Ukiyo-e means the Japanese pictures of the “floating world.” Ukiyo-e is also known as the Japanese era of woodblock prints. The Japanese woodblock prints happened before the Art Nouveau movement in Europe, but they influenced this movement.
The Japanese Ukiyo-e helped start the Art Nouveau movement and influenced many Art Nouveau artists with their artworks. Siegfried Bing, a French art dealer, imported many Japanese arts to Paris, including Ukiyo-e woodblock prints. He had an influential magazine that helped expose Japanese art; this helped influence the art nouveau art movement.
Table of Contents
- The Impact of Ukiyo-e on the Emergence of Art Nouveau
- Japanese Influences On European Art And Culture
- Siegfried Bing And Art Nouveau Influences
- Echoes of the East: Art Nouveau Artists Inspired by Japanese Art and Ukiyo-e Prints
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Related Questions
The Impact of Ukiyo-e on the Emergence of Art Nouveau
Ukiyo-e, a term translating to “pictures of the floating world,” refers to the Japanese art form renowned for its woodblock prints. This era in Japanese art history, predating the European Art Nouveau movement, played a significant role in shaping the latter.
The unique aesthetics and techniques of Ukiyo-e were instrumental in the genesis of Art Nouveau, profoundly influencing a myriad of artists within this movement. Key to this cultural exchange was Siegfried Bing, a French art dealer who imported numerous Japanese artworks, including Ukiyo-e prints, to Paris.
Through his influential magazine and other endeavors, Bing significantly promoted Japanese art, leaving an indelible mark on the Art Nouveau movement shaping its style and philosophy.
Japanese, Ukiyo-e, Trade And Art Nouveau
Before 1853, Japan was closed to the world. This means that the Japanese Ukiyo-e movement was essentially a Japanese art movement during the Edo period in Japan.
The United States forced Japan to open its doors to Western markets in 1853. The West started to become flooded with Japanese art, mainly the Japanese Ukiyo-e woodblock prints from the 1700s and 1800s.
At the same time that Japan was opening to the West, and the West was becoming flooded with examples of the Ukiyo-e woodblock prints, the 19th century also saw a change in commercial retailing and the mass production of goods produced to serve Europe’s growing urban populations.
One of these changes is that Art Nouveau started to become associated with luxury and was widely publicized to the masses with the expansion in advertising. A wide range of Art Nouveau products began to be marketed to the up-and-coming middle-class consumers who now had fashionable aspirations and newly acquired disposable incomes.
Japanese Ukiyo-e Prints And Art Nouveau
Art Nouveau was a decorative art style that flourished between 1890 and 1910 throughout Europe and America. Art Nouveau is characterized by long lines that would have many curves and turns.
Art Nouveau was an art form used in architecture, interior design, jewelry, glass, posters, and illustrations. The Art Nouveau movement was a deliberate attempt to create a new style.
Even though the Art Nouveau style was a deliberate new style, the artists were also heavily influenced by the linear patterns of Japanese woodblock prints from the Ukiyo-e era.

For example, Ivan Bilibin gained fame for his Russian and Slavis fairytale illustrations. In his print, “The Tale of The Golden Cockerel,” we see influences from the Japanese woodblock prints. The clothing’s colors, linear patterns, lines, and repeat patterns are similar to what many Japanese woodblock print artists used.

