Art is an intrinsic part of human history, serving as a mirror to our evolution, culture, and societal transformations.
To truly understand art, we need to look at the primitive cave paintings of early civilizations and the avant-garde masterpieces of the modern era. This helps us see that art has continually evolved, reflecting humanity’s creative ingenuity and the socio-political landscape of its time. This journey through art history showcases the evolution of creativity and highlights art’s enduring influence on society and culture.
Table of Contents
- The Dawn of Creativity: Prehistoric Art
- The Rise of Civilizations: Ancient Art
- The Middle Ages: Spirituality and Symbolism
- The Renaissance: Rebirth of Creativity
- The Baroque and Rococo Eras: Drama and Ornamentation
- The Age of Revolution: Neoclassicism and Romanticism
- Modern Art Movements: Breaking Boundaries
- Contemporary Art: Diversity and Innovation
- The Enduring Influence of Art
- Art: A Timeless Journey
- Related Questions
Read on as we explore the milestones of artistic evolution, delving into key periods and styles and their significance.
The Dawn of Creativity: Prehistoric Art
The story of art began over 40,000 years ago with the earliest known examples of human creativity—prehistoric cave paintings. Found in caves like Lascaux in France and Altamira in Spain, these paintings primarily depicted horses, bison, and deer. Crafted with natural pigments, they revealed a deep connection to nature and a desire to communicate visually.
Significance
Prehistoric art wasn’t merely decorative; it held spiritual and functional significance. Many researchers believe these paintings served as rituals for successful hunts or as expressions of awe for nature. They reveal early humans’ need to document their experiences and beliefs, laying the foundation for art as a storytelling medium.
Legacy
These early works remind us of art’s primal roots, proving that creativity is a fundamental human trait. The use of natural materials and the depiction of life remain timeless themes in art.
The Rise of Civilizations: Ancient Art
As societies developed, so did their artistic expressions. Ancient Egyptian, Mesopotamian, Greek, and Roman art became more complex, reflecting societal hierarchies, religious practices, and technological advancements.
Egyptian Art
Egyptian art, characterized by a strong connection to religion, often depicted gods, pharaohs, and the afterlife. Hieroglyphics combined language and visual art, demonstrating an advanced understanding of communication. Monumental works like the Pyramids of Giza and the Sphinx still awe modern audiences.
Greek and Roman Art
Greek art introduced the world to idealized forms and realistic human anatomy, as seen in sculptures like the Venus de Milo and Discobolus. Roman art expanded on Greek ideals, blending functionality and beauty in architectural marvels like the Colosseum and intricate mosaics.
Significance
Ancient art symbolizes humanity’s ability to harness creativity for religious, cultural, and functional purposes. These works highlight early advancements in techniques such as perspective and proportion, which continue to influence modern art.
The Middle Ages: Spirituality and Symbolism
During the Middle Ages (5th to 15th centuries), art was deeply tied to religion, particularly Christianity. The Byzantine, Romanesque, and Gothic periods saw the rise of religious iconography, cathedrals, and illuminated manuscripts.
Byzantine Art
Known for its gold mosaics and stylized figures, Byzantine art prioritized spirituality over realism. Churches like the Hagia Sophia became masterpieces of both art and architecture.
Gothic Art
The Gothic period introduced innovations like stained glass windows and flying buttresses. Cathedrals such as Notre Dame in Paris were adorned with intricate sculptures and vivid glasswork, reflecting humanity’s devotion to the divine.
Significance
Medieval art focused on conveying spiritual truths rather than realism, reminding us of art’s power to inspire faith and community.
The Renaissance: Rebirth of Creativity
The Renaissance (14th to 17th centuries) marked a monumental shift in art history as Europe experienced a cultural awakening. This period celebrated humanism, science, and the rediscovery of classical antiquity.
