Anyone who studies art history will learn about the Renaissance. One reason is that Renaissance produced so many great artists and works.
The Renaissance, a period of remarkable cultural, artistic, and intellectual growth, is often hailed as one of the most transformative eras in history. While its starting point is a subject of debate among scholars, most scholars feel the Renaissance started in the 14th Century in Italy. Then after that time, the Renaissance gradually unfolded across Europe, leaving a lasting impact on society.
Table of Contents
- When Did The Renaissance Start?
- 15 Characteristics That Make The Renaissance And Epoch Time Of Cultural Rebirth
- Humanism
- Rediscovery Of Ancient Knowledge
- Artistic Revolution
- Scientific Advancements
- Printing Press
- Rise Of Individualism
- Secularism
- Patronage Of The Arts
- Architectural Innovations
- Exploration And Discovery
- Revival Of Education
- Evolution Of Literature
- Cultural Exchange And Global Influences
- Rise Of Critical Thinking
- Socioeconomic Transformation
- Why Are These Renaissance Characteristics Important?
- Related Questions
When Did The Renaissance Start?
The Renaissance, widely regarded as the birthplace of modern civilization, originated in 14th-century Italy. Even though some scholars did not agree when it started, many feel it started in the 14th Century in Italy.
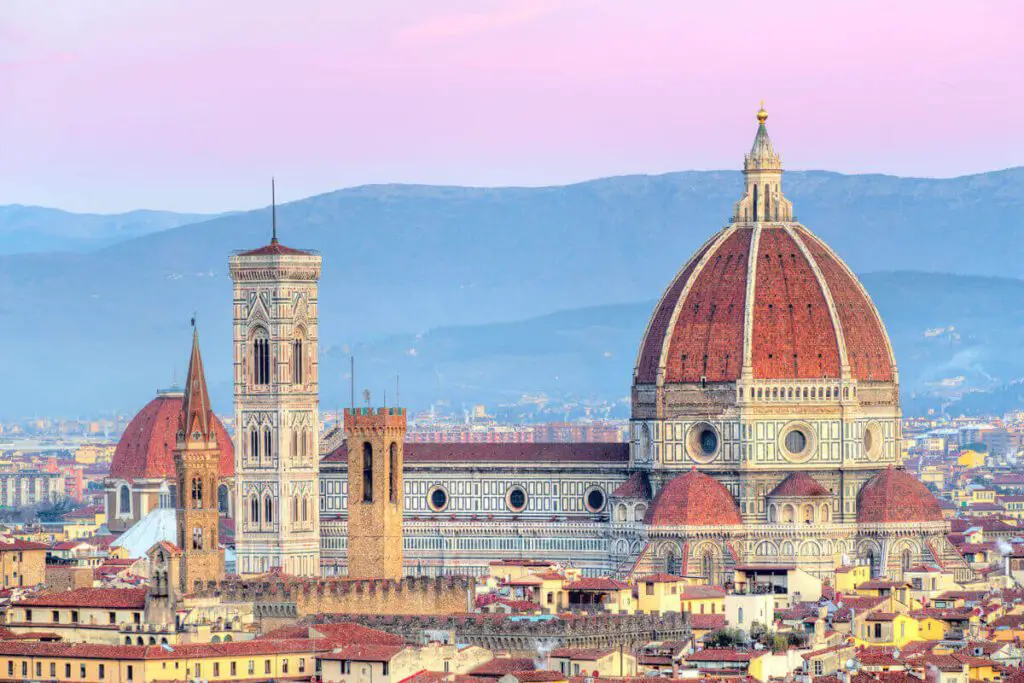

The Italian city-states, such as Florence, Venice, and Rome, served as epicenters of intellectual and artistic innovation, providing fertile ground for the Renaissance to take root. The revival of classical knowledge, the patronage of influential families and rulers, and the flourishing trade networks all contributed to the flourishing of this cultural rebirth.
Drawing inspiration from ancient Greek and Roman texts, Italian scholars and thinkers began to champion humanism as a critical philosophy of the era. Humanism emphasized the importance of human potential, individualism, and secularism, sparking a renewed interest in the humanities, arts, and sciences. This intellectual curiosity fueled a wave of scientific advancements and artistic revolutions, forever altering the course of history.