In the famous Japanese woodblock print of Two Samurai Fighting by Hokusai, you can see the substantial use of colors and repeated patterns on the clothing. In Ivan Bilibin’s work, we also see the repeat of the patterns in the clothing and other parts of the print.
Japanese Influences On European Art And Culture
With this expansion of Art Nouveau products in the second half of the 19th century also came a time when Japanese art and Ukiyo-e woodblock prints began to exert a significant influence on European art and culture. In short, Europe was fascinated with everything Japanese.
Daily Japanese products would arrive on the European shore, including porcelains, silks, fans, kimonos, and the famous Ukiyo-e Japanese woodblock prints. So popular was this movement that the word was coined to show the Japanese influence on European culture known as Japonism.
You can read our blog about how Impressionism and the Influence of Japonisme by clicking here.
Siegfried Bing And Art Nouveau Influences
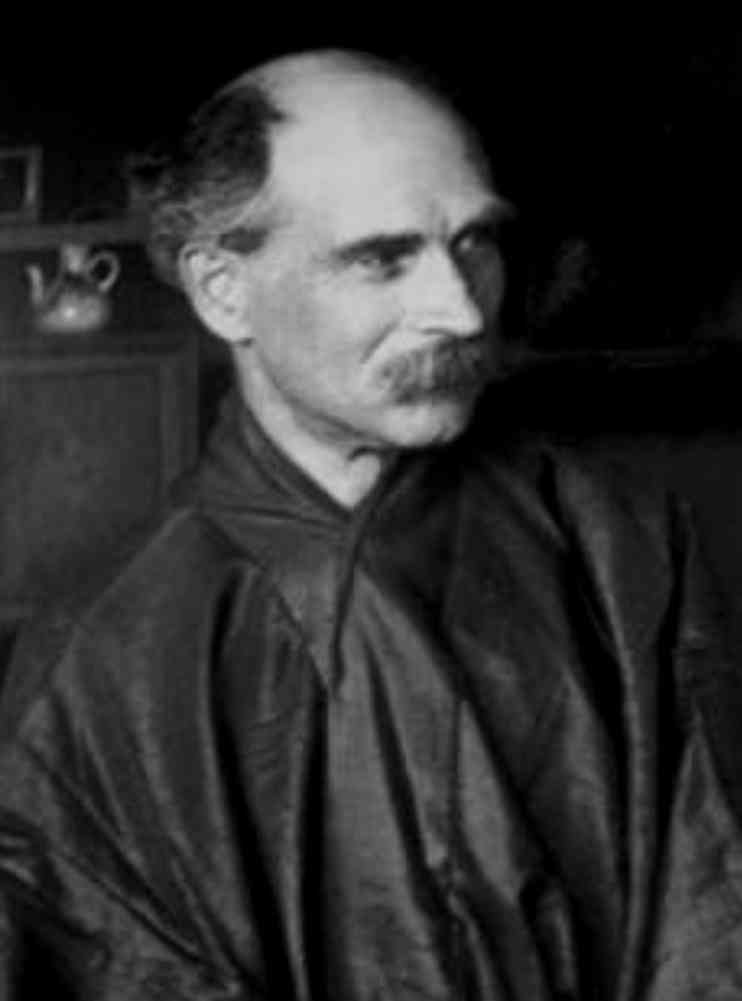

Siegfried Bing was a Hamburg-born businessman who became very influential in promoting Japanese art. Bing influenced the Art Nouveau movement.
From the 1870s onward, Bing ran an import business in Paris where he sold a lot of Japanese art, including many Ukiyo-e woodblock prints.

Bing also edited the influential monthly magazine called Le Japon Artistique. Many artists, including Art Nouveau and Impressionism artists, came to him to get Ukiyo-e woodblock prints and other Japanese art to use as inspiration.
In 1895, Bing opened a gallery called L’Art Nouveau. The gallery L’Art Nouveau sold jewelry, paintings, ceramics, Stained glass, and furniture from designers.
He sold many designers’ works, including Louis Comfort Tiffany, Georges de Feure, Eduard Colonna, Emile Galle, and Eugene Galliard. These artists and their works show the influence of Japanese art, culture, and especially Ukiyo-e woodblock prints.
Echoes of the East: Art Nouveau Artists Inspired by Japanese Art and Ukiyo-e Prints
The Art Nouveau movement, flourishing at the turn of the 20th century, is celebrated for its distinctive, flowing lines and naturalistic themes. However, a less explored facet of this artistic revolution is its profound indebtedness to Japanese art, including the captivating Ukiyo-e woodblock prints.
We seek to unravel the intricate tapestry of influences that Japanese art, with its elegant simplicity and emphasis on nature, wielded over Art Nouveau artists. We will delve into the stories of how Ukiyo-e, a genre that epitomizes the beauty of the transient and everyday, left an indelible impact on the works of these Western artists.
From the subtle integration of Japanese motifs to the adoption of compositional techniques, this journey will illuminate the cross-cultural dialogue that enriched and defined the Art Nouveau style.
Here is a selection of Art Nouveau Artists and how they were influenced by Japanese Art, including Ukiyo-e woodblock prints and their key work that shows this Japanese influence.
Louis Comfort Tiffany – Dogwood (1902 -1915)