Key Figures
Leonardo da Vinci:
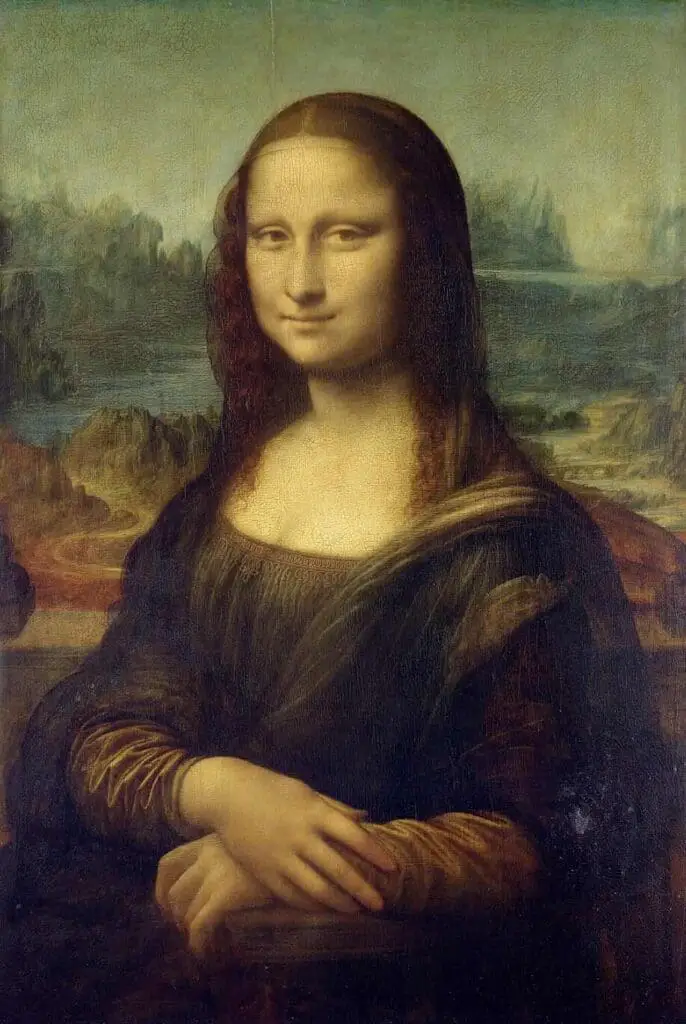

His masterpiece, the Mona Lisa, remains an iconic symbol of Renaissance innovation, blending realism and emotion.
Michelangelo:
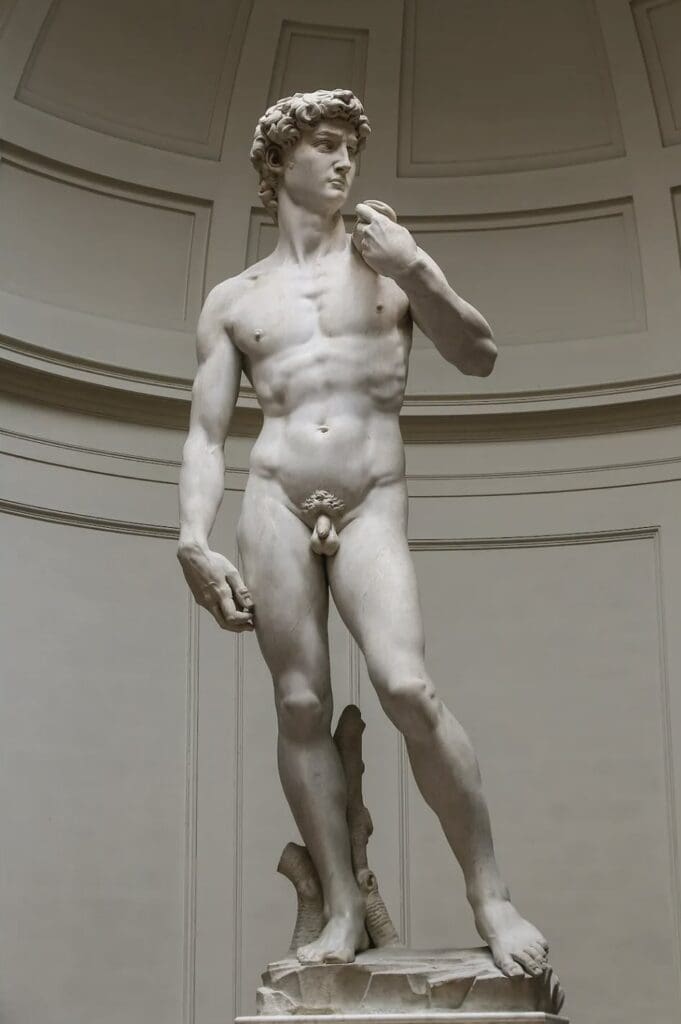

Renowned for his sculptures (David) and the Sistine Chapel ceiling, Michelangelo showcased the heights of human creativity.
