One of the significant movements of art is the Neoclassicism movement, yet it is a movement that is not talked about as much as other art movements.
Neoclassicism, or Classicism, emerged as a significant artistic movement in the 18th century in response to the ornate and frivolous Rococo style. It drew inspiration from the art and culture of ancient Greece and Rome, emphasizing simple linear design and archaeologically accurate depictions of Classical themes. With its focus on harmony, clarity, restraint, universality, and idealism, Neoclassicism left an indelible mark on the visual arts.
Table of Contents
- Neoclassicism: A Harmonious Revival Of Ancient Art
- Legacy And Significance Of Neoclassicism Art Explored
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Related Questions
Neoclassicism: A Harmonious Revival Of Ancient Art
Neoclassicism, also called Classicism, arose during the 18th century as a notable artistic movement in direct contrast to the ornate and extravagant Rococo style. This new artistic approach found its inspiration in the rich art and cultural heritage of ancient Greece and Rome.
Neoclassical artists sought to create works that embodied the austere beauty of antiquity, placing great importance on precise and linear designs while meticulously depicting Classical themes with archaeological accuracy. The movement’s fundamental principles of harmony, clarity, restraint, universality, and idealism have profoundly influenced the visual arts.
Read on as we explore Neoclassical art’s origins, influences, and characteristics and its lasting legacy.
Origins And Influences Of Neoclassicism
Neoclassicism originates from two significant factors: a reaction against the lavish Rococo style and a renewed interest in the art of antiquity. The Rococo period, which dominated European art from the 1720s, was characterized by its sensual and decorative nature.
Seeking a departure from this indulgent style, artists and intellectuals turned their attention to the classical world, driven by a growing fascination with the ancient Greek and Roman civilizations.
Archaeological discoveries played a crucial role in fueling this renewed interest. The excavation of the buried Roman cities of Herculaneum and Pompeii, beginning in the mid-18th century, provided artists and scholars with a wealth of artifacts and insights into the ancient world.
Alongside these discoveries, influential publications by figures such as Bernard de Montfaucon, Giovanni Battista Piranesi, the Comte de Caylus, and Robert Wood further stimulated interest in Classical antiquities. Through engravings and detailed descriptions, these publications disseminated knowledge of Roman monuments and artifacts throughout Europe, inspiring artists to explore the Classical past.
Characteristics Of Neoclassical Art
Neoclassical art aimed to capture the essence of ancient Greece and Rome by employing specific stylistic features. Artists of this period favored line over color, using crisp, precise contours to convey a sense of order and clarity.
Straight lines were preferred over curves, creating a formal and disciplined aesthetic. The compositions often employed frontality and closed arrangements, emphasizing balance and symmetry rather than dynamic or diagonal compositions.
Another notable characteristic of Neoclassical art was the preference for the general over the particular. Artists aimed to create images with universal appeal and archetypal significance. By stripping away transitory and individualistic aspects, they sought to depict idealized forms that embodied the timeless ideals of Classical beauty and harmony.
The Influence Of Johann Joachim Winckelmann On Neoclassical Art
German scholar Johann Joachim Winckelmann was one of the most influential figures in shaping Neoclassical art. His writings and theories significantly impacted the artistic and intellectual discourse of the time.
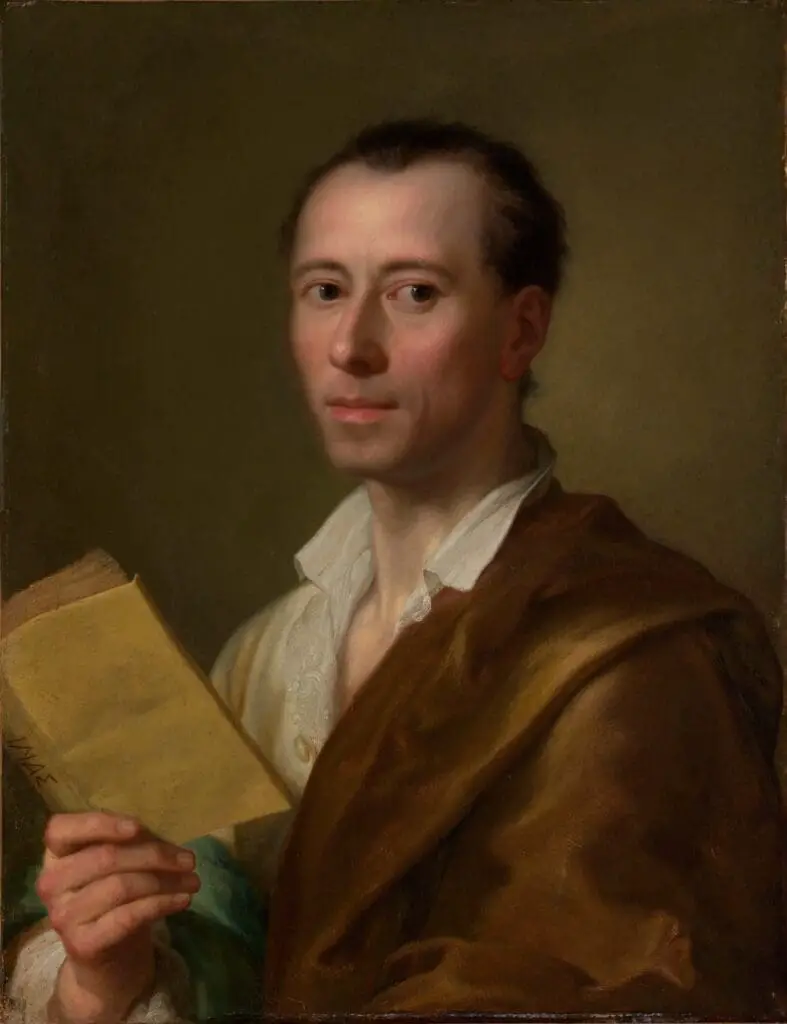

Winckelmann praised Greek sculpture for its “noble simplicity and quiet grandeur” and called upon artists to emulate the style. By imitating Greek art, he believed artists could achieve idealized representations of natural forms devoid of fleeting or distinctive qualities.