Louis Comfort Tiffany produced a stained glass window called Dogwood (1902-1915). The window composition shows Tiffany’s glass ability and admiration for Japanese art.
The window is asymmetrical and brilliantly shows the dogwood tree, including the branches and blossoms that are seen behind a trellis,
Tiffany shows us his love of Japan, Japanese art, and Art Nouveau and how they came from Europe to the shores of the United States.
Emile Galle’ – Flower Vase (1890)
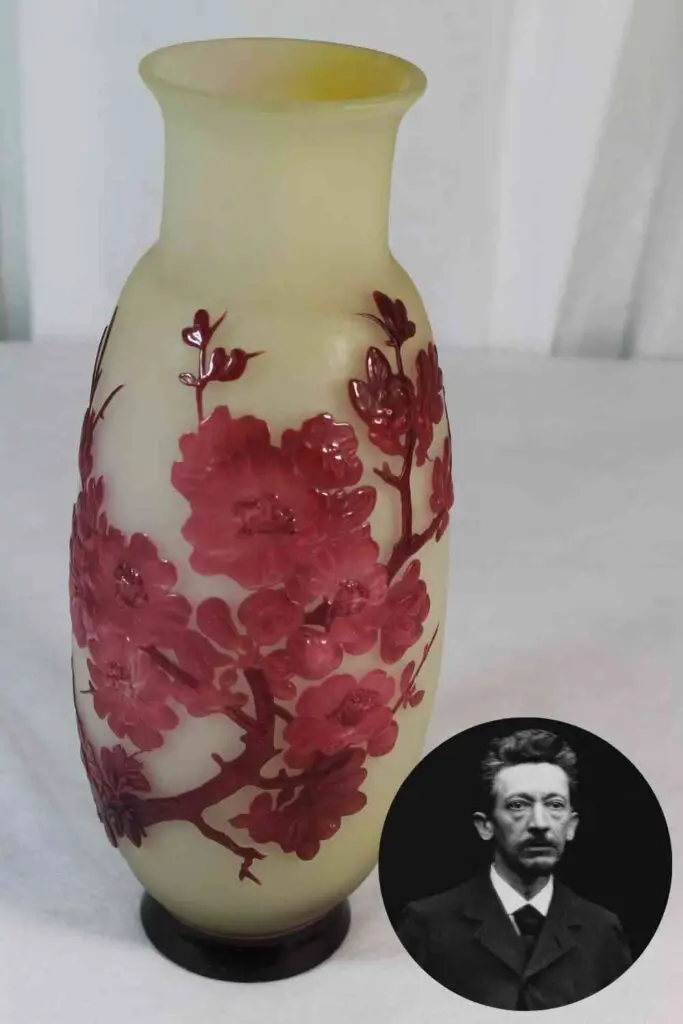

Emile Galle’ was a French glass artist and founder of Ecole de Nancy, a major school of the Art Nouveau movement. Galle’ was influenced by nature and Japanese art, including various Japanese motifs, such as flowers.
Emile was an artist who had his glass factory in Nancy, France, where he employed over 300 people to help him produce his glass designs for mass production. Upon his death, his wife and sister-in-law continued to run the factory, producing his works of art.
His Cameo glass, called a flower vase, is a one-piece that shows the Japanese influence, including the Ukiyo-e period of art on how he positioned the flower on the vase and what kind of flower he used.
George de Feure – Les Modes Cover, 1919