Raphael:
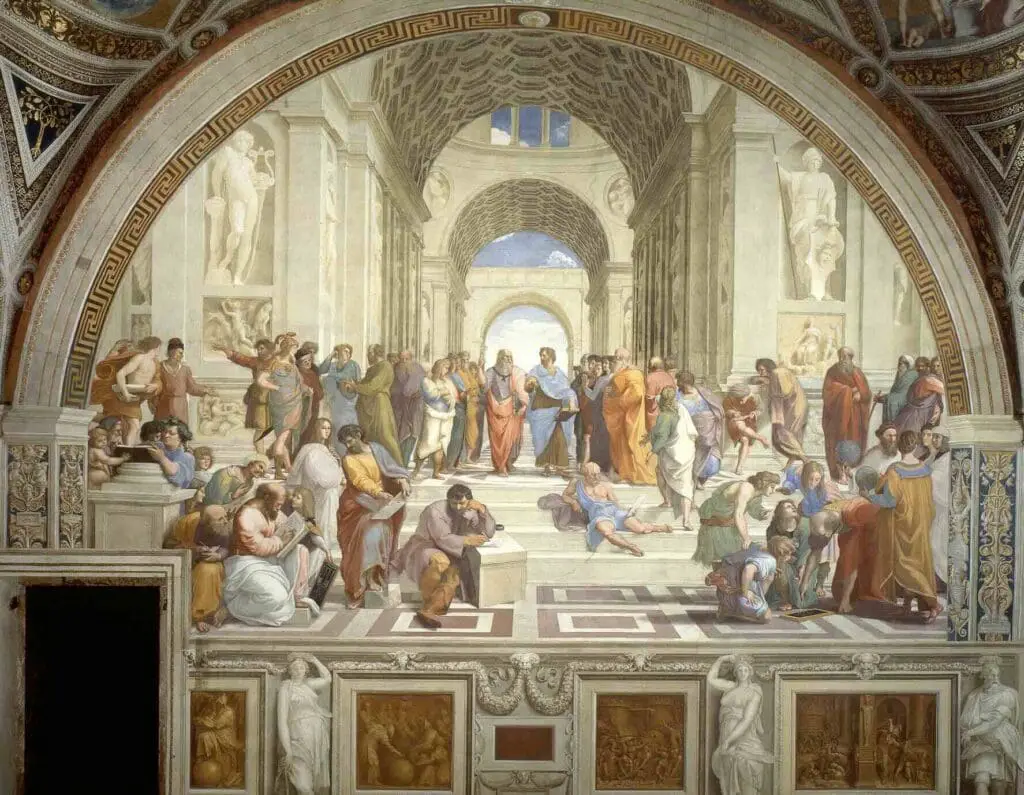

It is known for harmonious compositions like The School of Athens, which celebrated knowledge and philosophy.