As the Renaissance gained momentum in Italy, its influence gradually spread to other European countries. In the 15th century, we witnessed the diffusion of Renaissance ideals to France, Germany, and the Low Countries.
In the 16th century, the movement reached England, which blended with the unique characteristics of the English Renaissance, marked by the works of playwrights like William Shakespeare.
One of the defining characteristics of the Renaissance was the emphasis on the individual and the celebration of human achievements. This elevation of the individual led to a surge in self-expression, personal ambition, and the development of unique talents.
Artists such as Leonardo da Vinci, Michelangelo, and Raphael emerged during this period, producing timeless masterpieces that continue to captivate audiences today.
The Renaissance also brought about profound scientific, philosophical, and educational shifts. Figures like Nicolaus Copernicus, Galileo Galilei, and Francis Bacon challenged traditional beliefs, paving the way for the scientific revolution and the development of the scientific method.
The establishment of universities and humanist schools promoted education and intellectual growth, democratizing knowledge and paving the way for the Enlightenment.
The Renaissance propelled significant changes in society and the economy. The rise of wealthy patrons and the patronage system enabled artists, architects, and scholars to thrive, resulting in constructing magnificent buildings, producing iconic artworks, and disseminating of groundbreaking ideas.
The exploration and discovery of new lands during this era opened up new trade routes, expanded global connections, and fostered cultural exchange, setting the stage for the Age of Discovery.
The Renaissance’s origins can be traced back to 14th-century Italy, where a convergence of intellectual, artistic, and economic factors set the stage for a transformative cultural rebirth. From Italy, the Renaissance gradually spread throughout Europe, leaving an indelible mark on society, arts, sciences, and philosophy.
The impact of the Renaissance continues to resonate, shaping the foundations of modern civilization and inspiring generations to embrace the pursuit of knowledge, creativity, and human potential.
15 Characteristics That Make The Renaissance And Epoch Time Of Cultural Rebirth
Many essential characteristics helped form and definite the Renaissance era. Read on as we explore 15 major characteristics or changes brought about by this extraordinary epoch.
Humanism
At the core of the Renaissance, a philosophical and intellectual movement that emphasized the importance of human potential, individualism, and secularism.

Humanism led to a renewed interest in studying classical literature, history, and philosophy, shaping a new worldview centered around human achievements and capabilities.
Rediscovery Of Ancient Knowledge
During the Renaissance, scholars, and artists sought to revive and understand the wisdom of ancient Greek and Roman civilizations. Rediscovering texts such as those by Plato, Aristotle, and Cicero provided knowledge and inspired new avenues of thought and creativity.
Artistic Revolution
The Renaissance witnessed a revolution in artistic expression. Artists embraced naturalism, using techniques such as perspective and chiaroscuro to create realistic and visually striking works. The shift from medieval symbolism to humanistic themes and a focus on portraying the human form transformed the art world.
Scientific Advancements
The Renaissance marked a turning point in scientific discovery. Figures like Copernicus, Galileo, and Kepler challenged prevailing beliefs about the universe, paving the way for a new era of scientific exploration. Observational and experimental approaches to knowledge became prominent, leading to groundbreaking breakthroughs.
Printing Press
Johannes Gutenberg’s invention of the printing press in the mid-15th century revolutionized the dissemination of information. This technological advancement made books more accessible, increasing literacy rates, spreading ideas, and democratizing knowledge.
Rise Of Individualism
The Renaissance celebrated the individual and placed human beings at the center of the universe. The concept of individualism led to a focus on personal achievement, self-expression, and the development of unique talents and abilities.
Secularism
In contrast to the heavily religious focus of the Middle Ages, the Renaissance emphasized secular interests and pursuits. People began to explore worldly pleasures, embracing the beauty of life on earth rather than solely focusing on the afterlife.
Patronage Of The Arts
Powerful rulers, wealthy merchants, and influential families became patrons of the arts, providing financial support and fostering an environment conducive to artistic and intellectual growth. This patronage enabled artists, writers, and scholars to flourish, leaving a lasting legacy of masterpieces.