According to Winckelmann, such images would possess universal significance, transcending time and cultural boundaries.
Legacy And Significance Of Neoclassicism Art Explored
Neoclassicism left an enduring legacy in the world of art. It profoundly influenced the visual arts, architecture, literature, and politics. The movement’s emphasis on rationality, order, and idealized beauty aligned with the intellectual currents of the Enlightenment, which sought to apply reason and logic to all aspects of human existence.
Neoclassicism’s universal aesthetic appealed to the era’s sensibilities, and its visual language became associated with notions of cultural refinement, stability, and moral virtue.
Beyond the 18th and 19th centuries, Neoclassicism continued influencing subsequent artistic movements and styles. Its emphasis on structure, clarity, and timeless beauty resonated with artists throughout the 20th century and beyond.
Neoclassical elements can be observed in various art forms, including painting, sculpture, architecture, and contemporary design.
In the realm of painting, Neoclassicism’s legacy can be seen in the works of renowned artists such as Jacques-Louis David, Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres, and Antonio Canova. These artists continued to explore Classical themes and ideals, infusing their works with a sense of grandeur and a focus on idealized human figures.
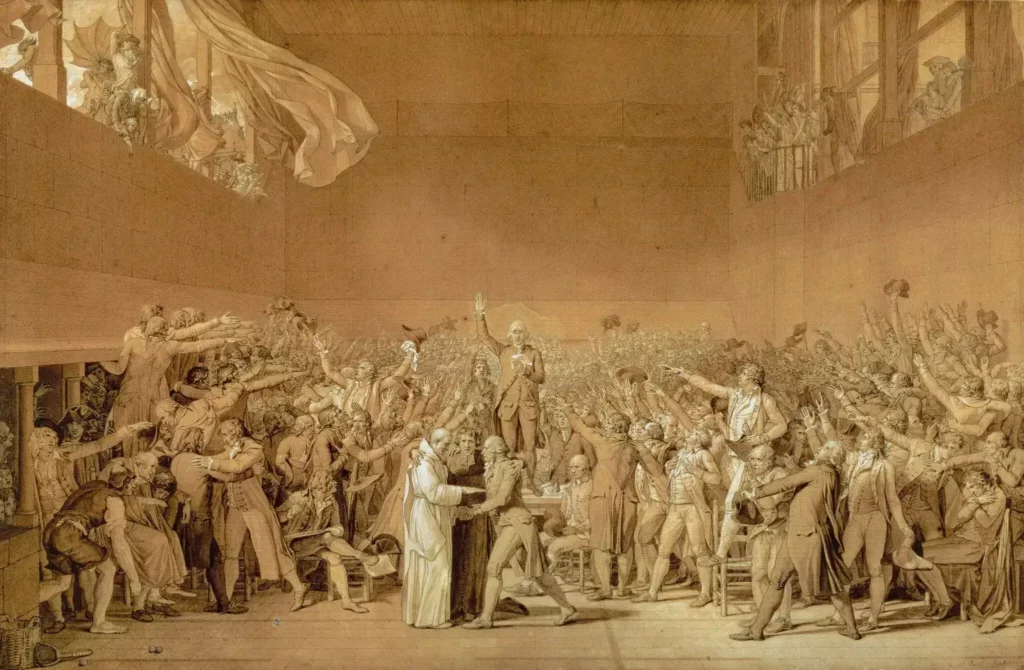


Their paintings often depicted historical or mythological narratives, reflecting the Neoclassical desire to convey moral and intellectual values through art.
Neoclassical architecture also flourished during the 18th and 19th centuries. Architects sought to recreate the grandeur of ancient Greek and Roman structures, using classical orders and proportions to achieve balance and harmony.
Prominent examples of Neoclassical architecture include the works of Andrea Palladio, who drew inspiration from ancient Roman architecture, and the iconic buildings of John Nash in Regency-era England.