Innovations
The Renaissance introduced techniques such as linear perspective, chiaroscuro (light and shadow), and anatomical accuracy, revolutionizing how artists depicted the world.
Significance
The Renaissance underscores art’s transformative power during cultural and intellectual advancement. It laid the groundwork for future movements, proving that art thrives when creativity and knowledge intersect.
The Baroque and Rococo Eras: Drama and Ornamentation
Following the Renaissance, the Baroque (17th century) and Rococo (18th century) periods brought drama, emotion, and extravagance to the forefront.
Baroque Art
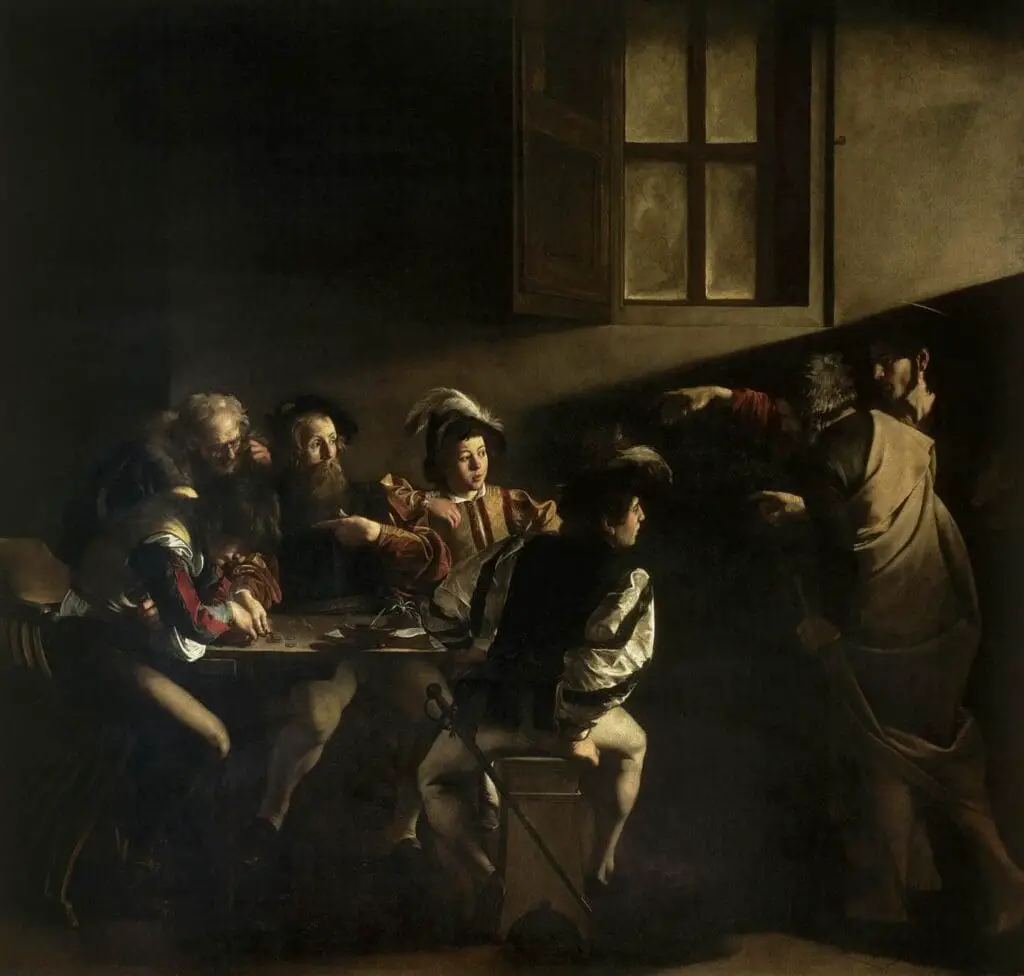

Baroque art was characterized by grandeur and intensity. It often featured dynamic compositions, dramatic lighting, and emotional depth. Works like Caravaggio’s The Calling of Saint Matthew and Bernini’s Ecstasy of Saint Teresa exemplify this period’s theatricality.