Architectural Innovations
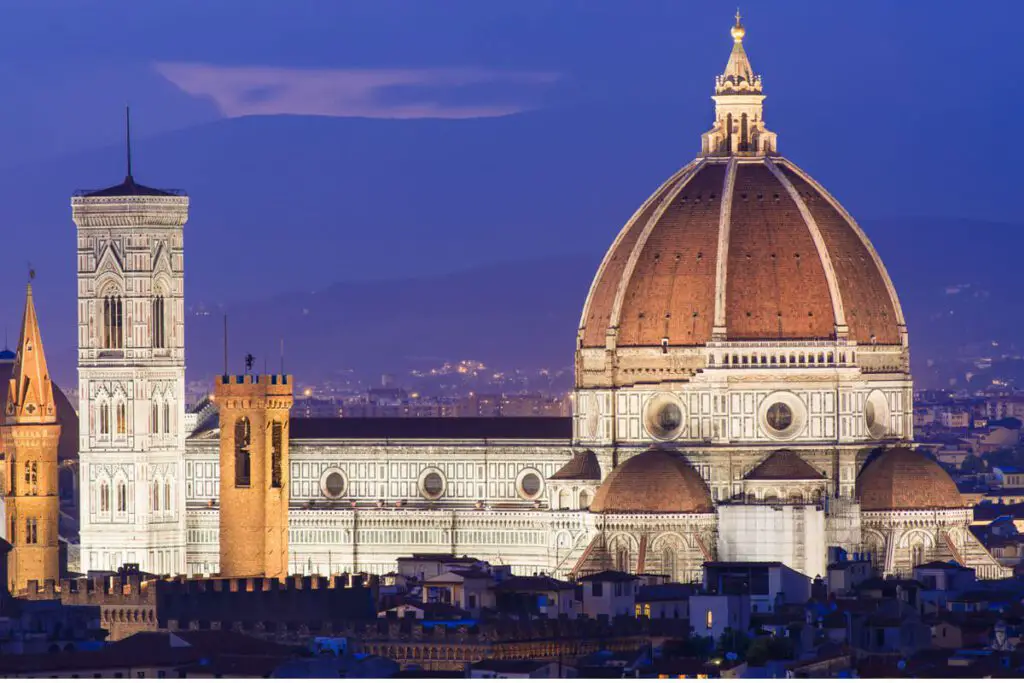

The Renaissance brought about revolutionary changes in architecture. Architects like Filippo Brunelleschi and Andrea Palladio, Cathedral of Santa Maria del Fiore reintroduced classical elements and proportionality, leading to the construction of awe-inspiring buildings, such as the dome of Florence Cathedral and Palladio’s villas.
Exploration And Discovery
The Renaissance was an age of exploration, driven by a thirst for knowledge and new trade routes. Explorers like Christopher Columbus and Vasco da Gama embarked on groundbreaking voyages, expanding geographical knowledge and opening up new commerce and cultural exchange possibilities.
Revival Of Education
The Renaissance witnessed a revival of education by establishing humanist schools and universities. Education was no longer solely the privilege of the elite, as the humanistic approach emphasized the importance of education for all individuals, fostering intellectual and cultural growth.
Evolution Of Literature
The Renaissance saw a significant evolution in literature—writers such as William Shakespeare, Miguel de Cervantes, and Dante.
Cultural Exchange And Global Influences
The Renaissance era was marked by increased cultural exchange and the blending of ideas from different regions. Exploring new lands and encounters with diverse cultures broadened intellectual horizons, incorporating exotic motifs, themes, and styles into various art forms.
Rise Of Critical Thinking
As humanist ideas spread, critical thinking and intellectual inquiry became central tenets of the Renaissance. Scholars and thinkers questioned traditional authorities, challenging long-held beliefs and fostering a spirit of skepticism that laid the foundation for the scientific and philosophical advancements of the following centuries.
Socioeconomic Transformation
The Renaissance brought about significant socioeconomic changes. The growth of trade, the accumulation of wealth, and the rise of the middle class led to a new social order. The expanding urban centers became hubs of cultural and commercial activity, fueling economic prosperity and social mobility.
