renaissance Art Explained
Early Renaissance and High Renaissance are both periods of the art of the Renaissance era. The entire Renaissance era shared a lot of the same characteristics. The High Renaissance was dominated by three major artists: Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Early Renaissance Vs. High Renaissance Art Explained.