Rococo Art
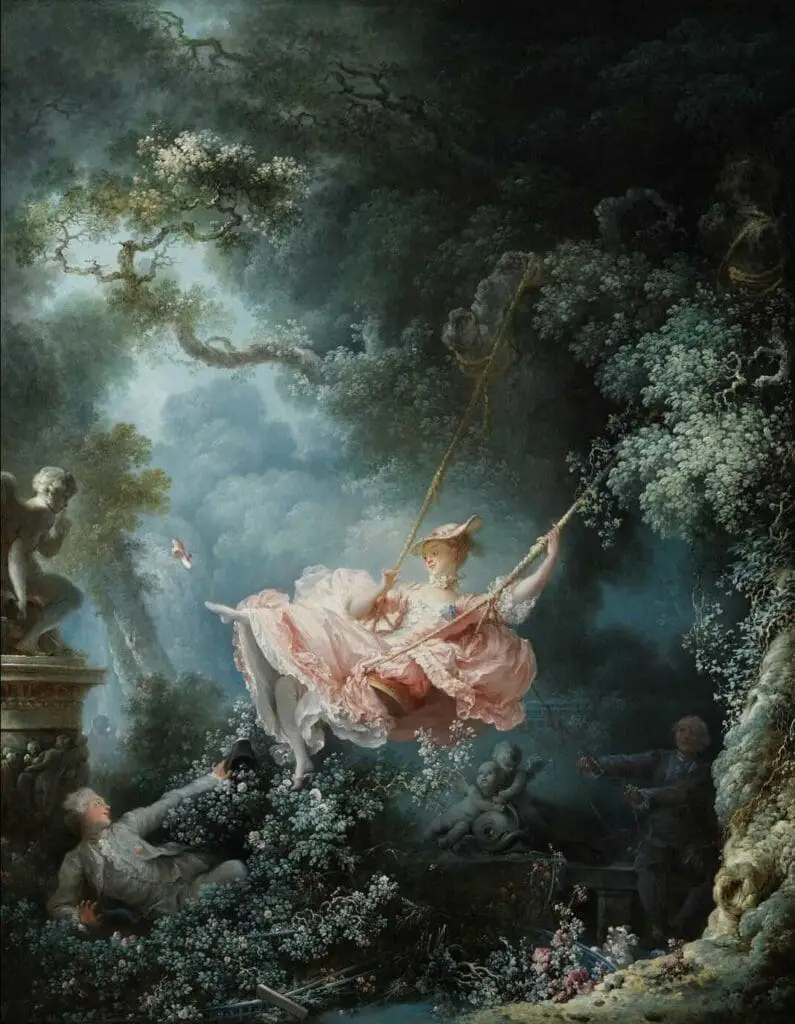

In contrast, Rococo art embraced lightness, playfulness, and decorative detail. Artists like Fragonard and Boucher painted idyllic scenes of leisure and romance, such as The Swing.
Significance
These periods reflect art’s adaptability, shifting between bold statements and lighthearted elegance to suit cultural tastes.
The Age of Revolution: Neoclassicism and Romanticism
The late 18th and early 19th centuries saw political revolutions mirrored by artistic transformations. Neoclassicism and Romanticism emerged as responses to societal change.
Neoclassicism
Inspired by classical antiquity, Neoclassicism emphasized order, simplicity, and patriotism. Artists like Jacques-Louis David painted works like The Death of Socrates, evoking moral ideals and revolutionary fervor.
Romanticism
Romantic art, in contrast, celebrated emotion, nature, and the sublime. Turner’s landscapes and Delacroix’s Liberty Leading the People encapsulate the movement’s focus on human passion and the power of nature.
Significance
These movements highlight art’s ability to reflect and influence societal change, capturing the spirit of revolution and individuality.