Even in the 20th century, Neoclassicism continued to be reinterpreted and incorporated into various artistic movements. The neoclassical revival in the early 20th century, often called “New Classicism,” sought to revive classical art and architecture principles.
Artists like Pablo Picasso and Amedeo Modigliani embraced Neoclassical aesthetics in their works, albeit with a modern twist. Neoclassical art’s simplicity, order, and timeless quality counterbalanced the time’s tumultuous and experimental artistic endeavors.
In contemporary design, echoes of Neoclassical elements can still be found. The use of classical motifs, symmetrical compositions, and clean lines in furniture, interior design, and fashion demonstrates the enduring influence of Neoclassicism.
The pursuit of elegance, balance, and refined aesthetics draws inspiration from the neoclassical principles of order and idealized beauty.
However, it is essential to note that Neoclassicism was not without its criticisms. As a movement that idealized ancient Greece and Rome, it often disregarded other civilizations’ cultural and artistic achievements. Its strict adherence to classical forms and themes sometimes resulted in a lack of innovation and originality.
Additionally, Neoclassicism’s association with political and social conservatism led to its decline in popularity during the 19th century as new artistic movements, such as Romanticism, emerged.
Neoclassicism emerged as a response to the luxury of the Rococo style and a rekindled interest in the art and culture of ancient Greece and Rome. Its emphasis on harmony, clarity, restraint, universality, and idealism resulted in a distinct aesthetic that left an indelible mark on art.
Neoclassicism’s influence extended beyond the 18th and 19th centuries, shaping subsequent artistic movements and styles. Its principles of order, structure, and timeless beauty continue to inspire artists and designers to this day, ensuring that the legacy of Neoclassicism remains relevant and influential in the ever-evolving world of art and aesthetics.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you are interested to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend just 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Neoclassicism in art, and when did it emerge?
Neoclassicism is an artistic movement that emerged in the 18th century as a reaction against the ornate Rococo style. It sought inspiration from the art and culture of ancient Greece and Rome.
How did Neoclassicism differ from the Rococo style that preceded it?
Neoclassicism differed from the Rococo style by embracing simplicity, clarity, and restraint. While Rococo was ornate and decorative, Neoclassicism aimed for a more rational and harmonious approach.
What were the key inspirations for Neoclassical artists?
Neoclassical artists drew inspiration primarily from ancient Greek and Roman art and culture. They admired the ideals of reason, order, and virtue embodied in Classical antiquity.
Who were some notable artists associated with the Neoclassical movement?
Prominent Neoclassical artists include Jacques-Louis David, Antonio Canova, and Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres. These artists played crucial roles in defining and popularizing the Neoclassical aesthetic.
How did Neoclassicism impact architecture during its heyday?
Neoclassical architecture embraced the use of classical orders and design principles. It influenced the construction of public buildings, monuments, and private residences, often conveying a sense of order and dignity.
What were the key characteristics of Neoclassical art?
Neoclassical art is characterized by its emphasis on clarity, simplicity, and idealized forms. Artists aimed to depict subjects with archaeological accuracy, often drawing from classical mythology and history.
In what ways did Neoclassicism reflect the political and intellectual climate of its time?
Neoclassicism was closely tied to the intellectual and political ideals of the Enlightenment. Its emphasis on reason, order, and virtue mirrored the Enlightenment’s focus on rationality and progress.
How did Neoclassical art contribute to the development of academic art institutions?
Neoclassical principles became central to academic art institutions, influencing the curriculum and standards for artistic education. Academic institutions emphasized the study of classical forms and techniques.
Did Neoclassicism have an impact on literature and music as well?
Yes, Neoclassicism had a significant impact on literature and music. In literature, it influenced the writing style, emphasizing clear language and moral themes. In music, composers like Mozart and Haydn incorporated classical forms and structures.
Why did Neoclassicism decline in popularity, and what succeeded it in the art world?
Neoclassicism declined in the early 19th century as artists sought new modes of expression. Romanticism emerged as a reaction against Neoclassical ideals, embracing emotion, individualism, and a more imaginative approach to artistic creation.
Related Questions
What Was The Focus Of Renaissance Art?
The focus of Renaissance art was on the classics of Greek and Rome, humanist philosophy, and the study of the human figure. Realism was also an essential part of renaissance art. The great artists of the Renaissance also became great anatomists and studied human beings.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Was The Focus Of Renaissance Art?.
What Is The Importance Of Art From The Renaissance Period?
Renaissance art is essential as it was a time of rebirth and discovery. Artists like Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael were at the forefront of that change, creation, and discovery. Renaissance art has influenced art and artists for many centuries and continues to influence artists today.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Is The Importance Of Art From The Renaissance Period?.
Early Renaissance Vs. High Renaissance Art Explained
Early Renaissance and High Renaissance are both periods of the art of the Renaissance era. The entire Renaissance era shared a lot of the same characteristics. The High Renaissance was dominated by three major artists: Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Early Renaissance Vs. High Renaissance Art Explained.