Why Are These Renaissance Characteristics Important?
Each of these characteristics or changes brought about by the Renaissance era played a pivotal role in shaping the world as we know it today; here are some reasons why understanding them and these changes is essential.

- The changes led to a shift in worldview, emphasizing human potential and individualism, which remains influential in modern society.
- Rediscovering ancient knowledge provided a solid foundation for future intellectual pursuits and new ideas.
- The artistic revolution transformed art aesthetics and influenced subsequent movements, leaving a rich legacy of artistic techniques and styles.
- Scientific advancements laid the groundwork for the scientific revolution and the subsequent rapid progress in various scientific disciplines.
- The printing press democratized knowledge, empowering individuals to access information and facilitating the spread of ideas, leading to further advancements in education and literacy.
- The emphasis on individualism fostered personal growth, self-expression, and the development of unique talents, shaping individual identity and personal freedom.
- The shift towards secularism allowed for a broader exploration of human experiences, encouraging a balanced approach to life and pursuing happiness in the present.
- The patronage of the arts ensured the preservation and flourishing of artistic masterpieces, enriching cultural heritage and inspiring future generations.
- Architectural innovations not only revolutionized the field of architecture but also left an indelible mark on urban landscapes, contributing to the cultural identity of cities.
- Exploration and discovery opened up new horizons, expanding geographical knowledge and facilitating cross-cultural interactions that continue to shape our interconnected world.
- The revival of education and emphasis on universal access to knowledge laid the groundwork for future advancements in education and the spread of literacy.
- The evolution of literature produced timeless literary works that continue to captivate and inspire readers, shaping the development of literary traditions and genres.
- Cultural exchange and global influences enriched artistic expressions, fostering a multicultural perspective and promoting a deeper understanding and appreciation of diverse cultures.
- The rise of critical thinking challenged established norms and laid the foundation for the scientific method, rational inquiry, and the pursuit of knowledge based on evidence and reason.
- The socioeconomic transformation propelled economic growth, social mobility, and urban development, shaping the foundations of modern economies and societies.
The Renaissance was a transformative period characterized by many changes and characteristics that profoundly influenced art, science, literature, and society. The era’s emphasis on humanism, artistic expression, scientific inquiry, and intellectual freedom laid the groundwork for cultural, intellectual, and social progress.
The impact of the Renaissance continues to reverberate through the ages, making it a pivotal period in human history.
Anita Louise Art is dedicated to art education, great artists, and inspiring others to find and create their art. We love art that uplifts and inspires. #ArtToMakeYouSmile! #ArtToMakeYouHappy!
If you want to see any of my art, you can find out more by clicking here. You can discover more by clicking here if you are interested in what inspires me and my paintings.
We have a free newsletter and would love you to be part of our community; you can subscribe to the newsletter by clicking here. If you have any questions, I would be happy to talk to you any time. You can reach me, Anita, by clicking here.
Subscribe to our Anita Louise Art YouTube Channel with great videos and information by clicking here.
Related Questions
Why Do People Say, ”Life Is Like Drawing Without An Eraser?
Often, artists, myself included, will use an eraser to remove any marks or measurements we may have made on a paper to measure out and organize their drawings or artwork on their canvas or paper. For most artists having a good eraser is essential.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Why Do People Say, ”Life Is Like Drawing Without An Eraser?.
Is Communism Good For The Arts?
Communism is not suitable for art, and for many artists under Communism, art should have a purpose and way to help further the communist ideals and ideology. In a Communist society, many artists are labeled dissidents; others are forced to use their talents to create propaganda art.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading Is Communism Good For The Arts?.
12 Years Leonardo Painted Mona Lisa’s Lips, Facts Or Fiction?
No evidence shows that Leonardo da Vinci spent 12 years painting the Mona Lisa smile. Most scholars believe that he painted the painting in 4 years but then had the painting much longer in his possession. He could have worked on it or adjusted it when he had it, but there is no evidence.
By clicking here, you can learn more by reading 12 Years Leonardo Painted Mona Lisa’s Lips, Facts Or Fiction?.