Modern Art Movements: Breaking Boundaries
The 19th and 20th centuries marked a period of unprecedented experimentation. Modern art shattered traditional norms, exploring new techniques, perspectives, and subjects.
Impressionism
Pioneered by artists like Claude Monet and Edgar Degas, Impressionism emphasized light, color, and movement. Works like Impressionism and Sunrise revolutionized art by prioritizing emotion over detail.
Expressionism
Artists like Edvard Munch (The Scream) explored raw emotion, using bold colors and distorted forms to convey psychological depth.
Cubism
Cubism, led by Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque, deconstructed objects into geometric shapes, challenging viewers to see the world differently.
Surrealism
Surrealists like Salvador Dalí (The Persistence of Memory) delved into the subconscious, creating dreamlike, thought-provoking imagery.
Abstract Art
Abstract artists like Wassily Kandinsky rejected realism entirely, focusing on color, form, and emotion to evoke meaning.
Significance
Modern art movements represent a turning point in art history. They emphasize individual expression and challenge traditional boundaries, reminding us that art is a constantly evolving dialogue.
Contemporary Art: Diversity and Innovation
Art continues to evolve today, embracing new mediums, technologies, and perspectives. Contemporary art reflects the complexities of modern society, tackling issues such as identity, politics, and climate change.
Key Trends
- Digital Art: Tools like AI and VR have opened new creative frontiers.
- Street Art: Artists like Banksy have redefined art as a form of activism and public engagement.
- Globalization: Artists from diverse backgrounds bring fresh perspectives to the global stage.
Significance
Contemporary art showcases the limitless possibilities of creativity, proving that art remains a vital part of human expression and innovation.
The Enduring Influence of Art
From cave paintings to modern masterpieces, the evolution of art reflects humanity’s journey through time. Each period, movement, and artist has contributed to a rich tapestry of creativity that continues to inspire and influence society.
Why It Matters
- Connection: Art connects us to our shared history, helping us understand the experiences and values of those who came before us.
- Inspiration: Creativity inspires innovation, encouraging us to think beyond conventional boundaries.
- Expression: Art remains a powerful tool for expressing identity, emotion, and ideas.
Art: A Timeless Journey
The evolution of art is a testament to humanity’s boundless creativity and resilience. From prehistoric cave paintings to today’s digital art, each era has left its mark, enriching our understanding of the world and ourselves.
As we continue to create, innovate, and explore, the legacy of art reminds us that creativity reflects who we are and guides us to who we can become. Art’s journey is far from over—it evolves with us, inspiring future generations to imagine, dream, and shape the world anew.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you want to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you anytime. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend just 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Related Questions
Vincent Van Gogh Is Known For His Art And Life
He is one of the world’s most renowned and celebrated artists today. Van Gogh’s legacy is defined not only by his captivating artwork but also by his extraordinary skill and passion for executing every brushstroke. Join us as we delve deeper into the world of this remarkable artist and unravel the reasons behind his enduring fame and the profound impact of his artistry.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Vincent Van Gogh Is Known For His Art And Life.
Vincent Van Gogh Roses 1889 And Flower Paintings
Vincent Van Gogh had a profound affinity for painting flowers, and one of his notable works in this genre is titled “Roses.” Join us as we delve into the enchanting world of his “Roses” painting and uncover the eight compelling reasons that fueled his passion for painting flowers.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Vincent Van Gogh Roses 1889 And Flower Paintings.
Vincent Van Gogh – The Langlois Bridge – 1888
While some of his works, like “The Langlois Bridge – 1888,” may be lesser-known than many other Van Gogh paintings, the painting offers a unique perspective into van Gogh’s life during a pivotal period. This artwork provides a glimpse into his surroundings during a crucial juncture in his artistic journey. Read on as we delve deeper into this painting to better understand the world Van Gogh was showing us with this artwork.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Vincent Van Gogh – The Langlois Bridge – 1888.