George de Feure was also influenced by Japanese art. His two elegant women’s designs for the cover of the Les Modes Christmas issue in 1919 clearly show Japanese influence with the Ukiyo-e woodblock prints and Japanese motifs and art.
George de Fuere adopted the love of Japanese art while working for Siegfried Bing. He carried the influence of the Japanese woodblock prints and his love of Japanese art for most of his art. This cover for Les Modes clearly shows his passion and influence with Japanese Ukiyo-e woodblock prints.
During this time in Europe and America, many artists were influenced by Japanese art. The Art Nouveau movement was a movement that sought a lot of inspiration from Japan; many of the Art Nouveau artists found inspiration in the Ukiyo-e Japanese woodblock print artists.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you are interested to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. If you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings, you can discover more by clicking here.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel filled with great videos and information by clicking here.
Join us for our podcast “5 Minutes With Art.” Spend just 5 minutes a week with us to discover and learn about great art and artists. You can find out more about our podcast by clicking here.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Ukiyo-e, and how does it relate to the birth of Art Nouveau?
Ukiyo-e refers to Japanese woodblock prints depicting the “floating world.” These prints, predating the Art Nouveau movement, played a pivotal role in influencing Art Nouveau artists and styles in Europe.
How did Ukiyo-e contribute to the Art Nouveau movement in Europe?
Ukiyo-e served as a significant source of inspiration for Art Nouveau artists. The intricate designs, flowing lines, and focus on nature seen in Ukiyo-e influenced the artistic principles of Art Nouveau.
Who was Siegfried Bing, and what role did he play in the interaction between Ukiyo-e and Art Nouveau?
Siegfried Bing, a French art dealer, played a crucial role by importing Japanese arts, including Ukiyo-e prints, to Paris. Through his influential magazine and exhibitions, Bing introduced Japanese aesthetics to European artists, contributing to the birth of Art Nouveau.
In what ways did Ukiyo-e woodblock prints impact the visual language of Art Nouveau?
Ukiyo-e prints introduced elements such as organic forms, asymmetry, and a focus on nature, which became key features of Art Nouveau aesthetics. The stylized depictions of landscapes and figures in Ukiyo-e inspired the flowing, curvilinear designs characteristic of Art Nouveau.
Which Art Nouveau artists were particularly influenced by Ukiyo-e?
Artists like Alphonse Mucha, Henri Toulouse-Lautrec, and Aubrey Beardsley were among those profoundly influenced by Ukiyo-e. These artists incorporated Japanese aesthetics into their works, contributing to the distinctive style of Art Nouveau.
How did the Japanese concept of the “floating world” align with the themes of Art Nouveau?
The “floating world” concept in Ukiyo-e, representing transient and fleeting beauty, resonated with Art Nouveau’s emphasis on the ephemeral and the natural world. Both movements embraced a sense of evanescence and the beauty found in everyday life.
Did Ukiyo-e influence only the visual aspects of Art Nouveau, or did it extend to other aspects as well?
Beyond visual elements, Ukiyo-e influenced the overall philosophy of Art Nouveau. The appreciation for craftsmanship, connection to nature, and a holistic approach to art and design were all inspired by the Japanese prints.
Were there any specific themes or motifs from Ukiyo-e that were commonly adopted in Art Nouveau artworks?
Nature, flora, fauna, and depictions of everyday life were prevalent themes in both Ukiyo-e and Art Nouveau. The stylized representations of these themes in Ukiyo-e prints influenced the organic and flowing designs characteristic of Art Nouveau.
How did the introduction of Japanese art by Siegfried Bing impact the perception of art in Europe during the late 19th century?
Siegfried Bing’s efforts to showcase Japanese art challenged conventional European artistic norms. The introduction of Ukiyo-e and other Japanese art forms broadened artistic horizons, paving the way for the embrace of new styles and philosophies, including those of Art Nouveau.
What lasting legacy did the Ukiyo-e influence leave on Art Nouveau, and how did it shape the subsequent evolution of art movements?
The Ukiyo-e influence on Art Nouveau left a lasting legacy in the form of a more organic, flowing, and nature-inspired approach to art and design. This influence continued to echo in subsequent art movements, contributing to the diversification of artistic expression in the 20th century.
Related Questions
Characteristics of Japanese Ukiyo-e Woodblock Prints
Japanese woodblock prints were produced to have a mass appeal to the Japanese audience. There are a lot of characteristics in the Japanese woodblock print, such as the asymmetry of design, how the artist experiments with composition, the artist’s use of flats spaces, and the use of colors.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Characteristics of Japanese Ukiyo-e Woodblock Printsach Other?.
What Are Some Japanese Woodblock Print Characteristics?
There are many characteristics of a Japanese woodblock print, from the woodblock print title, artist name, and publisher’s seal; other features also include the color and subject matter. Japanese woodblock prints also have different artistic art movements.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading What Are Some Japanese Woodblock Print Characteristics?.
What Is A Japanese Woodblock Print?
A Japanese woodblock print is, as the name implies, a print that is made by using carved woodblock and applying ink on the woodblocks to print a design on paper. The Japanese woodblock artists used the woodblocks to print artistic prints and even books. Artists have used the woodblock print technique in Japan for hundreds of years.
You can learn more by reading What Is A Japanese Woodblock Print? by clicking here.